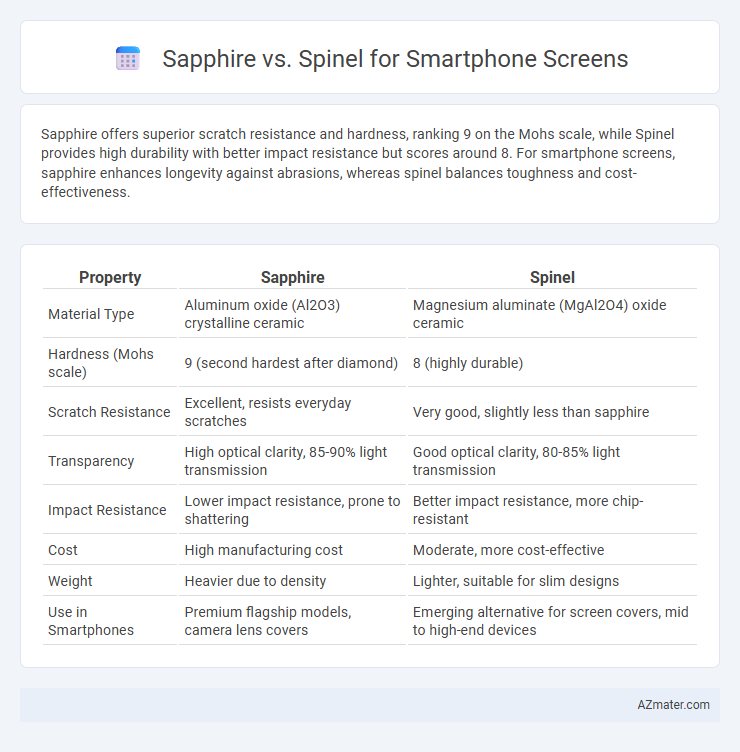
Sapphire offers superior scratch resistance and hardness, ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, while Spinel provides high durability with better impact resistance but scores around 8. For smartphone screens, sapphire enhances longevity against abrasions, whereas spinel balances toughness and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sapphire | Spinel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) crystalline ceramic | Magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) oxide ceramic |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 9 (second hardest after diamond) | 8 (highly durable) |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent, resists everyday scratches | Very good, slightly less than sapphire |
| Transparency | High optical clarity, 85-90% light transmission | Good optical clarity, 80-85% light transmission |
| Impact Resistance | Lower impact resistance, prone to shattering | Better impact resistance, more chip-resistant |
| Cost | High manufacturing cost | Moderate, more cost-effective |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter, suitable for slim designs |
| Use in Smartphones | Premium flagship models, camera lens covers | Emerging alternative for screen covers, mid to high-end devices |
Introduction: Sapphire vs Spinel for Smartphone Screens
Sapphire and spinel are two of the most advanced materials used in smartphone screen protection due to their exceptional hardness and scratch resistance. Sapphire ranks nearly 9 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest transparent materials, while spinel offers a Mohs hardness of around 8, combining durability with optical clarity. Both materials enhance smartphone display longevity, but sapphire is often preferred for premium models, whereas spinel provides a cost-effective alternative with competitive performance.
Material Composition and Structure
Sapphire, composed primarily of crystalline aluminum oxide (Al2O3), exhibits a hexagonal crystal structure that provides exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, making it ideal for premium smartphone screens. Spinel, a magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) with a cubic crystal structure, offers comparable hardness but with enhanced toughness and impact resistance due to its isotropic lattice. These material compositions and structural differences influence durability, transparency, and manufacturing costs in smartphone display applications.
Hardness and Scratch Resistance
Sapphire offers superior hardness with a rating of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it highly resistant to scratches compared to Spinel, which rates around 8. Spinel, while slightly less hard, still provides excellent scratch resistance and is more impact-resistant than sapphire. Both materials are used in premium smartphone screens, but sapphire's hardness makes it the preferred choice for maintaining scratch-free displays over time.
Clarity and Optical Transparency
Sapphire offers superior optical clarity and higher refractive index compared to spinel, providing sharper and more vibrant display visibility for smartphone screens. Spinel exhibits excellent transparency with a broad wavelength range and reduced light scattering, but typically falls short of sapphire's crispness in direct sunlight conditions. Both materials maintain high durability, yet sapphire's ability to maintain screen clarity under various lighting environments makes it the preferred choice for premium smartphone displays.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Sapphire offers exceptional hardness, ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, which translates to superior scratch resistance for smartphone screens compared to spinel, which is softer at around 8. Spinel, however, provides better impact resistance due to its crystalline structure, making it less prone to shattering upon drops. The choice between sapphire and spinel hinges on balancing the need for scratch durability with enhanced impact resilience in smartphone displays.
Manufacturing Process and Scalability
Sapphire screens are produced through complex single-crystal growth methods such as the Kyropoulos or Verneuil processes, which are time-consuming and costly, limiting large-scale manufacturing. Spinel, synthesized via sintering or hot-pressing techniques, allows for more cost-effective and scalable production while maintaining excellent hardness and optical clarity. The scalability challenges of sapphire restrict its widespread smartphone adoption, whereas spinel offers a viable alternative for mass-market devices due to its more efficient manufacturing process.
Cost Comparison: Sapphire vs Spinel
Sapphire screen materials cost significantly more than spinel, with sapphire typically priced at $400 per kilogram compared to spinel's $150 per kilogram, impacting smartphone manufacturing expenses. The higher production cost of synthetic sapphire, driven by complex crystal growth and machining processes, translates to increased retail prices for sapphire-equipped smartphones. Spinel offers a cost-effective alternative with comparable hardness and scratch resistance, making it appealing for budget-conscious smartphone manufacturers seeking durability without the premium price of sapphire.
Weight and Touch Sensitivity
Sapphire offers superior scratch resistance but is denser and heavier than spinel, which results in increased overall smartphone weight. Spinel provides a lighter alternative with slightly lower hardness but maintains excellent touch sensitivity due to its smooth surface and optical clarity. The choice between sapphire and spinel for smartphone screens balances durability with weight considerations and user experience in touch responsiveness.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Sapphire offers exceptional scratch resistance and durability, extending smartphone screen lifespan and reducing electronic waste, while its energy-intensive synthetic production raises environmental concerns. Spinel, derived from abundant and less resource-demanding materials, provides a more sustainable alternative with comparable hardness and clarity, promoting lower carbon emissions during manufacturing. Choosing spinel over sapphire supports eco-friendly practices by minimizing mining impacts and energy consumption without compromising screen performance.
Future Trends in Smartphone Screen Materials
Sapphire screens offer exceptional scratch resistance and durability but struggle with brittleness and higher production costs, while spinel materials provide a promising balance of hardness and impact resistance with improved manufacturing scalability. Future trends in smartphone screen materials are leaning towards advanced composites like spinel-based ceramics and hybrid coatings that enhance toughness, optical clarity, and cost-efficiency. Innovations in nanotechnology and thin-film deposition are expected to drive the adoption of spinel over sapphire, enabling more resilient and affordable smartphone displays.
Infographic: Sapphire vs Spinel for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com