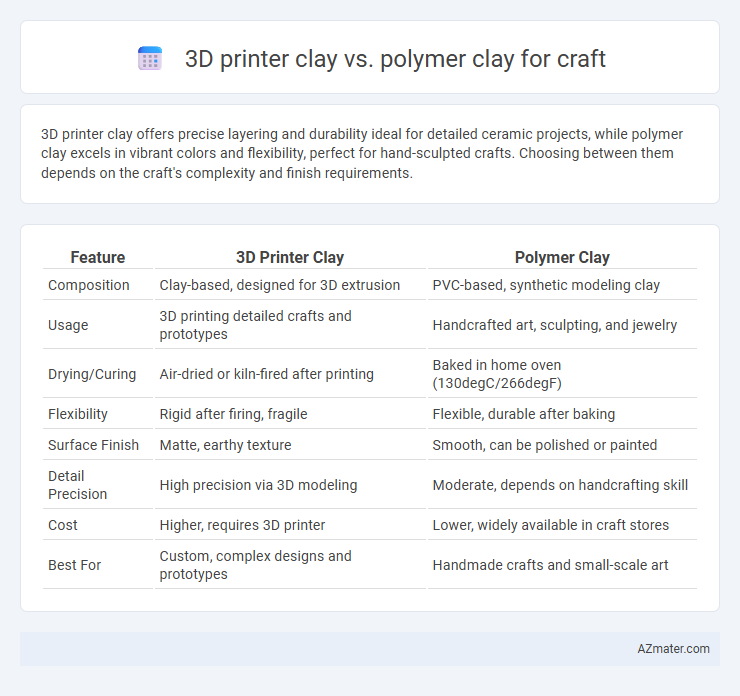
3D printer clay offers precise layering and durability ideal for detailed ceramic projects, while polymer clay excels in vibrant colors and flexibility, perfect for hand-sculpted crafts. Choosing between them depends on the craft's complexity and finish requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Polymer Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay-based, designed for 3D extrusion | PVC-based, synthetic modeling clay |
| Usage | 3D printing detailed crafts and prototypes | Handcrafted art, sculpting, and jewelry |
| Drying/Curing | Air-dried or kiln-fired after printing | Baked in home oven (130degC/266degF) |
| Flexibility | Rigid after firing, fragile | Flexible, durable after baking |
| Surface Finish | Matte, earthy texture | Smooth, can be polished or painted |
| Detail Precision | High precision via 3D modeling | Moderate, depends on handcrafting skill |
| Cost | Higher, requires 3D printer | Lower, widely available in craft stores |
| Best For | Custom, complex designs and prototypes | Handmade crafts and small-scale art |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Polymer Clay
3D printer clay, also known as ceramic filament, is a specialized material compatible with certain 3D printers that allows for the creation of intricate, kiln-fireable ceramic objects, providing precision and repeatability for artisanal crafts. Polymer clay, composed of synthetic plasticized PVC, offers a versatile, hand-moldable medium that hardens permanently through baking at low temperatures, favored by crafters for its ease of use and vibrant color options. Both clays cater to different crafting needs: 3D printer clay excels in sophisticated, technology-driven ceramic creations, while polymer clay suits traditional sculpting and mixed media projects.
Material Composition: 3D Printer Clay vs Polymer Clay
3D printer clay typically consists of a blend of natural clay particles with synthetic binders designed for extrusion through 3D printer nozzles, ensuring precise layer deposition and durability after firing. Polymer clay is a synthetic modeling material made primarily from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) mixed with plasticizers, which hardens through baking rather than firing, allowing for flexible, detailed crafting. The fundamental difference lies in 3D printer clay's ceramic properties suitable for kiln firing, while polymer clay remains a pliable, heat-cured plastic ideal for handcrafting.
Texture and Workability Comparison
3D printer clay offers a smooth, uniform texture ideal for detailed, precise modeling, while polymer clay presents a more pliable and tactile surface favored for handcrafting and sculpting. Workability of 3D printer clay depends on printer settings and can be less forgiving, requiring digital design adjustments, whereas polymer clay allows direct manipulation, easy blending, and shaping before curing. Both materials cater to different crafting needs, with polymer clay excelling in manual versatility and 3D printer clay providing high precision for complex geometries.
Tool Requirements and Accessibility
3D printer clay requires specialized equipment such as a compatible 3D printer and software for digital modeling, making it less accessible to hobbyists without technical expertise. Polymer clay demands minimal tools, often just basic sculpting utensils and a home oven for curing, offering greater accessibility to beginners and casual crafters. The digital nature of 3D printer clay enables precise, replicable designs, while polymer clay provides hands-on flexibility without reliance on technology.
Design Flexibility and Creative Potential
3D printer clay offers unparalleled design flexibility by allowing precise, repeatable, and intricate shapes through digital modeling, making it ideal for complex craft projects. Polymer clay provides rich creative potential with its malleable texture, enabling artists to hand-sculpt unique details and blend colors organically for personalized designs. Combining 3D printer clay's accuracy with polymer clay's tactile versatility expands artistic possibilities in craft making.
Durability and Finished Product Strength
3D printer clay offers enhanced durability and structural integrity due to its formulation designed for additive manufacturing processes, resulting in finished products with high strength and resistance to wear. Polymer clay, while versatile and suitable for detailed craftwork, generally lacks the same mechanical robustness and may be more prone to chipping or deformation under stress. For crafts demanding long-lasting, sturdy outcomes, 3D printer clay provides superior performance in terms of durability and finished product strength.
Cost Efficiency in Craft Projects
3D printer clay typically costs more upfront due to specialized materials and equipment but allows precise, repeatable designs, reducing long-term waste and project expenses. Polymer clay offers a lower initial cost and wide availability, making it ideal for small-scale or hobbyist crafts, but can generate more material waste during shaping and curing. Balancing cost efficiency depends on project scale and complexity, with 3D printer clay favored for detailed, batch production, and polymer clay suited for flexible, budget-conscious crafting.
Compatibility with Mixed Media and Finishes
3D printer clay offers exceptional compatibility with mixed media due to its smooth, malleable texture, allowing seamless integration with materials like metal, wood, and fabric, and supports diverse finishes including paints, glazes, and varnishes. Polymer clay is highly versatile in finishes, able to be baked to a durable, glossy or matte surface, and combines well with embossing powders, inks, and other craft supplies for mixed media projects. Both clays provide robust options for artists seeking tailored textures and finishes, but 3D printer clay's blendability with synthetic materials often surpasses traditional polymer clay in complex multimedia craft applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
3D printer clay, typically made from biodegradable materials like PLA, offers a more environmentally friendly option compared to polymer clay, which is derived from petroleum-based compounds and can release harmful fumes during curing. Polymer clay requires baking at high temperatures, posing potential health risks due to the emission of toxic volatile organic compounds (VOCs). In contrast, 3D printer clay hardens through additive layer manufacturing without the need for heat, reducing both environmental impact and safety concerns for crafters.
Best Uses and Recommendations for Crafters
3D printer clay excels in precise, repeatable sculpting ideal for detailed prototypes, jewelry molds, and small-scale production, while polymer clay suits handcrafting nuanced, colorful designs with easy oven curing. Crafters seeking rapid prototyping, reuse, and digital modeling favor 3D printer clay, whereas those focused on tactile artistry, vibrant textures, and custom shapes benefit from polymer clay. For best results, combine 3D printer clay's structural accuracy with polymer clay's artistic flexibility depending on project complexity and desired finish.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Polymer clay for Craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com