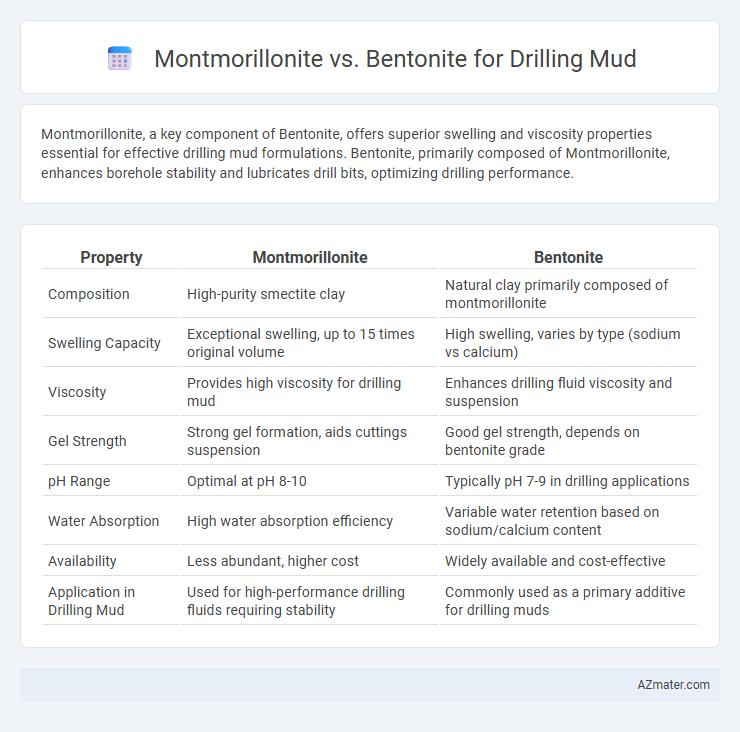
Montmorillonite, a key component of Bentonite, offers superior swelling and viscosity properties essential for effective drilling mud formulations. Bentonite, primarily composed of Montmorillonite, enhances borehole stability and lubricates drill bits, optimizing drilling performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Bentonite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High-purity smectite clay | Natural clay primarily composed of montmorillonite |
| Swelling Capacity | Exceptional swelling, up to 15 times original volume | High swelling, varies by type (sodium vs calcium) |
| Viscosity | Provides high viscosity for drilling mud | Enhances drilling fluid viscosity and suspension |
| Gel Strength | Strong gel formation, aids cuttings suspension | Good gel strength, depends on bentonite grade |
| pH Range | Optimal at pH 8-10 | Typically pH 7-9 in drilling applications |
| Water Absorption | High water absorption efficiency | Variable water retention based on sodium/calcium content |
| Availability | Less abundant, higher cost | Widely available and cost-effective |
| Application in Drilling Mud | Used for high-performance drilling fluids requiring stability | Commonly used as a primary additive for drilling muds |
Introduction: Importance of Clay Minerals in Drilling Mud
Clay minerals such as Montmorillonite and Bentonite play a critical role in drilling mud by enhancing its rheological properties and fluid loss control. Montmorillonite's high swelling capacity and cation exchange capacity improve mud viscosity and suspension stability, essential for efficient borehole cleaning. Bentonite, primarily composed of Montmorillonite, offers superior water absorption and gel strength, making it a preferred additive for maintaining drilling fluid consistency and lubricity in challenging drilling environments.
What is Montmorillonite?
Montmorillonite is a type of clay mineral characterized by its high swelling capacity and excellent absorption properties, making it a key component in drilling mud formulations. It consists primarily of smectite clay with a layered structure that allows it to retain water and increase the viscosity of drilling fluids for enhanced lubricity and stability. Unlike bentonite, which is predominantly composed of montmorillonite but can include other minerals, pure montmorillonite provides superior control over rheological properties in petroleum and geothermal drilling applications.
Understanding Bentonite: Composition and Properties
Bentonite is primarily composed of montmorillonite minerals, which provide exceptional swelling and water absorption properties essential for drilling mud applications. Its high cation exchange capacity and fine particle size contribute to excellent viscosity and suspension capabilities, enhancing cuttings transport during drilling. The unique clay structure of bentonite ensures stability and lubrication in boreholes, making it a crucial additive for efficient drilling fluid performance.
Key Similarities Between Montmorillonite and Bentonite
Montmorillonite and bentonite both consist primarily of smectite clay minerals with high swelling capacity, making them effective at increasing viscosity and sealing properties in drilling mud formulations. Their layered structure and cation exchange capacity contribute similarly to fluid retention, filtration control, and suspension stability during drilling operations. Both clays exhibit excellent rheological behavior that enhances wellbore stability and cutoff, essential for efficient drilling performance.
Chemical Differences: Montmorillonite vs Bentonite
Montmorillonite is a dominant clay mineral in bentonite, primarily composed of hydrated sodium calcium aluminum magnesium silicates with a high cation exchange capacity that influences its swelling and adsorption properties. Bentonite, primarily formed from weathered volcanic ash, contains varying proportions of montmorillonite along with other minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and cristobalite, affecting its chemical behavior in drilling mud formulations. The sodium-rich montmorillonite bentonite exhibits superior swelling and viscosity control in drilling mud compared to calcium-rich bentonite, which has reduced hydration and lower thixotropic properties due to its distinct ionic composition.
Performance in Drilling Applications
Montmorillonite and bentonite are both clay minerals used in drilling mud with distinct performance characteristics. Montmorillonite offers superior swelling and water absorption, enhancing viscosity and suspension of cuttings, while bentonite, primarily composed of montmorillonite but with additional minerals, provides better thermal stability and filtration control in drilling fluids. Bentonite's ability to maintain rheological properties under high temperature conditions makes it more effective for deep well drilling applications.
Rheological Properties and Swelling Capacity
Montmorillonite exhibits superior swelling capacity compared to bentonite, significantly enhancing the viscosity and gel strength of drilling muds due to its unique layered structure and high cation exchange capacity. Bentonite, predominantly composed of montmorillonite but with variable impurities, offers reliable rheological properties such as shear thinning behavior and thixotropy, crucial for effective cuttings suspension and borehole stability. The higher hydration rate and plastic viscosity of montmorillonite-rich drilling fluids improve suspension performance and filtration control, directly impacting drilling efficiency and wellbore integrity.
Filtration Control: Effectiveness in Drilling Fluid
Montmorillonite and Bentonite are both clay minerals essential for drilling mud, with Bentonite exhibiting superior filtration control due to its higher swelling capacity and plasticity, which effectively seals porous formations and minimizes fluid loss. Montmorillonite, a primary component of Bentonite, provides minor filtration benefits but lacks the consistency and volume needed for optimal drilling fluid performance. Bentonite's enhanced colloidal properties and cation exchange capacity ensure better suspension and stability, making it more effective in maintaining low filtration rates during drilling operations.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Montmorillonite and Bentonite differ significantly in cost and availability for drilling mud applications; Bentonite is generally more abundant and cost-effective due to its widespread deposits, making it the preferred choice in many regions. Montmorillonite, a primary component of Bentonite, may require more processing, increasing its cost and limiting its direct use. The ease of sourcing Bentonite locally reduces transportation expenses, enhancing its economic advantage over Montmorillonite in drilling fluid formulations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Clay for Drilling Mud
Montmorillonite offers higher swelling capacity and greater cation exchange capacity, making it ideal for enhancing viscosity and suspension in drilling mud formulations. Bentonite, primarily composed of montmorillonite but often mixed with other clays, provides cost-effective rheological properties and improved fluid loss control. Selecting the optimal clay depends on balancing performance requirements like viscosity, filtration control, and chemical compatibility with drilling conditions and budget constraints.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Bentonite for Drilling Mud
 azmater.com
azmater.com