Photonic ceramics offer superior light manipulation and thermal stability compared to traditional stoneware, enhancing functional and decorative pottery applications. Stoneware provides robustness and durability ideal for everyday use, while photonic ceramics enable advanced optical properties for innovative design.
Table of Comparison
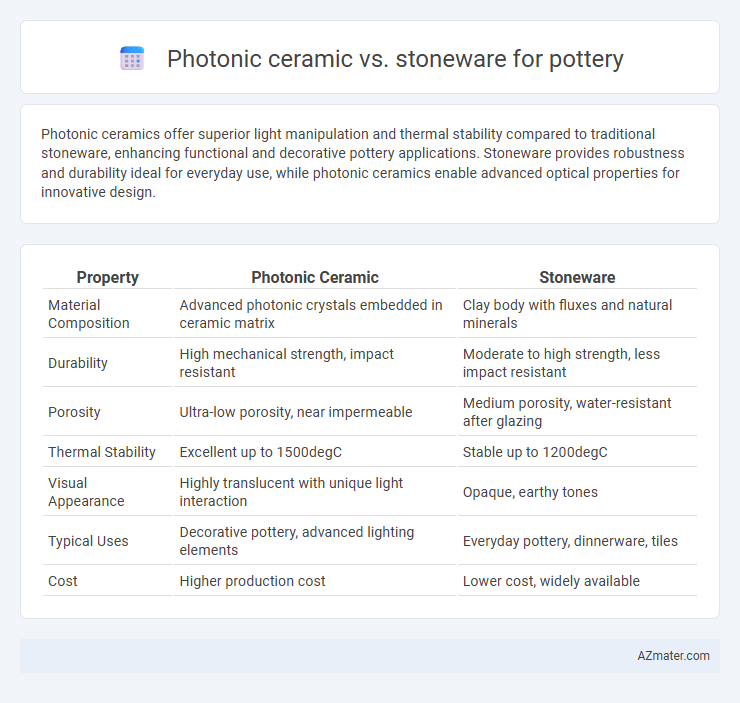
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced photonic crystals embedded in ceramic matrix | Clay body with fluxes and natural minerals |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, impact resistant | Moderate to high strength, less impact resistant |
| Porosity | Ultra-low porosity, near impermeable | Medium porosity, water-resistant after glazing |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent up to 1500degC | Stable up to 1200degC |
| Visual Appearance | Highly translucent with unique light interaction | Opaque, earthy tones |
| Typical Uses | Decorative pottery, advanced lighting elements | Everyday pottery, dinnerware, tiles |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction: Understanding Photonic Ceramic and Stoneware
Photonic ceramic harnesses advanced optical properties that enhance light manipulation, making it ideal for specialized pottery applications requiring luminous effects or high-tech functionality. Stoneware, a traditional ceramic type, is known for its durability, strength, and natural earthy finish, commonly used in functional pottery such as dinnerware and cookware. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with photonic ceramics emphasizing innovative light-related features and stoneware providing reliable everyday utility.
Material Composition: Photonic Ceramic vs Stoneware
Photonic ceramic is an advanced synthetic material composed primarily of engineered oxides and nanostructured particles designed to manipulate light, contrasting with traditional stoneware made from natural clay mixed with quartz, feldspar, and kaolin. The optimized molecular architecture of photonic ceramics enhances optical properties, making them suitable for high-tech applications, whereas stoneware's dense, vitrified matrix provides durability and thermal resistance ideal for functional pottery. Differences in mineral composition and processing methods result in photonic ceramics exhibiting superior translucency and light manipulation, while stoneware maintains robust mechanical strength and is widely used in everyday ceramic wares.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Photonic ceramic and stoneware differ significantly in their manufacturing processes, with photonic ceramics requiring precise control of nanoparticle dispersion and sintering at elevated temperatures to achieve desired optical properties, while stoneware undergoes traditional clay shaping and firing at high temperatures for durability and strength. Photonic ceramics often use advanced techniques like sol-gel processing and hot pressing, enabling tailored photonic bandgaps, whereas stoneware relies on conventional kiln firing between 1,100degC and 1,300degC for vitrification. The manufacturing complexity in photonic ceramics results in higher precision and performance in optical applications, contrasting with the more straightforward, large-scale production methods typical of stoneware pottery.
Physical Properties and Performance
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior thermal stability and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional stoneware, making them ideal for high-performance pottery applications. Their low porosity and high resistance to thermal shock allow for greater durability and longevity under extreme temperature variations. Stoneware, while robust and suitable for everyday use, typically has higher porosity and lower thermal resistance, limiting its performance in demanding environments.
Durability and Longevity
Photonic ceramic features advanced microstructure technology that enhances resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, significantly outperforming traditional stoneware in durability. Stoneware is known for its robustness and dense composition, offering good longevity under everyday use but may chip or crack under extreme conditions. Photonic ceramic's superior structural integrity ensures extended lifespan and resilience, making it ideal for high-performance and long-term applications in pottery.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finishes
Photonic ceramic offers vibrant, iridescent finishes due to its light-interacting nanoparticle coatings, creating dynamic surface appearances that change with viewing angles. Stoneware provides a more traditional matte or glossy surface, valued for its earthy, organic texture and rustic aesthetic appeal. The choice between photonic ceramic and stoneware largely depends on whether the desired pottery surface emphasizes modern luminosity or classic, natural finishes.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Differences
Photonic ceramics exhibit significantly higher thermal conductivity compared to traditional stoneware, enabling efficient heat dissipation in advanced electronic and photonic applications. Stoneware, with its lower thermal conductivity, performs better as an insulator in pottery, making it suitable for items that require heat retention. Electrically, photonic ceramics often possess semiconducting or insulating properties tailored for electronic devices, whereas stoneware remains an electrical insulator with negligible conductivity, ideal for non-conductive pottery uses.
Applications in Modern Pottery
Photonic ceramic materials in modern pottery offer enhanced optical properties and thermal stability, making them ideal for decorative art pieces and functional tableware that require durability and unique light interactions. Stoneware remains a popular choice for everyday pottery due to its strength, water resistance, and ability to withstand high firing temperatures, making it suitable for kitchenware and functional ceramics. Advances in photonic ceramics enable designers to experiment with innovative glazes and finishes, expanding the aesthetic possibilities beyond traditional stoneware applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Photonic ceramics, known for their advanced optical properties and high durability, generally incur higher production costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing techniques compared to traditional stoneware. Stoneware, widely available and produced using established, cost-effective methods, dominates the pottery market with its affordability and versatility. Market availability favors stoneware as it is extensively distributed through numerous retailers and artisans, while photonic ceramics remain niche, primarily accessible in specialized industrial and research applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Photonic ceramics, made from advanced materials requiring less energy-intensive processing, offer improved sustainability compared to traditional stoneware, which relies on high-temperature kilns emitting more CO2. Photonic ceramics often incorporate recyclable and non-toxic components, reducing environmental impact and waste generation during production. Stoneware's natural clay base is abundant but entails significant resource extraction and energy consumption, making photonic ceramics a greener alternative for eco-conscious pottery artisans.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Stoneware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com