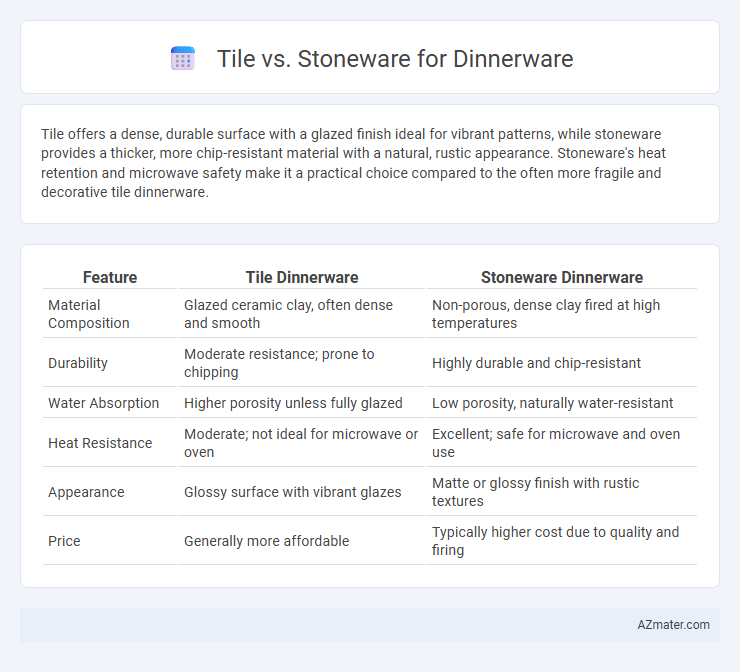
Tile offers a dense, durable surface with a glazed finish ideal for vibrant patterns, while stoneware provides a thicker, more chip-resistant material with a natural, rustic appearance. Stoneware's heat retention and microwave safety make it a practical choice compared to the often more fragile and decorative tile dinnerware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tile Dinnerware | Stoneware Dinnerware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glazed ceramic clay, often dense and smooth | Non-porous, dense clay fired at high temperatures |
| Durability | Moderate resistance; prone to chipping | Highly durable and chip-resistant |
| Water Absorption | Higher porosity unless fully glazed | Low porosity, naturally water-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate; not ideal for microwave or oven | Excellent; safe for microwave and oven use |
| Appearance | Glossy surface with vibrant glazes | Matte or glossy finish with rustic textures |
| Price | Generally more affordable | Typically higher cost due to quality and firing |
Introduction to Dinnerware Materials
Tile and stoneware are popular materials for dinnerware, each offering unique durability and aesthetic qualities. Tile dinnerware features a glazed, often decorative surface with high resistance to heat and scratching. Stoneware is a dense, non-porous ceramic fired at high temperatures, providing strength, chip resistance, and a rustic appearance ideal for everyday use.
Overview: Tile vs Stoneware for Dinnerware
Tile dinnerware typically features glazed ceramic surfaces that offer vibrant designs and high durability, making it ideal for decorative use and casual dining. Stoneware dinnerware is fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a denser, more chip-resistant material with a natural, earthy appearance preferred for everyday use. The choice between tile and stoneware dinnerware depends on balancing aesthetic appeal, durability, and functional requirements for meal presentation.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Tile dinnerware is typically made from ceramic clay mixtures fused at high temperatures, often glazed for durability and design versatility. Stoneware consists of denser clay fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a non-porous, chip-resistant finish that is more robust than standard tile ceramics. Manufacturing stoneware involves vitrification, which enhances strength and water resistance, whereas tile production emphasizes decorative surface treatments and thinner profiles.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Stoneware dinnerware offers superior durability and strength compared to tile-based dinnerware due to its dense, vitrified composition, which resists chipping and cracking under regular use. Tiles, often made from ceramic or porcelain with a glazed surface, tend to be more prone to surface scratches and fractures when subjected to impact or thermal shock. The inherent toughness of stoneware ensures longer-lasting dinnerware that withstands daily wear, making it a preferred choice for both casual and formal dining settings.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Tile dinnerware offers a modern, sleek aesthetic with vibrant glazing options and intricate patterns that enhance contemporary table settings. Stoneware provides a rustic, earthy appeal with natural textures and muted tones, perfect for a cozy, farmhouse-inspired look. Both materials deliver versatile design options, but tile excels in bold, glossy finishes while stoneware emphasizes handcrafted charm and durability.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Tile dinnerware tends to be heavier and less comfortable to handle due to its dense and rigid material composition, which can lead to fatigue during extended use. Stoneware offers a balanced weight, providing durability and sturdiness while maintaining ease of handling for everyday dining. When selecting dinnerware, considering the weight and grip is essential for comfort and practical usability.
Heat Resistance and Microwave Safety
Tile dinnerware, often made from ceramic or porcelain, offers moderate heat resistance but can be prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes, making it less ideal for high-heat cooking or frequent microwave use. Stoneware, fired at higher temperatures around 1200degC to 1300degC, boasts superior heat resistance and durability, allowing safe use in microwaves and conventional ovens without warping or damage. Choosing stoneware for dinnerware ensures enhanced microwave safety and consistent performance under thermal stress compared to tile-based options.
Maintenance, Cleaning, and Care
Tile dinnerware generally requires less maintenance than stoneware due to its glazed surface, which resists staining and scratches more effectively. Stoneware often needs gentle handwashing and avoidance of harsh detergents to maintain its natural, porous texture and prevent chipping. Proper care for both includes avoiding sudden temperature changes to reduce the risk of cracking and extending their longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tile dinnerware, often made from ceramic materials fired at lower temperatures than stoneware, generally requires less energy during production, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Stoneware, known for its durability and longevity, reduces the need for frequent replacement, thus minimizing waste over time. Both materials are typically recyclable and biodegradable, but choosing locally sourced raw materials and manufacturers with sustainable practices can significantly enhance the environmental benefits of either option.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Tile dinnerware typically costs less upfront than stoneware due to its simpler manufacturing process and abundant raw materials, making it a budget-friendly option for everyday use. Stoneware offers greater durability and chip resistance, resulting in longer lifespan and fewer replacement expenses, which enhances its overall value despite a higher initial price. Evaluating both options involves balancing initial cost savings of tile with stoneware's superior longevity and sustained aesthetic appeal for a more cost-effective long-term investment.
Infographic: Tile vs Stoneware for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com