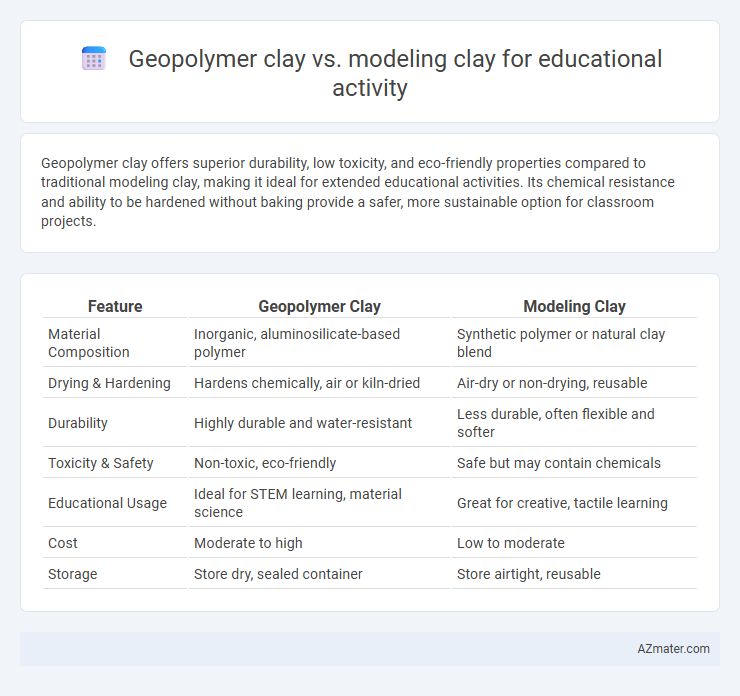
Geopolymer clay offers superior durability, low toxicity, and eco-friendly properties compared to traditional modeling clay, making it ideal for extended educational activities. Its chemical resistance and ability to be hardened without baking provide a safer, more sustainable option for classroom projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Clay | Modeling Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic, aluminosilicate-based polymer | Synthetic polymer or natural clay blend |
| Drying & Hardening | Hardens chemically, air or kiln-dried | Air-dry or non-drying, reusable |
| Durability | Highly durable and water-resistant | Less durable, often flexible and softer |
| Toxicity & Safety | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Safe but may contain chemicals |
| Educational Usage | Ideal for STEM learning, material science | Great for creative, tactile learning |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Storage | Store dry, sealed container | Store airtight, reusable |
Introduction to Geopolymer Clay and Modeling Clay
Geopolymer clay, composed of inorganic aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, offers durable and eco-friendly properties ideal for educational STEM activities focusing on chemistry and materials science. Modeling clay, typically made from polymer-based materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or natural dough-like substances, provides flexible, easily moldable characteristics favored in creative arts and early childhood education. Both clays serve distinct educational purposes, with geopolymer clay emphasizing material science experimentation and modeling clay supporting tactile skill development and imaginative play.
Key Differences Between Geopolymer Clay and Modeling Clay
Geopolymer clay is a durable, eco-friendly material that hardens through a chemical reaction involving inorganic minerals, making it ideal for permanent educational projects requiring strength and heat resistance. Modeling clay, often made from non-drying, pliable substances like oil or polymer-based compounds, remains soft and reusable, perfect for hands-on, flexible learning and repeated reshaping activities. Key differences include geopolymer clay's permanence and structural integrity versus modeling clay's malleability and reusability, influencing their specific educational applications.
Composition and Safety Considerations
Geopolymer clay is composed primarily of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, offering a non-toxic, heat-resistant, and durable medium suitable for classroom use. Modeling clay, typically made from plasticized hydrocarbons or natural waxes, may contain additives or chemicals that require supervision to avoid ingestion or prolonged skin contact. Both materials enhance tactile learning, but geopolymer clay's inorganic composition provides a safer alternative with minimal fumes and reduced allergenic potential.
Ease of Use in Educational Settings
Geopolymer clay offers a non-toxic, quick-drying alternative that is ideal for classroom environments, as it requires minimal preparation and is easy to mold for students of all ages. Modeling clay remains highly pliable and reusable, making it suitable for repeated practice and long-term projects, though it can be messier and less durable once dried. Educators often prefer geopolymer clay for hands-on lessons requiring fast set times and cleaner handling, while modeling clay suits activities focused on creativity and manipulation without immediate curing.
Durability and Long-Term Results
Geopolymer clay offers superior durability compared to traditional modeling clay, making it ideal for educational activities requiring long-term usage and preservation. Its chemical composition creates a hard, resilient structure that resists cracking and crumbling, ensuring models maintain their shape over time. Modeling clay, while flexible and easy to mold, tends to dry out and become brittle, limiting its effectiveness for projects needing lasting results.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer clay offers a sustainable alternative to traditional modeling clay by utilizing industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, significantly reducing environmental impact through lower carbon emissions and waste usage. Its non-toxic and biodegradable properties make it safe for educational settings, promoting eco-friendly hands-on learning experiences. Modeling clay, often composed of synthetic polymers and petroleum-based ingredients, poses challenges in biodegradability and waste management, limiting its sustainability in long-term educational use.
Cost Comparison for Classroom Use
Geopolymer clay generally costs more per pound than traditional modeling clay but offers enhanced durability and eco-friendly properties, making it a cost-effective option for repeated classroom use over time. Modeling clay is typically cheaper upfront and easy to use for short-term projects but may require frequent replacement due to drying out or breakage. Considering bulk purchasing options and project duration helps educators optimize budget allocation between both materials for classroom activities.
Creative Possibilities and Learning Outcomes
Geopolymer clay offers enhanced creative possibilities by allowing students to mold durable, heat-resistant structures that can be cured and preserved, providing hands-on experience with chemical reactions and material science. Modeling clay, widely used in educational activities, excels in flexibility and easy manipulation for imaginative play and rapid prototyping of shapes, fostering fine motor skills and spatial awareness. Using geopolymer clay in STEM education promotes understanding of engineering principles and durability testing, while modeling clay supports early developmental learning and artistic expression.
Age Appropriateness for Different Students
Geopolymer clay is suitable for older students, typically ages 12 and up, due to its chemical setting process and firmer texture, making it ideal for advanced educational activities involving sculpting techniques and durable models. Modeling clay is more appropriate for younger children, ages 3 and above, offering a softer, non-drying material that encourages creativity and fine motor skills development without the need for baking or curing. Choosing between geopolymer and modeling clay depends on the students' age, skill level, and the intended educational outcome, balancing safety and complexity.
Choosing the Right Clay for Educational Activities
Geopolymer clay offers durability, eco-friendliness, and non-toxicity, making it ideal for long-lasting educational projects and environmentally conscious classrooms. Modeling clay, known for its softness and ease of molding, supports fine motor skill development and repetitive hands-on practice without requiring baking or curing. Selecting the right clay depends on project goals: choose geopolymer clay for permanent displays and structural learning or modeling clay for flexible, immediate tactile experiences.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Modeling clay for Educational activity
 azmater.com
azmater.com