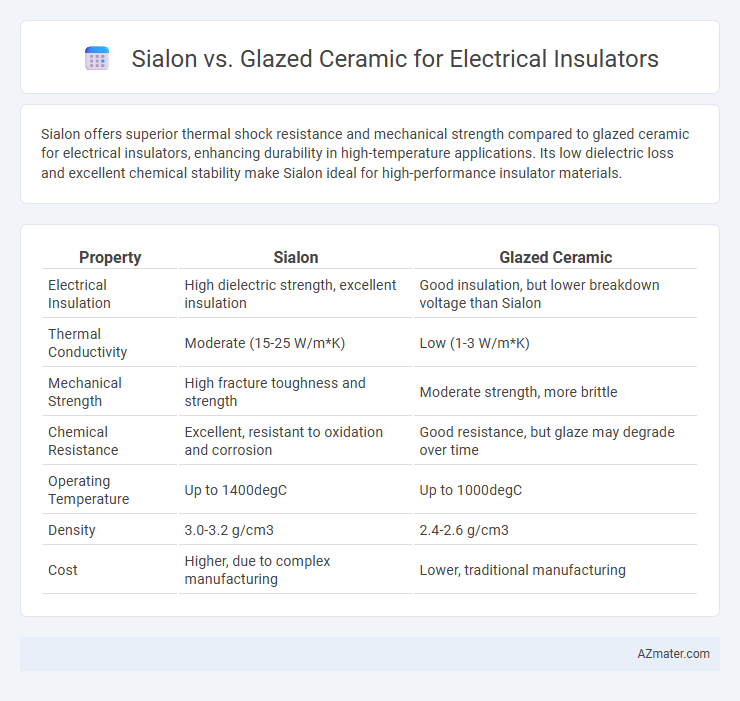
Sialon offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to glazed ceramic for electrical insulators, enhancing durability in high-temperature applications. Its low dielectric loss and excellent chemical stability make Sialon ideal for high-performance insulator materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sialon | Glazed Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, excellent insulation | Good insulation, but lower breakdown voltage than Sialon |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (15-25 W/m*K) | Low (1-3 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | High fracture toughness and strength | Moderate strength, more brittle |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to oxidation and corrosion | Good resistance, but glaze may degrade over time |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1400degC | Up to 1000degC |
| Density | 3.0-3.2 g/cm3 | 2.4-2.6 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Higher, due to complex manufacturing | Lower, traditional manufacturing |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators such as Sialon and glazed ceramic play a crucial role in preventing undesired current flow and ensuring electrical safety. Sialon insulators offer superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance due to their silicon-aluminum-oxynitride composition, making them ideal in high-stress environments. Glazed ceramic insulators, composed primarily of alumina with a vitreous coating, provide excellent surface insulation and resistance to environmental contamination, commonly used in outdoor power distribution systems.
Overview of Sialon Ceramics
Sialon ceramics, composed primarily of silicon, aluminum, oxygen, and nitrogen, exhibit exceptional mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation properties ideal for high-performance electrical insulators. Compared to glazed ceramics, Sialon offers superior resistance to thermal shock, wear, and corrosion, making it highly reliable in harsh environments. Its unique microstructure enables lower dielectric loss and enhanced durability, advancing the efficiency and lifespan of electrical insulation components.
Properties of Glazed Ceramic Insulators
Glazed ceramic insulators exhibit high dielectric strength, excellent resistance to weathering, and a smooth, glassy surface that effectively repels contaminants, reducing leakage currents. These insulators demonstrate superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, maintaining performance under mechanical stress and temperature variations. The glazed coating also enhances corrosion resistance, making them highly reliable for outdoor electrical transmission and distribution applications.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Sialon ceramics exhibit superior electrical insulation properties compared to glazed ceramics due to their higher dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity, which enhance reliability in high-voltage applications. The intrinsic microstructure of Sialon provides excellent resistance to electrical degradation and corona discharge, outperforming the glazed ceramic's more porous and less homogeneous surface. Electrical performance tests consistently show Sialon insulators maintain stable insulation resistance over wider temperature ranges, making them more efficient for demanding electrical environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Sialon ceramic offers superior mechanical strength compared to glazed ceramic, exhibiting higher fracture toughness and resistance to crack propagation, making it ideal for demanding electrical insulator applications. Its enhanced durability under thermal and mechanical stress ensures longer service life in harsh environments, outperforming glazed ceramics which are more prone to surface damage and wear. Sialon's chemical stability also contributes to maintaining insulating properties without degradation over extended periods, reinforcing its suitability for high-performance electrical insulation.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Sialon ceramic insulators exhibit superior thermal stability withstanding temperatures up to 1700degC, compared to glazed ceramic insulators which typically endure around 1000degC. The covalent bonding in Sialon contributes to excellent resistance against thermal shock and oxidation, outperforming traditional glazed ceramics that may degrade under rapid temperature fluctuations. Sialon's enhanced thermal conductivity and mechanical strength make it ideal for high-temperature electrical insulation applications requiring long-term reliability.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Sialon ceramics exhibit superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, chemical corrosion, and thermal shock compared to glazed ceramics, making them ideal for harsh electrical insulator applications. Their unique alumina-silicon nitride composition enhances durability against extreme weather conditions and acid rain. Glazed ceramics, while offering a smooth surface for insulation, tend to have lower chemical stability and can degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Sialon offers superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to glazed ceramic, but its higher raw material and processing costs increase overall manufacturing expenses. Glazed ceramic insulators are generally more economical due to established production techniques and lower material costs, making them suitable for standard electrical insulation applications. Cost-efficiency and scalability favor glazed ceramics, while Sialon is preferred for high-performance, demanding environments despite its higher fabrication complexity.
Typical Applications in Electrical Systems
Sialon ceramics are predominantly used in high-temperature electrical insulators for applications such as gas turbines, power generation, and high-voltage switches due to their excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength. Glazed ceramic insulators, commonly found in power transmission lines, transformers, and distribution networks, offer superior surface protection against moisture and contamination, enhancing insulation reliability in outdoor environments. Both materials are essential in electrical systems, with Sialon preferred for extreme thermal conditions and glazed ceramics favored for environmental durability.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Sialon or Glazed Ceramic
Sialon insulators offer superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to glazed ceramic, making them ideal for high-stress electrical applications. Glazed ceramics provide excellent electrical insulation and cost efficiency but may suffer from brittleness under extreme conditions. Selecting between Sialon and glazed ceramic depends on application demands for durability, electrical performance, and operating environment.
Infographic: Sialon vs Glazed ceramic for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com