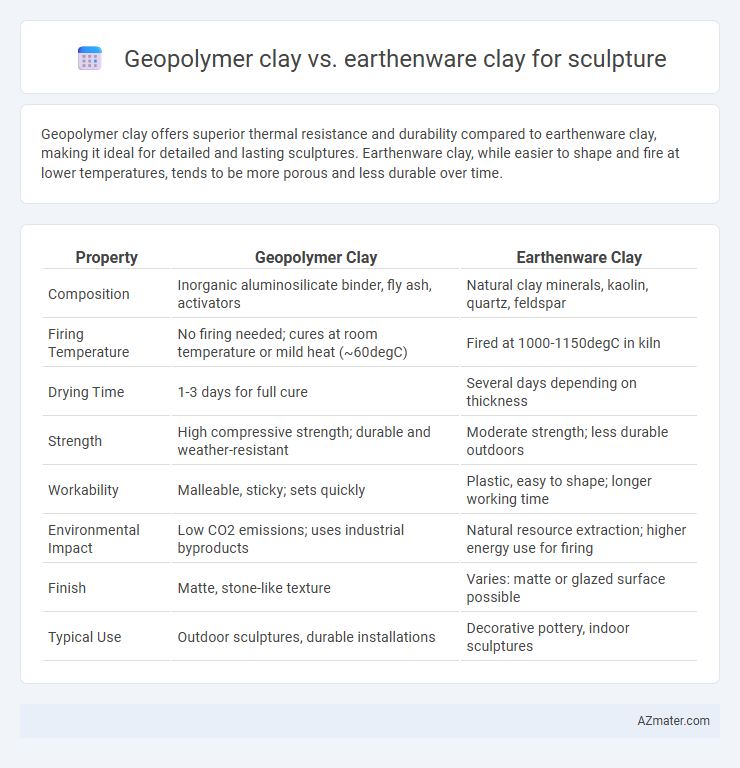
Geopolymer clay offers superior thermal resistance and durability compared to earthenware clay, making it ideal for detailed and lasting sculptures. Earthenware clay, while easier to shape and fire at lower temperatures, tends to be more porous and less durable over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geopolymer Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Inorganic aluminosilicate binder, fly ash, activators | Natural clay minerals, kaolin, quartz, feldspar |
| Firing Temperature | No firing needed; cures at room temperature or mild heat (~60degC) | Fired at 1000-1150degC in kiln |
| Drying Time | 1-3 days for full cure | Several days depending on thickness |
| Strength | High compressive strength; durable and weather-resistant | Moderate strength; less durable outdoors |
| Workability | Malleable, sticky; sets quickly | Plastic, easy to shape; longer working time |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions; uses industrial byproducts | Natural resource extraction; higher energy use for firing |
| Finish | Matte, stone-like texture | Varies: matte or glazed surface possible |
| Typical Use | Outdoor sculptures, durable installations | Decorative pottery, indoor sculptures |
Introduction to Geopolymer and Earthenware Clays
Geopolymer clay is an advanced, chemically bonded material composed mainly of aluminosilicate sources such as fly ash or metakaolin, offering superior durability and heat resistance compared to traditional clays. Earthenware clay, derived from natural clay deposits rich in iron oxides and silica, is widely used for its plasticity and ease of shaping but typically fires at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and less durable final product. Sculptors choose geopolymer clay for modern, high-strength applications while earthenware remains favored for classical techniques and aesthetic warmth.
Material Composition and Properties
Geopolymer clay consists primarily of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, resulting in a highly durable and heat-resistant substance ideal for intricate sculptural work. Earthenware clay is composed mainly of natural clay minerals like kaolinite and illite, firing at lower temperatures and exhibiting porous and softer characteristics that limit its durability but enhance workability. The inorganic polymer matrix of geopolymer clay provides superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to the more traditional, easily carved but fragile earthenware clay.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Geopolymer clay offers superior workability with its smooth, consistent texture and quick curing process, making it ideal for intricate sculpting techniques such as fine detailing and layering. Earthenware clay provides a more traditional, tactile experience with variable moisture content that allows longer working times for hand-building and coiling methods but requires careful drying to avoid cracking. Sculptors choosing between the two should consider geopolymer clay for precision and durability, while earthenware clay suits organic forms and slow, methodical construction.
Firing and Curing Processes
Geopolymer clay undergoes a chemical curing process at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures, eliminating the need for traditional kiln firing used in earthenware clay, which requires firing at temperatures typically between 1,000degC to 1,150degC to achieve vitrification and hardness. The low-energy curing of geopolymer clay results in reduced shrinkage and enhanced durability compared to the thermal firing of earthenware, which can cause cracking or warping if not properly controlled. This difference in processing makes geopolymer clay a more sustainable option for sculptors seeking strength and fire resistance without the energy-intensive kiln process.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer clay significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, minimizing reliance on natural clay extraction and lowering carbon emissions compared to earthenware clay. Earthenware clay, sourced directly from the Earth, often involves intensive mining processes that disrupt ecosystems and deplete natural resources. The durability and lower firing temperatures of geopolymers enhance sustainability by conserving energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions throughout the sculpting process.
Durability and Longevity of Sculptures
Geopolymer clay offers superior durability compared to earthenware clay, as it is resistant to cracking, weathering, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures. Earthenware clay, while easier to work with, is more porous and susceptible to moisture and temperature changes, which can compromise the longevity of sculptures over time. Sculptors seeking long-lasting, weather-resistant pieces often prefer geopolymer clay due to its enhanced structural integrity and low permeability.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Geopolymer clay offers a smoother and more uniform surface finish compared to earthenware clay, making it ideal for detailed sculptures that require fine textures and sharp edges. Earthenware clay, known for its warm, natural tones and porous texture, provides a rustic and organic aesthetic often preferred for traditional or earthy sculptures. While geopolymer clay can mimic stone or metal finishes through various additives and surface treatments, earthenware maintains a distinct tactile quality that enhances its visual depth and rustic charm.
Cost and Availability
Geopolymer clay offers cost efficiency due to its use of industrial waste materials, making it more affordable than traditional earthenware clay, which relies on natural clay deposits that can fluctuate in price based on regional availability. Availability of geopolymer clay is generally more consistent worldwide because it is manufactured from readily accessible industrial byproducts, whereas earthenware clay availability depends heavily on local geology and mining practices. Artists seeking budget-friendly, reliably sourced sculpting materials often find geopolymer clay a practical alternative to conventional earthenware options.
Suitable Applications in Sculpture
Geopolymer clay excels in outdoor and industrial sculpture applications due to its high durability, resistance to fire, and minimal shrinkage during curing, making it ideal for large-scale or functional artworks. Earthenware clay is preferable for fine detail and traditional sculpting techniques, offering easier workability and vibrant glaze compatibility but requiring kiln firing and more careful handling to avoid cracking. Sculptors often select geopolymer clay for structural pieces needing longevity, while earthenware suits decorative, indoor sculptures emphasizing color and texture.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Project
Geopolymer clay offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for sculptures requiring long-lasting structural integrity and outdoor display. Earthenware clay, prized for its traditional aesthetic and ease of sculpting, is more porous and less durable, best suited for indoor projects and detailed artistic expression. Selecting between geopolymer and earthenware clay depends on the sculpture's intended use, environmental exposure, and desired finish characteristics.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Earthenware clay for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com