Casting slip clay offers high fluidity and fine particle size ideal for detailed mold casting, while ball clay provides strong plasticity and binding properties that enhance mold strength and flexibility. Selecting slip clay improves surface finish, whereas ball clay ensures better mold durability during the casting process.
Table of Comparison
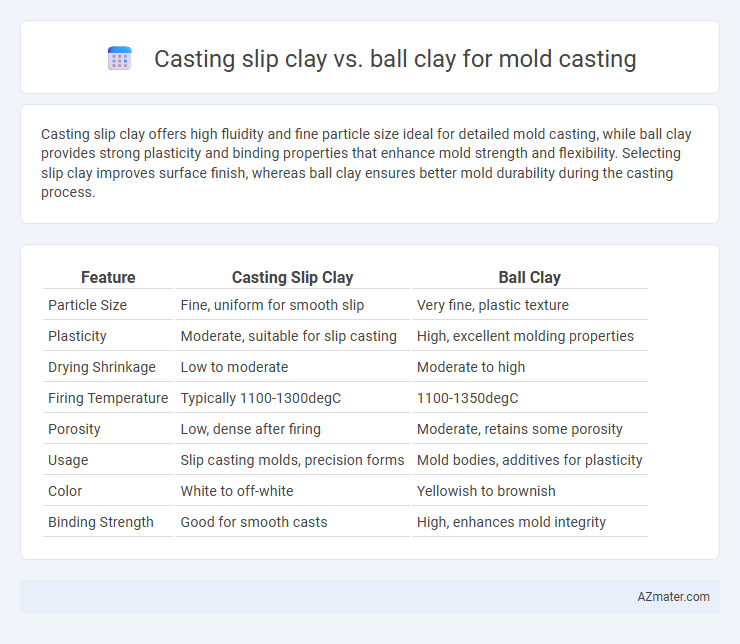
| Feature | Casting Slip Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Fine, uniform for smooth slip | Very fine, plastic texture |
| Plasticity | Moderate, suitable for slip casting | High, excellent molding properties |
| Drying Shrinkage | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1100-1300degC | 1100-1350degC |
| Porosity | Low, dense after firing | Moderate, retains some porosity |
| Usage | Slip casting molds, precision forms | Mold bodies, additives for plasticity |
| Color | White to off-white | Yellowish to brownish |
| Binding Strength | Good for smooth casts | High, enhances mold integrity |
Introduction to Casting Slip Clay and Ball Clay
Casting slip clay is a liquid suspension primarily composed of fine-grained kaolin, silica, and feldspar, designed for mold casting due to its smooth texture and excellent flow properties. Ball clay contains a high percentage of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, offering plasticity and strength but is generally less refined than casting slip clay, affecting mold detail reproduction. Both clays play crucial roles in ceramic mold casting, with casting slip clay favored for precise, fine-detail molds while ball clay enhances plasticity and workability in the casting process.
Composition Differences: Slip Clay vs Ball Clay
Slip clay typically contains higher levels of kaolin and feldspar, providing smooth flow and excellent plasticity essential for mold casting. Ball clay is richer in organic matter and has finer particles, which enhance plasticity but reduce drying strength compared to slip clay. The distinct mineral compositions influence their behavior during casting, with slip clay offering superior casting performance due to balanced refractory properties and workability.
Plasticity and Workability in Mold Casting
Casting slip clay exhibits higher plasticity than ball clay, providing superior workability essential for mold casting processes. The elevated plasticity allows casting slip clay to easily conform to mold details, resulting in precise and smooth ceramic formations. In contrast, ball clay, while still plastic, is less workable and may require additives to enhance its casting performance.
Shrinkage Rates and Drying Behavior
Casting slip clay generally exhibits lower shrinkage rates compared to ball clay, making it more dimensionally stable during the mold casting process. Its drying behavior is more uniform and less prone to cracking, due to a balanced particle size distribution and reduced plasticity. Ball clay, with higher plasticity and finer particles, tends to shrink more and requires careful drying to prevent warping or splitting in cast molds.
Firing Temperatures and Maturation
Casting slip clay typically matures at lower firing temperatures ranging from cone 04 to cone 06 (approximately 999degC to 1046degC), making it ideal for delicate mold casting with minimal shrinkage and good green strength. Ball clay requires higher firing temperatures, usually between cone 6 to cone 10 (around 1220degC to 1300degC), to achieve full maturation, resulting in increased plasticity and strength but with more pronounced shrinkage during firing. The choice between casting slip clay and ball clay significantly impacts the final mold casting durability and surface finish due to these differing maturation profiles.
Surface Finish and Texture Comparison
Casting slip clay offers a finer particle size and higher plasticity than ball clay, resulting in a smoother surface finish with fewer imperfections for mold casting. Ball clay, while providing good workability and strength, tends to produce a slightly rougher texture due to its larger particle size and lower purity. Optimal surface finish in mold casting is achieved by balancing slip viscosity and clay composition, where casting slip clay excels in delivering a polished, refined texture.
Strength and Durability of Final Products
Casting slip clay offers superior strength and durability in mold casting due to its high plasticity and fine particle size, which contribute to a dense and uniform final product. Ball clay, while highly plastic and flexible, tends to introduce more shrinkage and less mechanical strength in the final cast piece, making it less ideal for applications requiring robust durability. The mineral composition and particle size distribution of casting slip clay result in enhanced fired strength and resistance to cracking compared to ball clay molds.
Common Applications in Mold Casting
Casting slip clay, known for its fine particle size and smooth texture, is commonly used in creating detailed molds and precision casting in ceramics, offering excellent fluidity and surface finish. Ball clay, valued for its plasticity and strength, is frequently employed in mold casting for forming durable and flexible molds, especially in producing large or complex shapes that require resistance to deformation. Both clays are essential in mold casting, with slip clay preferred for intricate designs and ball clay for robust, reusable molds.
Cost Efficiency and Material Availability
Casting slip clay offers cost efficiency due to its affordability and ease of preparation, making it ideal for large-scale mold casting projects with tight budgets. Ball clay, while generally more expensive, provides superior plasticity and finer particle size, enhancing mold detail but potentially increasing material costs. Availability of casting slip clay is widespread, whereas ball clay can be more region-specific, impacting sourcing and supply chain stability for manufacturers.
Selecting the Right Clay for Your Mold Casting Project
Selecting the right clay for mold casting depends on the specific project requirements, where casting slip clay offers higher plasticity and smooth surface finish ideal for detailed molds, while ball clay provides excellent workability and strength for durable molds that withstand repeated use. Casting slip clay, typically prepared with fine particles suspended in water, ensures precision in delicate designs but may require slower drying to avoid cracking. Ball clay's natural fine particle size and high plasticity contribute to its resilience and flexibility, making it preferred for larger-scale or more robust mold castings.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs Ball clay for Mold casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com