Grog clay contains pre-fired clay particles that improve brick strength and reduce shrinkage, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Red clay, rich in iron oxide, offers good plasticity and color but requires precise firing to prevent cracking in brick manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
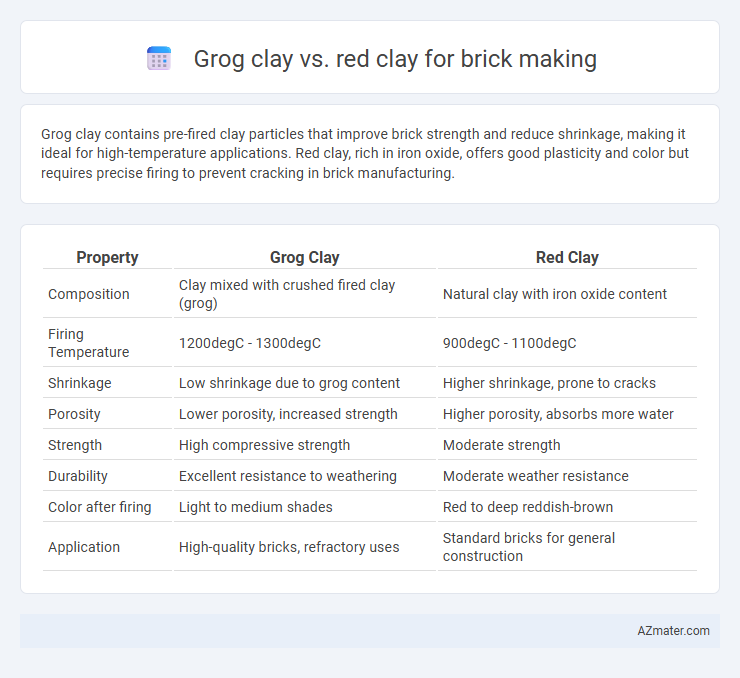
| Property | Grog Clay | Red Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with crushed fired clay (grog) | Natural clay with iron oxide content |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1300degC | 900degC - 1100degC |
| Shrinkage | Low shrinkage due to grog content | Higher shrinkage, prone to cracks |
| Porosity | Lower porosity, increased strength | Higher porosity, absorbs more water |
| Strength | High compressive strength | Moderate strength |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to weathering | Moderate weather resistance |
| Color after firing | Light to medium shades | Red to deep reddish-brown |
| Application | High-quality bricks, refractory uses | Standard bricks for general construction |
Introduction to Grog Clay and Red Clay
Grog clay is a type of fire clay mixed with crushed, pre-fired clay fragments, enhancing thermal stability and reducing shrinkage during brick firing. Red clay, rich in iron oxide, is commonly used for its natural reddish color and good plasticity, making it suitable for general brick production. Both clays serve distinct purposes, with grog clay favored for refractory bricks and red clay preferred for conventional red bricks.
Composition and Characteristics of Grog Clay
Grog clay contains ground, fired clay particles that enhance brick durability by reducing shrinkage and increasing thermal shock resistance, while red clay is rich in iron oxide, providing natural reddish coloration but higher shrinkage rates. The composition of grog clay includes silica and alumina with pre-fired grog fragments that act as inert fillers, improving mechanical strength and preventing cracking during drying and firing. These characteristics make grog clay particularly suitable for heavy-duty bricks and refractory applications, contrasting with red clay's common use in traditional brick masonry for aesthetic appeal.
Properties and Features of Red Clay
Red clay, known for its high iron oxide content, provides superior plasticity and workability, making it ideal for brick making. It offers excellent durability, good thermal insulation, and strong resistance to weathering due to its dense particle structure. Compared to grog clay, red clay typically yields bricks with a smoother finish and consistent color, enhancing aesthetic appeal in construction.
Brick-Making Process: Grog Clay vs. Red Clay
Grog clay contains pre-fired clay particles that enhance thermal shock resistance and reduce shrinkage during the brick-making process, resulting in stronger and more durable bricks. Red clay, composed primarily of iron oxide-rich minerals, offers excellent plasticity and workability but can experience greater shrinkage and cracking if not properly managed. The addition of grog in clay improves the brick's dimensional stability and firing behavior compared to red clay alone, making it preferable for specialized or high-performance brick production.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Grog clay enhances brick strength and durability by incorporating pre-fired clay particles, which improve resistance to cracking and thermal shock compared to red clay. Red clay bricks typically have lower compressive strength and are more susceptible to weathering due to their higher plasticity and organic content. The inclusion of grog in clay mixtures results in bricks with superior mechanical properties and longer lifespan in construction.
Thermal Performance in Finished Bricks
Grog clay enhances thermal performance in finished bricks by providing increased heat resistance and improved insulation due to its pre-fired grog particles that reduce shrinkage and enhance porosity. Red clay, while commonly used, typically offers lower thermal insulation and higher thermal conductivity, resulting in bricks that retain more heat and cool down slower. The incorporation of grog clay results in bricks with superior thermal stability and energy efficiency, ideal for construction requiring enhanced temperature regulation.
Workability and Handling Differences
Grog clay contains fired, crushed material that enhances workability by reducing plasticity and shrinkage, making it easier to handle and shape during brick making compared to red clay. Red clay, rich in iron oxide, tends to be more plastic and sticky, which can complicate handling and increase the risk of deformation during drying and firing. The inclusion of grog in clay mixtures improves structural stability and reduces drying time, providing a more consistent and manageable brick production process.
Cost and Availability Factors
Grog clay offers higher durability and thermal resistance but often comes at a higher cost due to specialized processing and limited regional availability compared to red clay. Red clay remains the preferred choice in brick making because of its widespread abundance, lower price, and ease of sourcing in many construction markets. Cost-efficiency and local availability make red clay significantly more economical for large-scale brick production.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Grog clay is commonly used in refractory bricks due to its high resistance to thermal shock and durability, making it ideal for kiln linings, furnaces, and industrial ovens. Red clay, with its rich iron oxide content, is preferred for architectural and decorative bricks, offering excellent strength and aesthetic appeal for residential and commercial building facades. The choice between grog clay and red clay depends on the application's temperature requirements and structural versus ornamental needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Grog clay, composed of crushed fired clay, enhances brick durability and reduces shrinkage, minimizing waste during manufacturing, which supports environmental sustainability. Red clay, abundant and natural, requires less processing but may lead to higher thermal energy consumption during firing due to its moisture content. Selecting grog clay can lower carbon emissions by improving kiln efficiency and extending brick lifespan, while red clay's local availability reduces transportation-related environmental impact.
Infographic: Grog clay vs Red clay for Brick making
 azmater.com
azmater.com