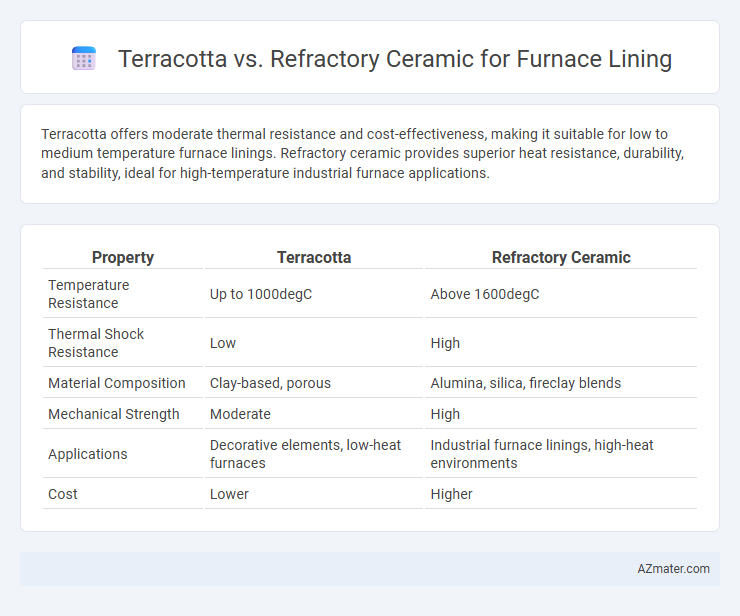
Terracotta offers moderate thermal resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for low to medium temperature furnace linings. Refractory ceramic provides superior heat resistance, durability, and stability, ideal for high-temperature industrial furnace applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Terracotta | Refractory Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1000degC | Above 1600degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Material Composition | Clay-based, porous | Alumina, silica, fireclay blends |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Decorative elements, low-heat furnaces | Industrial furnace linings, high-heat environments |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials determine thermal efficiency, durability, and resistance to high temperatures in industrial applications. Terracotta, composed primarily of fired clay, offers moderate heat resistance and is often used in low to medium temperature furnaces. In contrast, refractory ceramic materials, made from advanced silicates and alumina compounds, provide superior insulation, withstand extreme temperatures above 1500degC, and enhance furnace lifespan.
Understanding Terracotta: Composition and Properties
Terracotta, primarily composed of clay and fired at lower temperatures than refractory ceramics, exhibits moderate thermal resistance and porosity ideal for aesthetic or low-heat furnace linings. Its silica and alumina content define its durability but limit its ability to withstand extreme temperatures above 1000degC, where refractory ceramics excel. The material's microstructure grants good thermal insulation but lower mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to refractory ceramics used in high-temperature furnace linings.
Overview of Refractory Ceramic: Types and Characteristics
Refractory ceramics used in furnace linings are primarily composed of alumina, silica, and magnesite, designed to withstand extreme temperatures exceeding 1600degC while maintaining structural integrity. Common types include fireclay, high alumina, and silicon carbide bricks, each offering unique properties such as thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength suitable for varying industrial applications. These ceramics exhibit low thermal conductivity and high melting points, making them ideal for environments in steelmaking, glass manufacturing, and petrochemical processing where durability and heat resistance are critical.
Heat Resistance: Terracotta vs Refractory Ceramic
Refractory ceramic exhibits significantly higher heat resistance than terracotta, withstanding temperatures exceeding 1,500degC compared to terracotta's limit near 1,000degC. This superior thermal tolerance makes refractory ceramic ideal for furnace linings exposed to intense, sustained heat. Terracotta, while effective for moderate heat applications, lacks the durability and thermal stability required for industrial furnace environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Terracotta offers moderate mechanical strength suitable for low to medium temperature furnace linings, but it lacks the durability of refractory ceramics which are engineered to withstand extreme thermal stress and corrosive environments. Refractory ceramics provide superior mechanical strength with high resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, and chemical degradation, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial furnace applications. The enhanced durability of refractory ceramics leads to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs compared to terracotta, especially in demanding operational conditions.
Thermal Efficiency and Insulation Performance
Terracotta exhibits moderate thermal efficiency with a thermal conductivity typically ranging between 1.0 to 2.0 W/m*K, making it suitable for low to medium temperature furnace lining applications. Refractory ceramic materials offer superior insulation performance, often featuring thermal conductivities below 1.0 W/m*K, enabling better heat retention and energy savings in high-temperature furnace environments above 1000degC. The enhanced thermal stability and lower heat loss of refractory ceramics significantly improve furnace operational efficiency compared to terracotta linings.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Terracotta furnace linings offer a lower initial investment due to affordable raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects. Refractory ceramics, while more expensive upfront because of advanced compositions and higher thermal resistance, provide superior durability and reduced maintenance costs over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership highlights refractory ceramics as a cost-effective choice in long-term industrial applications where furnace longevity and energy efficiency are critical.
Installation Process and Maintenance Requirements
Terracotta furnace linings offer easier installation due to their lightweight and pre-formed modular shapes, reducing setup time and labor costs compared to the heavier, denser refractory ceramic materials. Refractory ceramic linings require longer curing and drying processes to achieve maximum strength, demanding skilled labor and careful temperature controls during installation. Maintenance for terracotta is simpler with quicker repairs and replacements, whereas refractory ceramics demand periodic inspections and specialized patching to address potential cracks and thermal wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Terracotta exhibits lower environmental impact due to its natural clay composition and energy-efficient firing process, resulting in reduced carbon emissions compared to refractory ceramics. Refractory ceramics often require high-temperature processing and synthetic raw materials, leading to higher energy consumption and greater ecological footprint. Sustainability considerations favor terracotta for furnace lining when prioritizing resource renewability and minimized greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations for Furnace Lining
Terracotta and refractory ceramic differ significantly in thermal resistance and durability, making material selection critical for furnace lining performance. Refractory ceramic offers superior heat tolerance, chemical stability, and lifespan, ideal for high-temperature industrial applications, while terracotta suits lower-temperature environments with less demanding thermal cycles. Consider operating temperature, thermal shock resistance, chemical exposure, and cost-effectiveness when choosing between terracotta and refractory ceramic to optimize furnace efficiency and longevity.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Refractory Ceramic for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com