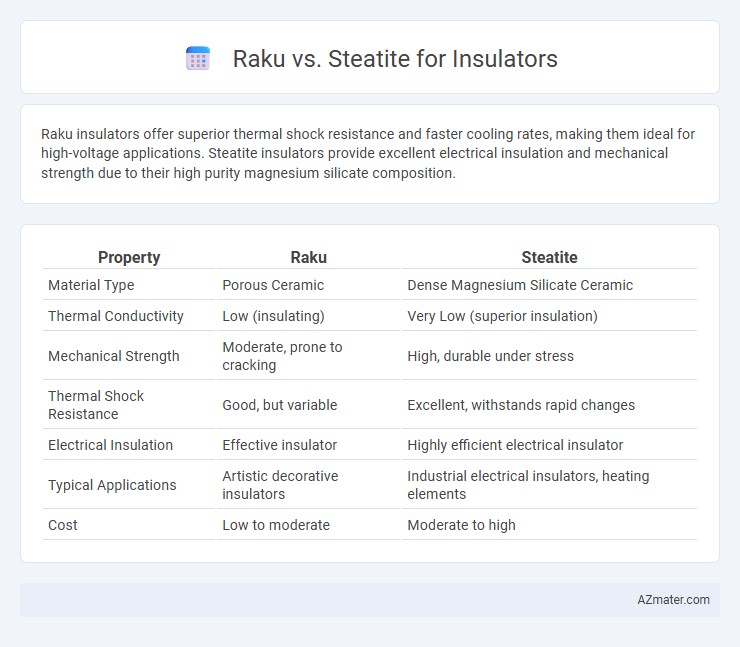
Raku insulators offer superior thermal shock resistance and faster cooling rates, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Steatite insulators provide excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength due to their high purity magnesium silicate composition.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Raku | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous Ceramic | Dense Magnesium Silicate Ceramic |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (insulating) | Very Low (superior insulation) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, durable under stress |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good, but variable | Excellent, withstands rapid changes |
| Electrical Insulation | Effective insulator | Highly efficient electrical insulator |
| Typical Applications | Artistic decorative insulators | Industrial electrical insulators, heating elements |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Raku and Steatite Insulators
Raku insulators are ceramic-based materials known for their high thermal shock resistance and durability in electrical applications, making them suitable for high-voltage insulation. Steatite insulators, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offer excellent mechanical strength, low dielectric loss, and thermal stability, widely used in electrical and electronic insulation. The choice between Raku and Steatite often depends on specific performance requirements such as resistance to heat, mechanical stress, and electrical insulation properties.
Material Composition and Structure
Raku insulators are typically made from a high-density ceramic material with a porous structure that provides excellent thermal shock resistance and electrical insulation properties. Steatite insulators consist mainly of natural magnesite and talc, resulting in a dense, hard composition with superior dielectric strength and moisture resistance. The microstructure of steatite grants it enhanced mechanical strength and durability compared to the more brittle, thermally adaptable raku ceramics.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Raku insulators exhibit moderate thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1,200degC, making them suitable for high-temperature but not extreme environments. Steatite insulators offer superior thermal resistance, often enduring temperatures exceeding 1,400degC due to their high alumina and silica content, which enhances their stability under thermal stress. The choice between Raku and Steatite depends on the specific thermal demands of the application, with Steatite preferred in scenarios requiring enhanced heat endurance and insulation longevity.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Raku offers high electrical resistance and excellent dielectric strength, making it suitable for insulating components exposed to moderate electrical stress. Steatite excels with outstanding dielectric properties, exhibiting low dielectric loss and high breakdown voltage, ideal for high-voltage insulation applications. The superior thermal stability and moisture resistance of Steatite further enhance its performance as a reliable electrical insulator compared to Raku.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Raku insulators exhibit higher mechanical strength with better resistance to impact and thermal shock compared to steatite, making them suitable for demanding electrical environments. Steatite, while offering good electrical insulation, tends to have lower mechanical durability and is more prone to cracking under mechanical stress. The enhanced toughness and longevity of Raku insulators contribute to their preference in high-performance and industrial applications where mechanical robustness is critical.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Raku insulators undergo a rapid firing and cooling process that induces thermal shock resistance but limits scalability due to inconsistent material properties and higher defect rates. Steatite insulators are manufactured through powder pressing and high-temperature sintering, enabling precise control over density and mechanical strength, thus supporting large-scale, repeatable production. The scalability of steatite is favored in industrial settings because its manufacturing process yields uniform electrical insulation performance and cost-effective mass production.
Cost Analysis: Raku vs Steatite
Raku insulators typically offer lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and readily available raw materials compared to steatite, which requires more specialized processing and higher purity raw materials, increasing its price. However, steatite provides better durability and higher resistance to thermal shock, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including performance lifespan and reliability, often favors steatite for high-stress applications despite its higher upfront cost.
Common Applications in Industry
Raku insulators are commonly used in high-voltage electrical equipment due to their excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for power transmission and distribution systems. Steatite insulators find widespread application in telecommunications and electronics industries because of their high dielectric strength and stability under varying environmental conditions. Both materials are preferred for industrial components requiring reliable electrical insulation and durability under stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Raku ceramics, with lower firing temperatures, consume less energy and produce fewer carbon emissions compared to high-fired steatite insulators, enhancing environmental sustainability. Steatite, a naturally abundant magnesium-rich mineral, offers excellent durability and recyclability, reducing waste over its lifecycle. Selecting Raku or steatite insulators involves balancing energy-efficient production against long-term material resilience for optimal eco-friendly choices.
Choosing the Right Insulator for Your Needs
Raku insulators offer high thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for applications involving rapid temperature changes, while steatite insulators provide superior mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation under high voltage conditions. Choosing the right insulator depends on factors such as operating temperature, mechanical stress, and electrical requirements, with steatite preferred for heavy-duty industrial use and raku suited for thermal cycling environments. Evaluating these properties ensures optimal performance and longevity in insulation systems.
Infographic: Raku vs Steatite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com