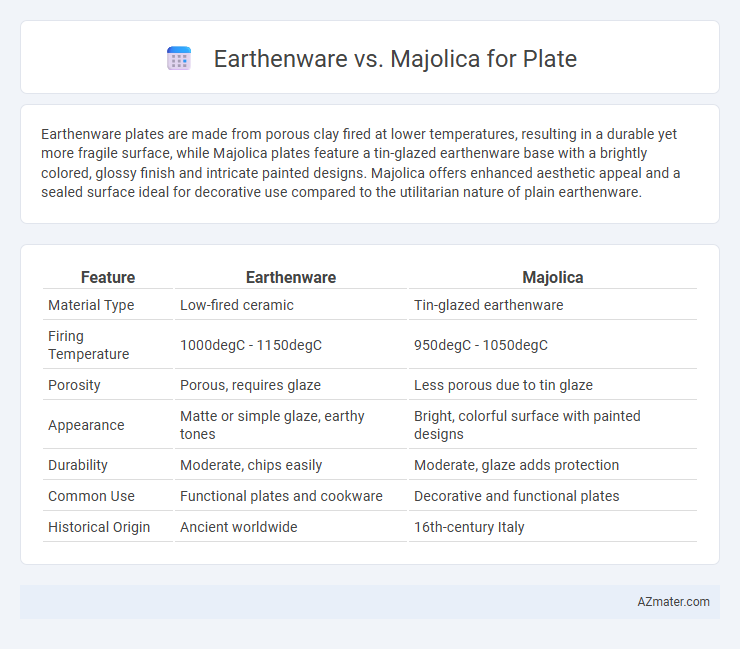
Earthenware plates are made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a durable yet more fragile surface, while Majolica plates feature a tin-glazed earthenware base with a brightly colored, glossy finish and intricate painted designs. Majolica offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and a sealed surface ideal for decorative use compared to the utilitarian nature of plain earthenware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Earthenware | Majolica |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-fired ceramic | Tin-glazed earthenware |
| Firing Temperature | 1000degC - 1150degC | 950degC - 1050degC |
| Porosity | Porous, requires glaze | Less porous due to tin glaze |
| Appearance | Matte or simple glaze, earthy tones | Bright, colorful surface with painted designs |
| Durability | Moderate, chips easily | Moderate, glaze adds protection |
| Common Use | Functional plates and cookware | Decorative and functional plates |
| Historical Origin | Ancient worldwide | 16th-century Italy |
Understanding Earthenware: Key Characteristics
Earthenware plates are crafted from porous clay and fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000degC to 1,150degC, resulting in a slightly porous and softer finish compared to other ceramics. Earthenware's key characteristics include its rich, earthy tones and a rustic texture, often combined with a glaze to improve durability and prevent water absorption. This type of ceramic offers excellent heat retention but requires careful handling to avoid chipping and is not as vitrified as stoneware or porcelain.
What is Majolica? Origins and Features
Majolica is a type of earthenware pottery that originated in the Italian Renaissance, characterized by its vibrant, tin-glazed surface that creates a glossy and colorful finish. Distinct from standard earthenware, Majolica features intricate hand-painted designs and a white opaque glaze that enhances the brilliance of the pigments. Its origins trace back to the 15th century in Italy, where artisans developed this technique to mimic the appearance of porcelain while utilizing local clay and glazing methods for decorative plates.
Material Composition: Earthenware vs Majolica
Earthenware is made from clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and less durable material that often requires glazing to be watertight. Majolica, a type of earthenware, features a tin-glazed surface that creates a bright, opaque white finish ideal for detailed painted designs. The tin glaze on majolica not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also improves the plate's resistance to liquids compared to traditional earthenware.
Visual Differences Between Earthenware and Majolica Plates
Earthenware plates have a rustic, porous texture with a matte or dull finish, often showcasing natural clay tones ranging from reddish-brown to cream. Majolica plates are characterized by a glossy, vibrant glaze with intricate hand-painted designs and bright, vivid colors such as blues, greens, and yellows. The visual contrast between earthenware's understated, earthy appearance and majolica's ornate, colorful surface highlights their distinct artistic and cultural aesthetics.
Durability and Longevity Compared
Earthenware plates typically have a porous structure, making them less durable and more prone to chipping or cracking over time compared to Majolica, which is a type of tin-glazed earthenware with a dense glaze that enhances strength and longevity. Majolica's protective glaze provides a moisture-resistant surface, improving its ability to withstand daily use and extending its lifespan significantly beyond standard earthenware. For long-term durability and frequent use, Majolica plates are generally a superior choice due to their enhanced resistance to wear and structural integrity.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Earthenware plates are porous and require a glaze that is lead-free and food-safe to prevent contamination and ensure safety for daily use. Majolica, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, offers a non-porous surface that enhances food compatibility by reducing absorption of liquids and bacteria. Both materials must meet FDA or EU food safety standards to guarantee that their glazes do not leach harmful substances when in contact with food.
Artistic Styles and Decorative Techniques
Earthenware plates often showcase rustic, hand-painted designs with natural pigments, emphasizing traditional and folk-art styles that highlight texture and organic forms. Majolica plates are distinguished by their vibrant, opaque glazes applied over tin-coated earthenware, creating glossy, colorful surfaces that feature intricate patterns and Renaissance-inspired motifs. The decorative techniques in majolica involve detailed brushwork and layering of glazes to achieve depth and brilliance, contrasting with the simpler, matte finishes typical of earthenware.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
Earthenware plates are generally more affordable due to lower production costs and widespread availability, making them accessible for everyday use and budget-conscious consumers. Majolica plates, characterized by their vibrant, hand-painted designs and tin-glazed finish, tend to be more expensive because of the detailed craftsmanship and artistic value. While earthenware is commonly found in standard kitchenware collections, majolica is often available in specialty stores or artisan markets, influencing its accessibility depending on location and market demand.
Popular Uses in Tableware and Decoration
Earthenware plates are widely popular for casual dining due to their durability and rustic charm, often featured in everyday tableware and farmhouse-style decor. Majolica plates, characterized by their vibrant, hand-painted glazes, are preferred for decorative purposes and special occasions, bringing a touch of artistic elegance to dining settings. Both types serve distinct roles, with earthenware excelling in practicality and majolica prized for ornamental appeal.
Choosing the Right Plate: Earthenware or Majolica?
Earthenware plates are porous, fired at lower temperatures, and often feature a rustic, matte finish ideal for everyday use and casual dining. Majolica plates undergo a tin-glaze process, creating a vibrant, glossy surface with intricate patterns, making them perfect for decorative settings or special occasions. Choosing between earthenware and majolica depends on your preference for durability, aesthetic appeal, and suitability for daily versus formal use.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Majolica for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com