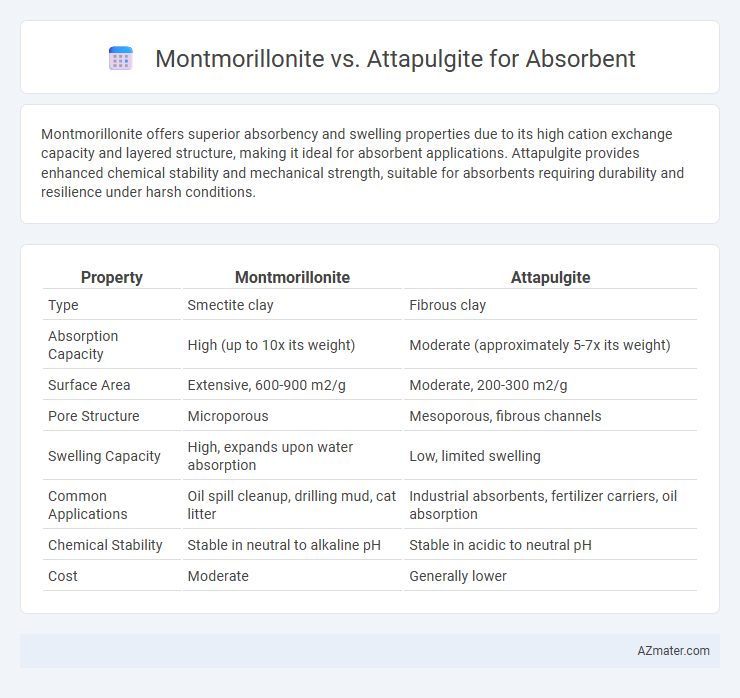
Montmorillonite offers superior absorbency and swelling properties due to its high cation exchange capacity and layered structure, making it ideal for absorbent applications. Attapulgite provides enhanced chemical stability and mechanical strength, suitable for absorbents requiring durability and resilience under harsh conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Attapulgite |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Smectite clay | Fibrous clay |
| Absorption Capacity | High (up to 10x its weight) | Moderate (approximately 5-7x its weight) |
| Surface Area | Extensive, 600-900 m2/g | Moderate, 200-300 m2/g |
| Pore Structure | Microporous | Mesoporous, fibrous channels |
| Swelling Capacity | High, expands upon water absorption | Low, limited swelling |
| Common Applications | Oil spill cleanup, drilling mud, cat litter | Industrial absorbents, fertilizer carriers, oil absorption |
| Chemical Stability | Stable in neutral to alkaline pH | Stable in acidic to neutral pH |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally lower |
Introduction to Montmorillonite and Attapulgite
Montmorillonite and attapulgite are two prominent clay minerals widely used as absorbents due to their unique structural properties. Montmorillonite, a smectite clay, exhibits exceptional swelling capacity and high cation exchange capacity, making it highly effective for liquid absorption and contaminant removal. Attapulgite, also known as palygorskite, features a fibrous structure that provides superior adsorption and oil retention capabilities, often preferred in industrial and environmental applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Montmorillonite and attapulgite are both clay minerals used as absorbents, with distinct chemical compositions and structures influencing their performance. Montmorillonite, a smectite group mineral, consists mainly of hydrated sodium calcium aluminum magnesium silicates forming a 2:1 layered structure with high cation exchange capacity and swelling properties. Attapulgite, a magnesium aluminum silicate in the palygorskite group, has a fibrous chain structure resulting in lower swelling but enhanced viscosity and adsorption due to its high surface area and porosity.
Absorption Mechanisms of Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite exhibits superior absorbent properties due to its layered silicate structure, which allows intercalation of water molecules and organic compounds through cation exchange and swelling mechanisms. Its high specific surface area and strong hydration capacity enable efficient adsorption of liquids and contaminants, outperforming attapulgite's fibrous structure that primarily relies on capillary action. The expansive interlayer spacing in montmorillonite facilitates enhanced absorption and retention of fluids, making it particularly effective in environmental and industrial applications.
Absorption Mechanisms of Attapulgite
Attapulgite exhibits superior absorption capabilities compared to Montmorillonite due to its unique fibrous crystal structure, which creates a high surface area and extensive porosity for efficient liquid uptake. Its absorption mechanism primarily involves capillary action and physical adsorption within the interwoven fiber network, allowing rapid and effective trapping of oils, water, and other fluids. This structural composition makes Attapulgite highly effective in applications such as oil spill cleanup, industrial absorbents, and moisture control, outperforming Montmorillonite in both absorption rate and capacity.
Efficiency of Absorbency: Montmorillonite vs Attapulgite
Montmorillonite exhibits superior absorbency due to its high cation exchange capacity and layered structure, enabling it to retain more water and fluids compared to attapulgite. Attapulgite, with its fibrous morphology, offers rapid initial absorption but lower overall liquid retention than montmorillonite. Efficiency in absorbency applications favors montmorillonite for sustained moisture control, while attapulgite suits scenarios requiring quick liquid uptake.
Applications in Industrial Absorbents
Montmorillonite offers superior swelling properties and high cation exchange capacity, making it ideal for oil spill cleanup and chemical spill absorbents in industrial settings. Attapulgite's fibrous structure provides excellent adsorption and mechanical strength, enhancing its use in drilling muds, waste treatment, and industrial absorbents targeting heavy metal ions. Both clays are preferred in different absorbent applications due to their unique absorption mechanisms and environmental compatibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Montmorillonite and Attapulgite both serve as effective absorbents with distinct environmental impacts and sustainability profiles. Montmorillonite, a type of smectite clay, offers high swelling capacity and natural abundance, allowing for eco-friendly extraction with minimal habitat disruption compared to synthetic alternatives. Attapulgite's fibrous structure provides excellent adsorption but can require more energy-intensive processing, influencing its overall sustainability footprint in environmental applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Montmorillonite generally offers a lower cost per unit due to its abundant deposits and wide mining distribution, making it more readily available in global markets compared to Attapulgite. Attapulgite, while effective as an absorbent, often incurs higher costs linked to limited geographic availability and more complex extraction processes. The supply chain for Montmorillonite benefits from established infrastructure, providing a more consistent and cost-effective source for industrial absorbent applications.
Pros and Cons: Montmorillonite vs Attapulgite
Montmorillonite offers excellent water absorption and swelling properties, making it ideal for applications requiring high moisture retention, but it can lose effectiveness in high salinity environments. Attapulgite provides superior adsorption capacity for oils and organic compounds due to its fibrous structure, yet it generally has lower swelling capability and moisture retention compared to Montmorillonite. Choosing between Montmorillonite and Attapulgite depends on the specific absorbent need--moisture retention favors Montmorillonite, while oil adsorption suits Attapulgite better.
Choosing the Right Absorbent: Key Considerations
Montmorillonite offers superior absorption capacity due to its high swelling properties and large surface area, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid liquid uptake. Attapulgite, known for its fibrous structure and excellent thixotropic behavior, provides better structural stability in absorbent formulations, especially in oil and grease management. Selecting the right absorbent depends on the specific needs for absorption rate, fluid viscosity, and final product consistency, with montmorillonite favored for maximum absorption and attapulgite chosen for enhanced structural integrity.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Attapulgite for Absorbent
 azmater.com
azmater.com