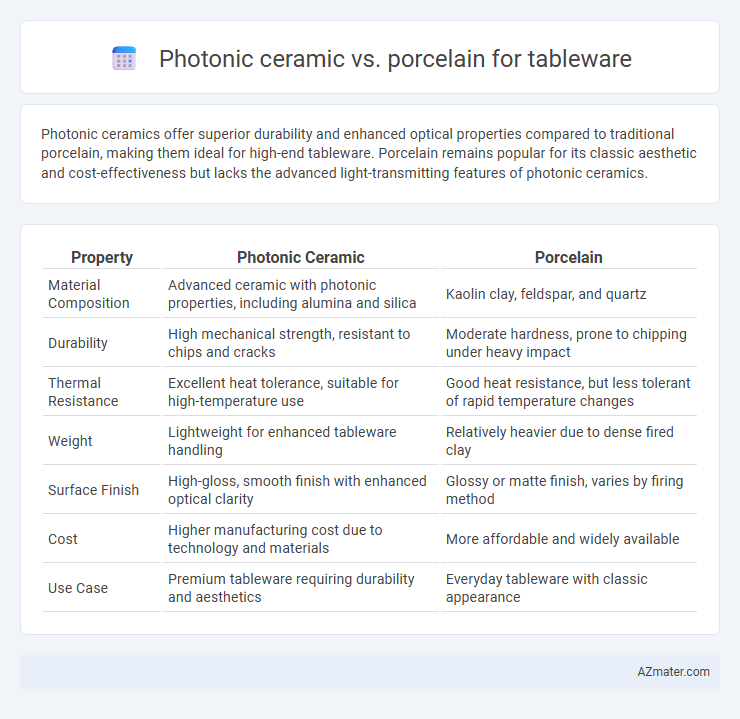
Photonic ceramics offer superior durability and enhanced optical properties compared to traditional porcelain, making them ideal for high-end tableware. Porcelain remains popular for its classic aesthetic and cost-effectiveness but lacks the advanced light-transmitting features of photonic ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced ceramic with photonic properties, including alumina and silica | Kaolin clay, feldspar, and quartz |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, resistant to chips and cracks | Moderate hardness, prone to chipping under heavy impact |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent heat tolerance, suitable for high-temperature use | Good heat resistance, but less tolerant of rapid temperature changes |
| Weight | Lightweight for enhanced tableware handling | Relatively heavier due to dense fired clay |
| Surface Finish | High-gloss, smooth finish with enhanced optical clarity | Glossy or matte finish, varies by firing method |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to technology and materials | More affordable and widely available |
| Use Case | Premium tableware requiring durability and aesthetics | Everyday tableware with classic appearance |
Introduction to Photonic Ceramic and Porcelain Tableware
Photonic ceramic tableware uses advanced nanomaterials that enhance light interaction, offering superior durability and thermal stability compared to traditional materials. Porcelain tableware, crafted from fine kaolin clay fired at high temperatures, is renowned for its translucence, strength, and classic aesthetic appeal. Both materials provide distinct functional and aesthetic benefits suitable for different dining experiences and designs.
Material Composition: Photonic Ceramic vs Porcelain
Photonic ceramic tableware is composed of advanced ceramic materials integrated with photonic crystals that enhance light reflection and durability, providing a modern, high-tech aesthetic. Porcelain is traditionally made from kaolin clay combined with feldspar and quartz, fired at high temperatures to create a dense, vitrified, and translucent finish known for its classic elegance. The material composition of photonic ceramics offers superior optical properties and resilience compared to the more brittle yet timeless porcelain, making it ideal for contemporary tableware applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Photonic ceramic tableware utilizes advanced sintering techniques and controlled crystallization to achieve enhanced translucency and strength, leveraging nano-sized particles for superior optical properties. Porcelain, produced through traditional kaolin clay firing at high temperatures, relies on vitrification to create its characteristic hardness and whiteness but lacks the precise nanoscale engineering seen in photonic ceramics. The manufacturing process of photonic ceramics offers more control over microstructure, resulting in improved durability and aesthetic qualities compared to conventional porcelain production.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior durability compared to porcelain due to their enhanced structural integrity and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-impact or rapid temperature changes in tableware. Porcelain, while also strong and resilient, tends to be more brittle and prone to chipping under mechanical stress, limiting its longevity in heavy-use environments. The advanced microstructure of photonic ceramics provides improved fracture toughness and hardness, significantly outperforming traditional porcelain in strength analysis for tableware applications.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Versatility
Photonic ceramic offers a unique aesthetic with its translucent finish and subtle luminosity, allowing intricate lighting effects that enhance tableware design. Porcelain is prized for its smooth, glossy surface and classic white appearance, providing a timeless elegance suited for various dining settings. Both materials support diverse design techniques; photonic ceramic excels in modern, light-interactive pieces, while porcelain remains versatile for traditional and contemporary styles.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior heat resistance and thermal shock tolerance compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-temperature applications in tableware. Their advanced thermal properties allow rapid heat distribution and retention without cracking, unlike traditional porcelain which may suffer from thermal stress under sudden temperature changes. This enhanced performance ensures photonic ceramic tableware maintains structural integrity and safety during intense heating or cooling cycles.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior safety features in tableware due to their non-toxic, lead-free composition and high resistance to thermal shock, ensuring no harmful substances leach into food during use. Porcelain, while popular for its elegance, may contain trace amounts of lead or cadmium in glazes, raising concerns about long-term food safety unless certified food-safe and lead-free. Both materials are compatible with food, but photonic ceramics offer enhanced hygiene and durability, making them a safer choice for everyday tableware use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Photonic ceramics offer enhanced durability and energy efficiency in manufacturing processes compared to traditional porcelain, resulting in a lower carbon footprint during production. Porcelain, while biodegradable and recyclable, often requires higher firing temperatures and longer kiln times, increasing energy consumption and associated emissions. Choosing photonic ceramic tableware supports sustainable practices by reducing waste through improved material longevity and minimizing environmental impact in the ceramic industry.
Pricing and Market Availability
Photonic ceramic tableware generally commands a higher price point due to its advanced light-enhancing properties and innovative material composition, offering improved durability and aesthetic appeal. Porcelain remains widely available and more affordable, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and extensive market presence, making it a cost-effective choice for everyday use. Market availability favors porcelain, which dominates retail channels and bulk supply, while photonic ceramic is often found in niche or premium segments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Tableware Needs
Photonic ceramic offers exceptional durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for everyday use and microwave-safe applications, whereas porcelain excels in elegance and translucency, suitable for formal dining settings. The choice between photonic ceramic and porcelain depends on balancing practicality and aesthetic preference, with photonic ceramic providing robustness and porcelain delivering refined appearance. Consider factors such as heat resistance, fragility, and style to select tableware that meets both functional and design requirements.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Porcelain for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com