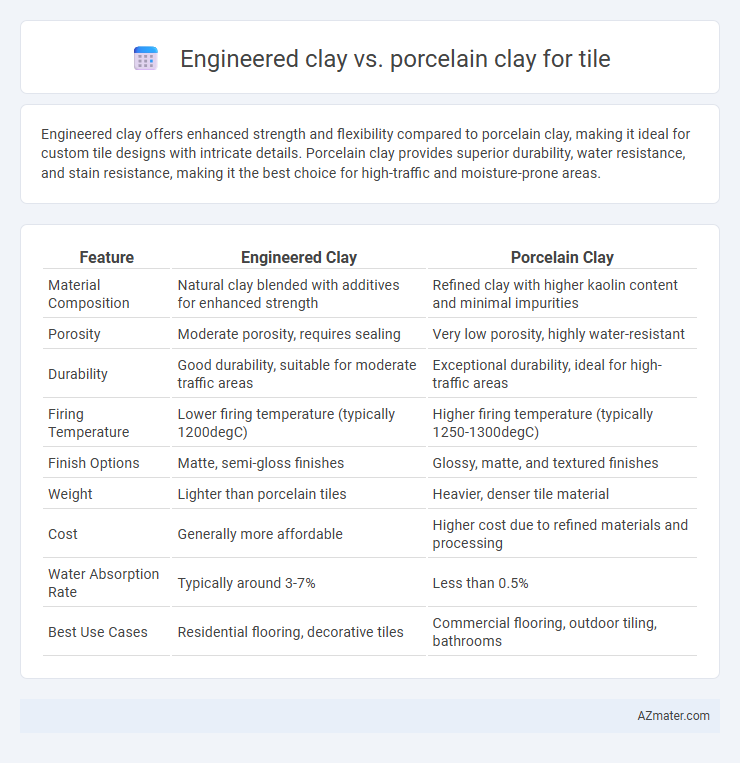
Engineered clay offers enhanced strength and flexibility compared to porcelain clay, making it ideal for custom tile designs with intricate details. Porcelain clay provides superior durability, water resistance, and stain resistance, making it the best choice for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Engineered Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay blended with additives for enhanced strength | Refined clay with higher kaolin content and minimal impurities |
| Porosity | Moderate porosity, requires sealing | Very low porosity, highly water-resistant |
| Durability | Good durability, suitable for moderate traffic areas | Exceptional durability, ideal for high-traffic areas |
| Firing Temperature | Lower firing temperature (typically 1200degC) | Higher firing temperature (typically 1250-1300degC) |
| Finish Options | Matte, semi-gloss finishes | Glossy, matte, and textured finishes |
| Weight | Lighter than porcelain tiles | Heavier, denser tile material |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Higher cost due to refined materials and processing |
| Water Absorption Rate | Typically around 3-7% | Less than 0.5% |
| Best Use Cases | Residential flooring, decorative tiles | Commercial flooring, outdoor tiling, bathrooms |
Introduction to Engineered Clay and Porcelain Clay
Engineered clay combines natural clay with additives to enhance strength, durability, and workability, making it ideal for tile production with consistent quality and reduced shrinkage. Porcelain clay, composed primarily of kaolin, quartz, and feldspar, undergoes high-temperature firing that results in a dense, low-porosity tile with exceptional hardness and water resistance. Both materials serve distinct purposes in tile manufacturing, with engineered clay favoring flexibility and porcelain clay excelling in wear resistance and longevity.
Composition Differences Between Engineered and Porcelain Clay
Engineered clay for tiles incorporates a blend of natural clay, feldspar, silica, and additives designed to enhance plasticity and drying properties, whereas porcelain clay primarily consists of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz with a higher density and lower impurity content. Porcelain clay undergoes higher firing temperatures, resulting in a vitrified, non-porous surface with greater strength and water resistance compared to engineered clay. The composition differences directly impact the tile's durability, texture, and suitability for various applications, with porcelain tiles favored for their refined particle size and homogenous microstructure.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Engineered clay undergoes a precise blending of natural clays and additives, followed by controlled plastic shaping and low-temperature firing, resulting in durable and versatile tile properties. Porcelain clay is manufactured through the vitrification process at extremely high temperatures, exceeding 1200degC, which produces denser, less porous, and highly water-resistant tiles. The difference in firing temperatures and raw material composition significantly impacts the mechanical strength and moisture absorption rates of both tile types.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Engineered clay offers enhanced durability and strength due to its controlled composition and firing process, making it resistant to cracking and chipping under heavy loads. Porcelain clay, known for its high density and low porosity, provides superior mechanical strength and exceptional resistance to wear, moisture, and chemical exposure. Comparative analysis indicates porcelain tiles generally outperform engineered clay in longevity and strength, especially in high-traffic or outdoor environments.
Water Absorption and Resistance Properties
Engineered clay tiles typically exhibit higher water absorption rates, ranging between 3-6%, compared to porcelain clay tiles which usually absorb less than 0.5%, making porcelain superior in water resistance. Porcelain tiles, made from denser clay and fired at higher temperatures, offer enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, stains, and frost, ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. In contrast, engineered clay tiles, due to their higher porosity, are more susceptible to water damage and require sealing for improved performance in moist environments.
Aesthetic Varieties and Finishes
Engineered clay offers a wide range of aesthetic varieties including vibrant colors, intricate patterns, and textures that mimic natural materials, making it ideal for customized tile designs. Porcelain clay provides superior finishes characterized by a dense, smooth surface with a refined sheen that enhances both contemporary and traditional styles. The durability of porcelain allows for matte, glossy, and polished finishes that maintain their aesthetic appeal over time, whereas engineered clay tiles excel in artistic and decorative customization.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Engineered clay tiles offer faster installation due to their uniform size and reduced water absorption, minimizing the risk of cracking during setting compared to porcelain clay tiles. Porcelain clay tiles require careful handling and precise substrate preparation because of their density and hardness, which can extend the installation time but provide superior durability. Maintenance for engineered clay tiles is simpler with routine cleaning sufficing, while porcelain clay tiles benefit from high resistance to stains and moisture, reducing long-term upkeep efforts.
Cost Comparison: Engineered Clay vs Porcelain Clay Tiles
Engineered clay tiles generally cost between $4 to $7 per square foot, offering a more budget-friendly option compared to porcelain clay tiles, which range from $5 to $15 per square foot depending on quality and finish. Porcelain tiles, known for higher durability and lower water absorption, justify their premium price in long-term maintenance savings and longevity. Cost considerations should also factor in installation expenses, as porcelain requires more specialized labor, increasing overall project costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered clay for tile production typically requires lower firing temperatures and reduces raw material waste, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional porcelain clay. Porcelain clay, while denser and more durable, demands higher energy consumption during kiln firing, increasing its environmental impact. Choosing engineered clay supports sustainability goals by minimizing energy use and promoting eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Best Applications for Engineered and Porcelain Tile
Engineered clay offers superior flexibility and is ideal for custom, handcrafted tile designs requiring intricate shapes and lighter installations, making it perfect for decorative wall tiles and artisanal flooring. Porcelain clay provides exceptional durability and water resistance, suited for high-traffic areas such as commercial floors, outdoor spaces, and wet environments like bathrooms and kitchens. Choosing engineered clay enhances aesthetic versatility, while porcelain clay guarantees long-lasting performance in demanding applications.
Infographic: Engineered clay vs Porcelain clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com