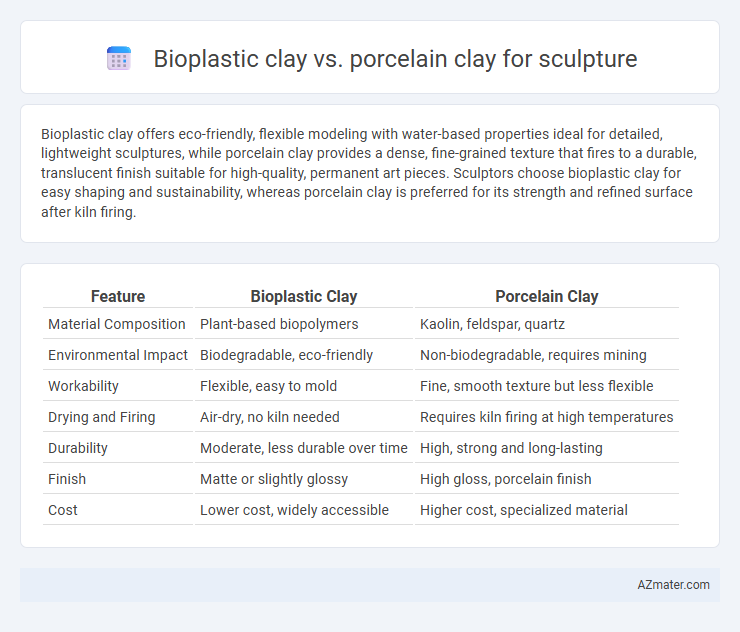
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly, flexible modeling with water-based properties ideal for detailed, lightweight sculptures, while porcelain clay provides a dense, fine-grained texture that fires to a durable, translucent finish suitable for high-quality, permanent art pieces. Sculptors choose bioplastic clay for easy shaping and sustainability, whereas porcelain clay is preferred for its strength and refined surface after kiln firing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant-based biopolymers | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, requires mining |
| Workability | Flexible, easy to mold | Fine, smooth texture but less flexible |
| Drying and Firing | Air-dry, no kiln needed | Requires kiln firing at high temperatures |
| Durability | Moderate, less durable over time | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Finish | Matte or slightly glossy | High gloss, porcelain finish |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely accessible | Higher cost, specialized material |
Introduction to Bioplastic Clay and Porcelain Clay
Bioplastic clay is a modern sculpting material made from biodegradable polymers and natural ingredients, offering flexibility, lightweight properties, and easy drying without firing. Porcelain clay, a high-quality ceramic material composed primarily of kaolin, silica, and feldspar, is valued for its durability, fine texture, and ability to achieve intricate details after kiln firing. Sculptors choose bioplastic clay for quick, eco-friendly projects and porcelain clay for permanent, refined artworks requiring strength and smooth finishes.
Composition and Material Origins
Bioplastic clay is composed primarily of biodegradable polymers mixed with natural fibers, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or cellulose, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional clays. Porcelain clay, on the other hand, consists of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, sourced from fine white clay deposits with a natural mineral composition that vitrifies at high temperatures for a smooth, glass-like finish. The distinct material origins affect their workability and durability, with bioplastic clay favoring flexibility and environmental sustainability, while porcelain clay offers exceptional strength and translucency after firing.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Bioplastic clay offers superior workability due to its flexible, air-dry properties, making it ideal for intricate, detailed sculpting and quick modifications without the need for firing. Porcelain clay, while less flexible, excels in fine detail and smooth finishes but requires careful handling and kiln firing, which limits immediate adjustments during the sculpting process. Sculptors often choose bioplastic clay for experimental, layered techniques and porcelain clay for refined, permanent artworks requiring high durability.
Drying Time and Flexibility
Bioplastic clay offers significantly shorter drying times, often drying within hours due to its polymer base, making it ideal for quick project turnarounds. Porcelain clay requires a much longer drying period, sometimes days to weeks, as it is water-based and needs gradual moisture evaporation to prevent cracking. Flexibility in bioplastic clay remains high even after drying, allowing minor adjustments, whereas porcelain becomes rigid and fragile once fired, demanding careful handling during sculpting and finishing.
Surface Finish and Texture Differences
Bioplastic clay offers a smooth, flexible surface ideal for intricate textures and fine details, while porcelain clay provides a more refined, dense finish with a naturally glossy appearance after firing. Porcelain's surface becomes hard and translucent, enhancing the sculpture's elegance, whereas bioplastic clay remains matte and pliable, suitable for easy manipulation and repeated reshaping. The choice between them impacts the tactile quality and visual refinement of the final sculpture, with porcelain preferred for polished finishes and bioplastic for versatile textural experimentation.
Durability and Longevity of Sculptures
Bioplastic clay offers moderate durability, often suitable for temporary or experimental sculptures due to its flexibility and lightweight nature but tends to degrade over time with exposure to moisture or UV light. Porcelain clay provides exceptional durability and longevity, as fired porcelain becomes highly resistant to chipping, cracking, and environmental damage, making it ideal for long-lasting, fine art sculptures. Sculptures crafted from porcelain clay maintain structural integrity and aesthetic quality for centuries, outperforming bioplastic in both aging resilience and archival potential.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastic clay offers significant environmental benefits due to its biodegradability and renewable plant-based materials, reducing landfill waste and carbon footprint compared to traditional Porcelain clay, which involves energy-intensive firing processes and mining of non-renewable kaolin clay. Porcelain clay's high firing temperatures contribute to greater CO2 emissions and resource depletion, whereas bioplastic clays often cure at room temperature, minimizing environmental impact. Sustainable sculptors increasingly prefer bioplastic clay for eco-friendly art practices that prioritize lower energy consumption and reduced ecological degradation.
Firing Requirements and Thermal Properties
Bioplastic clay typically requires low or no firing temperatures, as it's often air-dry or oven-bake clay, making it unsuitable for high-heat kiln processes used in ceramics. Porcelain clay demands high firing temperatures, usually between 1200degC to 1400degC, to achieve its characteristic durability, translucency, and vitrification. Thermal expansion in porcelain is minimal, providing superior resistance to cracking during firing, whereas bioplastic clay lacks this property due to its polymer base and is prone to deformation or damage under heat.
Cost Factors and Accessibility
Bioplastic clay is generally more affordable and widely accessible compared to porcelain clay, making it a popular choice for beginners and hobbyists. Porcelain clay, known for its fine texture and durability, tends to be more expensive and less readily available due to its specialized production and firing requirements. The higher cost and limited accessibility of porcelain clay often make bioplastic clay the preferred option for cost-conscious sculptors seeking flexibility and ease of use.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Sculpture
Bioplastic clay offers flexibility and lightweight properties ideal for intricate and temporary sculpture designs, while porcelain clay provides durability, smooth texture, and a refined finish suited for long-lasting, high-quality artworks. Selecting the right clay depends on the desired sculpture's durability, detail precision, and final application, where bioplastic clay excels in ease of shaping and porcelain clay in strength and fine detail retention. Artists prioritizing longevity and professional-grade aesthetics often opt for porcelain, whereas those needing versatility and quick modeling choose bioplastic clay.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Porcelain clay for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com