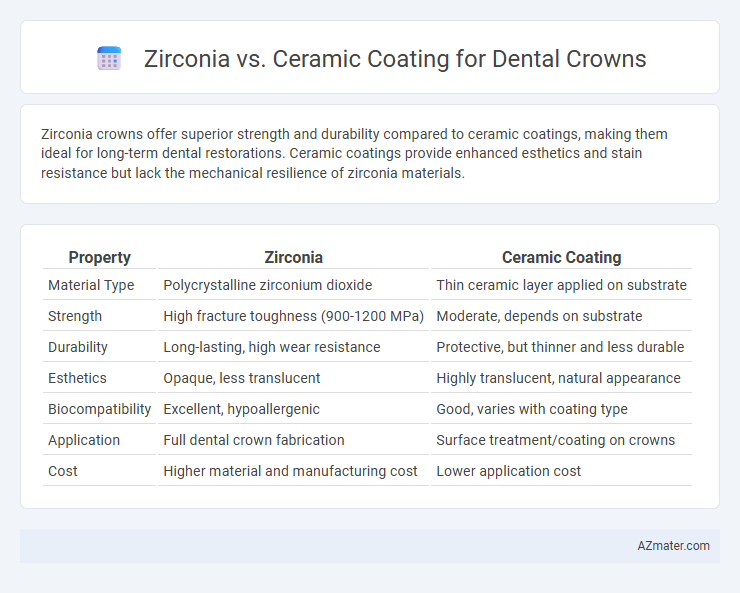
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and durability compared to ceramic coatings, making them ideal for long-term dental restorations. Ceramic coatings provide enhanced esthetics and stain resistance but lack the mechanical resilience of zirconia materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconia | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polycrystalline zirconium dioxide | Thin ceramic layer applied on substrate |
| Strength | High fracture toughness (900-1200 MPa) | Moderate, depends on substrate |
| Durability | Long-lasting, high wear resistance | Protective, but thinner and less durable |
| Esthetics | Opaque, less translucent | Highly translucent, natural appearance |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, hypoallergenic | Good, varies with coating type |
| Application | Full dental crown fabrication | Surface treatment/coating on crowns |
| Cost | Higher material and manufacturing cost | Lower application cost |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crown materials primarily consist of zirconia and ceramic, each offering distinct advantages for restorative dentistry. Zirconia crowns are highly durable, biocompatible, and resistant to fractures, making them suitable for high-stress areas such as molars. Ceramic crowns provide superior aesthetics with a translucent appearance that closely mimics natural teeth, ideal for visible front teeth restorations.
What is Zirconia in Dental Crowns?
Zirconia in dental crowns is a high-strength, biocompatible ceramic material known for its durability and natural tooth-like appearance. It offers superior resistance to fracture and wear compared to traditional ceramics, making it ideal for long-lasting restorations in both anterior and posterior teeth. Its translucency and color closely mimic natural enamel, providing aesthetic benefits alongside functional performance.
Ceramic Coating: Definition and Uses in Dentistry
Ceramic coating in dentistry refers to a thin, durable layer of biocompatible ceramic material applied to dental crowns to enhance aesthetics and protect the underlying structure. This coating improves wear resistance, reduces plaque accumulation, and provides a natural tooth-like appearance, making it ideal for anterior restorations. Compared to zirconia, ceramic coatings offer superior translucency and color matching, enhancing the overall cosmetic outcome of dental crowns.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior strength and durability compared to traditional ceramic coatings due to their high fracture toughness and resistance to wear under bite forces. Ceramic coatings, while aesthetically pleasing with excellent translucency, are more prone to chipping and cracking over time, especially in areas subjected to heavy occlusal pressure. Zirconia's robust crystalline structure ensures longer-lasting performance, making it the preferred choice for posterior crowns requiring enhanced mechanical resilience.
Aesthetics: Natural Look and Color Matching
Zirconia crowns offer exceptional aesthetics with a natural translucent appearance that closely mimics real tooth enamel, making them ideal for visible front teeth restorations. Ceramic coatings enhance the color matching capabilities of dental crowns by allowing precise customization to blend seamlessly with surrounding teeth shades. The combination of zirconia's strength and ceramic's color versatility ensures durable crowns with superior visual appeal and lifelike translucency.
Biocompatibility and Allergic Reactions
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit exceptional biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions and tissue irritation due to their inert, metal-free composition. Ceramic coatings on crowns, while aesthetically pleasing, may carry a slightly higher risk of causing sensitivity or allergic responses in some patients due to potential impurities or glaze degradation over time. Clinical studies highlight zirconia's superior performance in maintaining gum health and reducing inflammation compared to coated ceramics, making it a preferred choice for patients with metal allergies or hypersensitivities.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior longevity and wear resistance due to their high fracture toughness and biocompatibility, making them less prone to chipping and wear over time compared to ceramic coatings. Ceramic coatings, while aesthetically pleasing, tend to wear down more quickly and may require more frequent replacement or repair in high-stress dental environments. Clinical studies indicate that zirconia crowns maintain structural integrity and function effectively for over 10-15 years, outperforming ceramic-coated alternatives in durability.
Suitability for Different Dental Applications
Zirconia dental crowns offer exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for molars and areas requiring high bite force resistance, while ceramic coatings provide superior aesthetics for front teeth due to their natural translucency and color match. Zirconia's biocompatibility and fracture toughness suit long-term dental applications, whereas ceramic coatings excel in enhancing the appearance of dental restorations without compromising functionality. Selecting between zirconia and ceramic coatings depends on the specific dental application, balancing structural demands with visual outcomes for optimal patient satisfaction.
Cost Analysis: Zirconia vs Ceramic Coating
Zirconia dental crowns typically incur higher upfront costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior durability, averaging between $800 to $2,500 per crown. Ceramic coatings, often applied as a thin layer over metal or ceramic bases, present a more affordable alternative, with prices ranging from $500 to $1,500, but may require more frequent replacements due to lower wear resistance. Evaluating long-term value involves considering both initial expenses and maintenance frequency, where zirconia's longevity can offset its higher initial investment compared to ceramic-coated options.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Zirconia crowns offer exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for molars and areas requiring high bite resistance, while ceramic crowns provide superior natural aesthetics suited for visible front teeth. Factors to consider when choosing between zirconia and ceramic coatings include the crown's location, patient's bite force, and aesthetic demands, along with biocompatibility and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating these elements ensures optimal longevity, functionality, and visual integration of the dental restoration.
Infographic: Zirconia vs Ceramic coating for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com