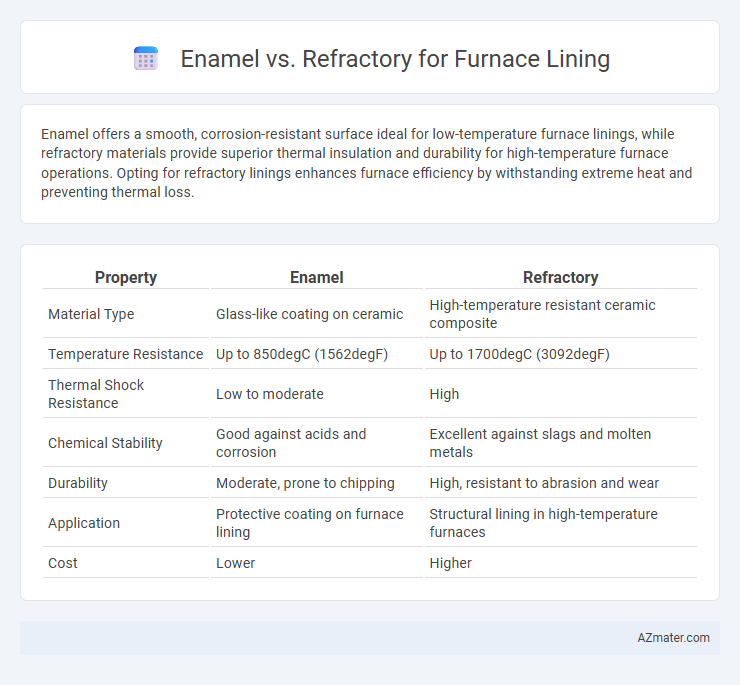
Enamel offers a smooth, corrosion-resistant surface ideal for low-temperature furnace linings, while refractory materials provide superior thermal insulation and durability for high-temperature furnace operations. Opting for refractory linings enhances furnace efficiency by withstanding extreme heat and preventing thermal loss.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass-like coating on ceramic | High-temperature resistant ceramic composite |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 850degC (1562degF) | Up to 1700degC (3092degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Chemical Stability | Good against acids and corrosion | Excellent against slags and molten metals |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | High, resistant to abrasion and wear |
| Application | Protective coating on furnace lining | Structural lining in high-temperature furnaces |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials play a critical role in maintaining thermal insulation and structural integrity under extreme temperatures. Enamel coatings provide a smooth, protective surface resistant to corrosion and metal adherence, ideal for moderate thermal conditions. Refractory materials, composed of high-temperature ceramics or castables, offer superior durability and heat resistance essential for intense furnace environments.
What is Enamel Lining?
Enamel lining is a protective coating made from fused glass applied to furnace interiors to provide corrosion resistance and thermal insulation. It offers a smooth, non-porous surface that prevents chemical attack and metal wear in high-temperature environments. Enamel linings are especially effective in furnaces processing acidic or abrasive materials, extending the lifespan of the equipment compared to traditional refractory linings.
What is Refractory Lining?
Refractory lining refers to a heat-resistant material applied inside furnaces to protect structural components from extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. Unlike enamel coatings, refractory linings are composed of specialized ceramics and firebricks that provide superior thermal insulation and durability in industrial furnace environments. This lining ensures efficient heat retention, enhances furnace lifespan, and minimizes maintenance costs.
Comparative Thermal Resistance
Enamel coatings for furnace lining provide moderate thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 600degC, whereas refractory materials are designed for high-temperature durability, often resisting heat beyond 1500degC. Refractory linings offer superior insulation and thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for extreme furnace environments, while enamel suits lower temperature applications with protective and aesthetic benefits. The choice between enamel and refractory depends on maximum operating temperatures and the furnace's thermal cycling demands.
Chemical Corrosion Resistance: Enamel vs Refractory
Enamel linings exhibit superior chemical corrosion resistance due to their dense, non-porous glassy surface that prevents aggressive substances from penetrating and degrading the furnace structure. In contrast, refractory linings, typically composed of ceramic or castable materials, are more susceptible to chemical attack because their porous nature can absorb corrosive agents, leading to gradual deterioration. The enhanced chemical stability of enamel makes it an ideal choice for environments exposed to acidic or alkali vapors, whereas refractory materials may require more frequent maintenance in such conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Refractory linings for furnaces exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to enamel coatings, due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling without cracking or spalling. Enamel linings offer moderate mechanical resistance but are prone to chipping and degradation under intense thermal stress and abrasive environments. Selecting refractory materials such as alumina or silica-based bricks ensures long-lasting performance and structural integrity in high-temperature industrial applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Enamel furnace linings require precise surface preparation and controlled firing temperatures during installation to ensure a smooth, durable coating resistant to corrosion and thermal shock. Refractory linings involve installing high-temperature resistant bricks or castables that demand careful curing and regular inspections to prevent cracking and spalling under extreme thermal cycles. Maintenance for enamel linings typically includes routine checks for chips and reapplication, while refractory linings require periodic replacement of damaged sections and monitoring for structural integrity to maximize furnace lifespan.
Cost Analysis: Enamel vs Refractory
Enamel furnace lining offers a lower initial cost compared to refractory materials but may require more frequent maintenance and replacement, leading to higher long-term expenses. Refractory linings involve higher upfront investment due to material and installation complexity but provide superior durability and thermal resistance, reducing downtime and repair costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including lifespan and performance under high temperatures, is essential for selecting between enamel and refractory furnace linings.
Suitability for Different Furnace Types
Enamel linings offer optimal corrosion resistance and thermal insulation, making them suitable for electric and glass melting furnaces operating at moderate temperatures. Refractory linings, composed of ceramic and fireclay materials, excel in withstanding extreme heat and mechanical wear, ideal for blast furnaces and coke ovens. Selecting between enamel and refractory depends on furnace temperature range, chemical exposure, and durability requirements specific to industrial applications.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Furnace Lining
Choosing the optimal furnace lining involves evaluating the thermal resistance, chemical stability, and lifespan of enamel versus refractory materials. Enamel provides a smooth, corrosion-resistant surface ideal for moderate temperatures, while refractory linings excel in withstanding extreme heat and mechanical stress. For high-temperature industrial applications, refractory materials offer superior durability and performance, ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
Infographic: Enamel vs Refractory for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com