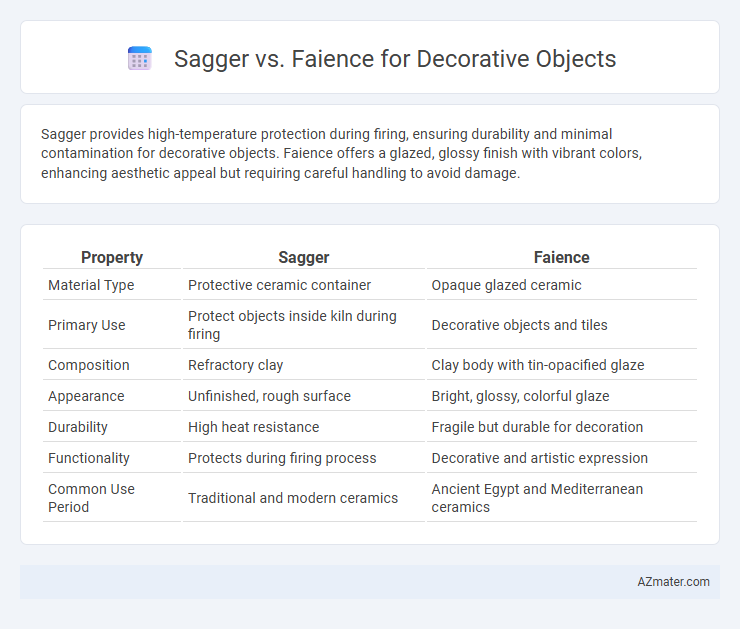
Sagger provides high-temperature protection during firing, ensuring durability and minimal contamination for decorative objects. Faience offers a glazed, glossy finish with vibrant colors, enhancing aesthetic appeal but requiring careful handling to avoid damage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Protective ceramic container | Opaque glazed ceramic |
| Primary Use | Protect objects inside kiln during firing | Decorative objects and tiles |
| Composition | Refractory clay | Clay body with tin-opacified glaze |
| Appearance | Unfinished, rough surface | Bright, glossy, colorful glaze |
| Durability | High heat resistance | Fragile but durable for decoration |
| Functionality | Protects during firing process | Decorative and artistic expression |
| Common Use Period | Traditional and modern ceramics | Ancient Egypt and Mediterranean ceramics |
Introduction: Understanding Sagger and Faience
Sagger is a protective ceramic container used during firing to shield decorative objects from direct flame and ash, ensuring even heat distribution and surface preservation. Faience refers to glazed non-clay ceramic ware, often characterized by its bright, glass-like finish achieved through a tin-opacified glaze applied over a quartz-based body. Comparing sagger and faience highlights their distinct roles in the production and protection of decorative ceramics, with saggers focusing on firing techniques and faience emphasizing aesthetic surface qualities.
Historical Background of Sagger and Faience
Sagger, historically used since the Bronze Age, functioned as a protective container for ceramics during kiln firing, preventing direct flame exposure and enabling uniform heat distribution. Faience emerged in ancient Egypt around 4000 BCE as a glazed non-clay ceramic material, prized for its brilliant blue-green finish used extensively in decorative objects and jewelry. Both saggers and faience illustrate early technological advancements in ceramics, reflecting distinct cultural practices in artifact production and preservation.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Faience
Sagger is typically made from refractory clay designed to withstand high kiln temperatures and protect delicate ceramics during firing, acting as a durable container rather than a decorative material. Faience, on the other hand, is a glazed non-clay ceramic material composed primarily of silica, alkali, and metallic oxides, used to create brightly colored decorative objects and tiles. The key difference lies in Sagger's function as a protective shell with high thermal resistance, whereas Faience is valued for its vibrant, glass-like surface and ornamental qualities.
Production Techniques: Comparing Methods
Sagger production involves placing the decorative object inside a protective ceramic container to shield it from direct flame and ash during firing, resulting in enhanced surface quality and reduced defects. Faience, on the other hand, employs a tin-glazing technique where objects are coated with a lead glaze containing tin oxide, creating a bright white, opaque surface ideal for painted decoration. Comparing methods highlights saggers as a firing aid for improved finish, whereas faience focuses on glazing for vivid color application and aesthetic enhancement.
Surface Finishes and Aesthetic Qualities
Sagger firing produces a matte, textured surface finish that enhances depth and subtle color variations, ideal for rustic or earthy decorative objects. Faience glazing results in a glossy, vibrant, and smooth surface with rich, translucent hues, perfect for elegant and detailed ornamental pieces. The choice between sagger and faience directly influences the tactile feel and visual appeal, with sagger offering natural matte aesthetics and faience delivering luminous, refined finishes.
Durability and Longevity in Decorative Use
Sagger offers superior durability for decorative objects due to its protective, refractory quality that shields ceramics from direct flame and thermal shock, enhancing longevity in high-heat environments. Faience, composed of glazed earthenware with a silica-based glaze, provides vibrant aesthetics but is more prone to chipping and wear over time compared to saggar-fired ceramics. For long-lasting decorative use, saggar-fired pieces generally maintain structural integrity better, ensuring sustained appearance and durability.
Typical Applications in Decorative Objects
Sagger and faience both serve crucial roles in the production of decorative objects, with saggers commonly providing protective kiln containers that prevent direct flame contact, ensuring delicate items retain their intricate designs and finishes during firing. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material, is predominantly used for creating colorful, ornamental items such as jewelry, tiles, and small sculptures, prized for its vibrant hues and glossy surface. Typical applications of saggers include the safeguarding of porcelain and glassware, while faience is favored in decorative motifs and historic-style artifacts, each enhancing aesthetic quality through their specialized functions.
Cost and Accessibility: Which Is More Affordable?
Sagger and faience differ significantly in cost and accessibility, with saggers generally being more affordable due to their straightforward production using inexpensive refractory clay materials. Faience, often composed of glazed ceramic with intricate motifs, typically involves higher costs related to skilled craftsmanship and specialized glazing techniques. Accessibility to saggers is broader, especially in industrial and studio pottery settings, while faience may be more limited to artisanal markets due to its decorative complexity and higher price point.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sagger firing uses protective ceramic containers to shield decorative objects from direct flame exposure, reducing glaze defects and minimizing waste through controlled kiln environments, thereby improving material efficiency. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware technique, often requires high-temperature firings and can involve toxic lead-based glazes, posing greater environmental hazards and challenges in sustainable disposal. Opting for sagger firing reduces emissions and energy consumption due to improved kiln atmosphere control, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable ceramic decoration.
Choosing Between Sagger and Faience for Your Décor
Choosing between sagger and faience for decorative objects depends on the desired aesthetic and durability; sagger offers protection and subtle glaze effects from high-temperature firing, while faience showcases vibrant, opaque glazes with intricate designs due to its tin-glazed surface. Sagger is ideal for earthy, rustic decor emphasizing natural textures, whereas faience suits bright, colorful settings where detailed patterns enhance visual appeal. Consider the intended environment and maintenance needs, as faience tends to require more careful handling to preserve its glossy finish.
Infographic: Sagger vs Faience for Decorative Object
 azmater.com
azmater.com