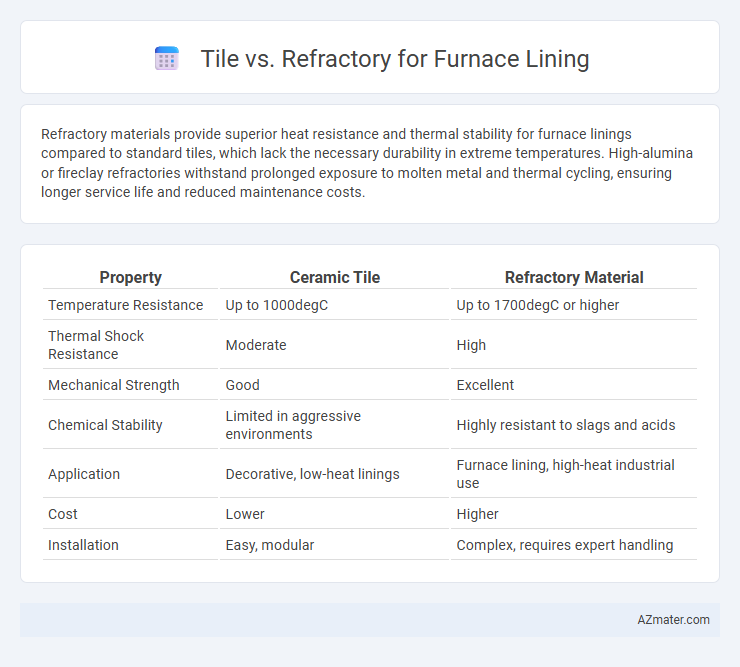
Refractory materials provide superior heat resistance and thermal stability for furnace linings compared to standard tiles, which lack the necessary durability in extreme temperatures. High-alumina or fireclay refractories withstand prolonged exposure to molten metal and thermal cycling, ensuring longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Tile | Refractory Material |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1700degC or higher |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Stability | Limited in aggressive environments | Highly resistant to slags and acids |
| Application | Decorative, low-heat linings | Furnace lining, high-heat industrial use |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Installation | Easy, modular | Complex, requires expert handling |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials play a critical role in thermal insulation and structural integrity within high-temperature environments. Tile linings, typically made from ceramic or fireclay, offer excellent thermal shock resistance and are suitable for moderate temperature ranges. Refractory linings, composed of high-alumina, silica, or magnesite bricks, provide superior durability and heat resistance essential for extreme furnace operating conditions.
Overview of Tile Lining
Tile lining in furnace applications offers superior thermal conductivity and durability compared to traditional refractory linings, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial processes. These ceramic tiles resist thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear, extending furnace lifespan while maintaining energy efficiency. The precision installation of tile linings also improves heat distribution and reduces maintenance frequency, enhancing overall operational performance.
Overview of Refractory Lining
Refractory lining in furnaces consists of heat-resistant materials designed to withstand extreme temperatures and protect the structural integrity of the furnace. Unlike tiles, which are typically rigid and segmented, refractory linings are often cast or packed in place, providing seamless insulation that reduces heat loss and enhances thermal efficiency. These linings are engineered from high-density materials like fireclay, alumina, or silica, ensuring durability and resistance to chemical corrosion within high-temperature industrial environments.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Tile furnace linings typically offer moderate thermal insulation with heat resistance up to 1200degC, suitable for less intense industrial applications. Refractory linings provide superior thermal performance, enduring temperatures beyond 1600degC and maintaining structural integrity under rapid temperature fluctuations. Their higher thermal mass and low thermal conductivity effectively minimize heat loss, enhancing energy efficiency and longevity in high-temperature furnace environments.
Durability and Lifespan
Refractory materials exhibit superior durability and lifespan in furnace lining applications due to their high resistance to extreme heat, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion. Tiles, while easier to install and replace, generally offer shorter service life under continuous high-temperature conditions and mechanical stress. Selecting refractory linings enhances furnace efficiency by maintaining structural integrity over extended operational periods, reducing maintenance frequency and downtime.
Installation Process and Complexity
Tile installation for furnace lining involves precise cutting and fitting of ceramic or porcelain materials, requiring skilled labor to ensure tight joints and a smooth surface for optimal heat resistance. Refractory lining installation is more complex due to the need for mixing and applying refractory castables or bricks, demanding specialized knowledge to maintain proper curing times and thermal expansion control. The refractory process generally requires longer preparation and drying periods, making it more time-consuming and labor-intensive compared to tile installation.
Cost Analysis: Tile vs Refractory
Tile furnace linings offer a lower initial material cost compared to refractory linings, making them a budget-friendly option for smaller industrial operations. Refractory linings, while generally more expensive upfront, provide superior durability and thermal resistance, leading to lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that refractory linings may deliver better long-term economic efficiency despite their higher initial investment.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Tile furnace linings offer quicker installation and easier spot repairs due to their modular nature, reducing downtime during maintenance compared to refractory linings. Refractory linings provide superior thermal resistance and longer lifespan but require specialized skills and more extensive downtime for repairs or replacement. Proper evaluation of maintenance frequency and repair complexity is crucial when choosing between tile and refractory linings for efficient furnace operation.
Suitability for Different Furnace Types
Tile furnace linings are ideal for moderate-temperature applications such as heat treatment and annealing furnaces due to their high thermal conductivity and ease of installation. Refractory linings offer superior resistance to extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion, making them suitable for blast furnaces, steel-making, and glass-melting furnaces. Choosing between tile and refractory materials depends largely on the operating temperature, fuel type, and exposure to slag or molten metal within the furnace environment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Lining Material
Selecting the best furnace lining material depends on the specific thermal and mechanical demands of the application. Refractory linings offer superior heat resistance and durability for high-temperature industrial furnaces, while tile linings provide cost-effective insulation with easier installation for lower-temperature or less demanding environments. Evaluating factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and maintenance requirements ensures the optimal choice between tile and refractory for efficient furnace performance.
Infographic: Tile vs Refractory for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com