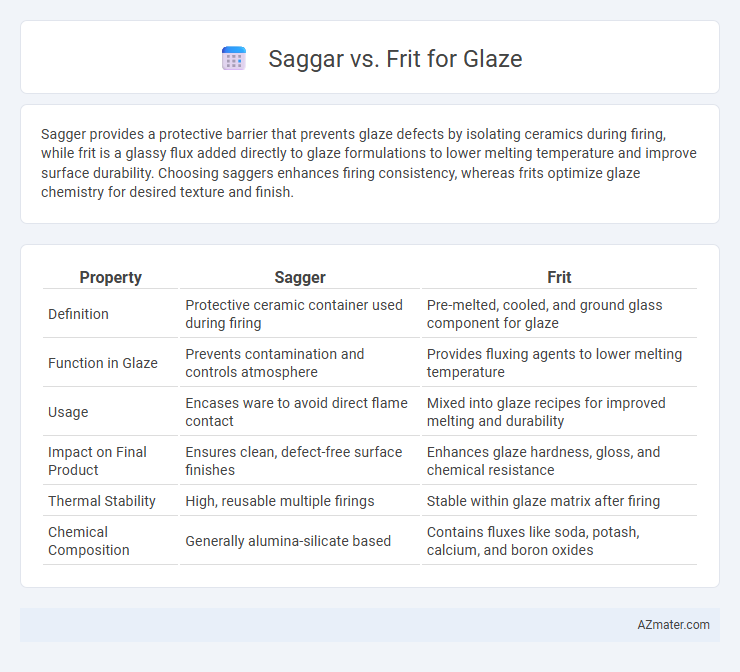
Sagger provides a protective barrier that prevents glaze defects by isolating ceramics during firing, while frit is a glassy flux added directly to glaze formulations to lower melting temperature and improve surface durability. Choosing saggers enhances firing consistency, whereas frits optimize glaze chemistry for desired texture and finish.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Frit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protective ceramic container used during firing | Pre-melted, cooled, and ground glass component for glaze |
| Function in Glaze | Prevents contamination and controls atmosphere | Provides fluxing agents to lower melting temperature |
| Usage | Encases ware to avoid direct flame contact | Mixed into glaze recipes for improved melting and durability |
| Impact on Final Product | Ensures clean, defect-free surface finishes | Enhances glaze hardness, gloss, and chemical resistance |
| Thermal Stability | High, reusable multiple firings | Stable within glaze matrix after firing |
| Chemical Composition | Generally alumina-silicate based | Contains fluxes like soda, potash, calcium, and boron oxides |
Introduction to Saggers and Frits in Ceramic Glazes
Saggers are protective containers made from refractory materials used in ceramic firing to isolate pieces from direct flame and atmosphere, ensuring consistent glaze effects and preventing contamination. Frits are fused, quenched, and granulated materials that act as fluxes in ceramic glazes, lowering melting points and promoting chemical stability during firing. Combining saggers and frits in ceramic glaze processes enhances surface quality, color retention, and firing control, crucial for achieving desired glaze characteristics.
What Is a Sagger and How Is It Used?
A sagger is a protective container made from refractory materials, used in ceramic glazing to shield pottery from direct flame, ash, and kiln debris during firing. It enables controlled atmosphere effects and precise glaze outcomes by isolating the piece inside the kiln, preventing contamination and uneven heat exposure. Saggers are essential for achieving specific glaze textures and colors that are difficult to obtain with direct firing methods.
Defining Frit: Purpose and Composition
Frit is a crucial component in glaze formulation, consisting primarily of fused, rapidly cooled mixtures of various raw minerals and oxides designed to melt at lower temperatures. Its primary purpose is to act as a glass former, flux, or stabilizer, enhancing glaze durability, texture, and melting behavior without the impurities found in raw materials. Unlike sagger materials used for protective atmospheres during firing, frit directly influences glaze chemistry and surface qualities.
Key Differences Between Sagger and Frit
Saggers provide a protective container made from refractory materials that shield ceramic pieces from direct flame and contaminants during firing, preserving glaze quality and surface texture. Frit, a pre-melted and rapidly cooled glass, acts as a flux in glaze formulation, lowering the melting point and influencing the final glaze's texture and color. The key difference lies in their function: saggers serve as physical protective barriers in the kiln, while frit functions chemically within the glaze itself to control melting and surface characteristics.
Effects on Glaze Finish and Quality
Sagger firing creates a controlled atmosphere that reduces oxygen, resulting in deeper, richer glaze colors and a smoother, more textured finish. Frit, a vitrified glass component added to glaze recipes, enhances durability and promotes a glossy, even coating with improved chemical resistance. Combining saggers with frit can optimize glaze quality by balancing surface texture and long-lasting visual appeal.
Advantages of Using Saggers in Firing
Saggers provide significant advantages in glaze firing by creating a controlled microenvironment that protects ceramic pieces from direct flame and ash contamination, resulting in cleaner and more consistent glaze finishes. Their ability to shield against volatile elements enhances color development and surface texture uniformity, reducing defects such as pinholes or blisters. Furthermore, saggers enable the incorporation of materials for atmospheric effects, expanding creative possibilities in glaze outcomes.
Benefits of Using Frits in Glaze Formulation
Frits in glaze formulation offer benefits such as enhanced chemical stability, consistent melting behavior, and reduced toxicity compared to raw materials like saggers. Their pre-melted and rapidly cooled composition ensures uniformity in glaze texture and color, improving the final surface quality. Using frits minimizes raw material inconsistencies and firing defects, leading to more predictable and efficient ceramic production.
Applications in Different Glazing Techniques
Sagger and frit serve distinct roles in glazing, with sagger primarily used as a protective container that shields ceramics from direct flame or ash, enabling oxidation or reduction atmospheres during firing. Frit is a pre-melted glass powder integrated into glazes to control melting point, texture, and color development, enhancing glaze durability and uniformity. In complex glazing techniques, saggers allow for layered surface effects and prevent contamination, while frit ensures consistent chemical reactions and glossy finishes across diverse ceramic styles.
Cost and Accessibility Comparison
Saggers offer a reusable, protective container for glaze firing, often increasing initial costs due to the need for durable materials but improving long-term value through multiple uses; they are less accessible for beginners due to required kiln space and setup complexity. Frit, a pre-ground glass flux, is generally more affordable and widely accessible for potters and ceramic artists, readily available in powders or powders mixed into glaze, making it easier to incorporate into glaze recipes without specialized equipment. Choosing saggers raises upfront costs and logistical considerations, while frit maximizes cost-effectiveness and accessibility for most glaze applications.
Choosing Between Sagger and Frit for Your Project
Choosing between sagger and frit for your glaze project depends on the desired outcome and firing conditions. Saggers provide protection from kiln atmosphere, allowing for more controlled surface textures and colors by shielding ceramics from direct flame and ash. Frits are pre-melted glass materials that enhance glaze durability and reduce issues like speckling, making them ideal for achieving smooth, stable finishes in high-temperature firings.
Infographic: Sagger vs Frit for Glaze
 azmater.com
azmater.com