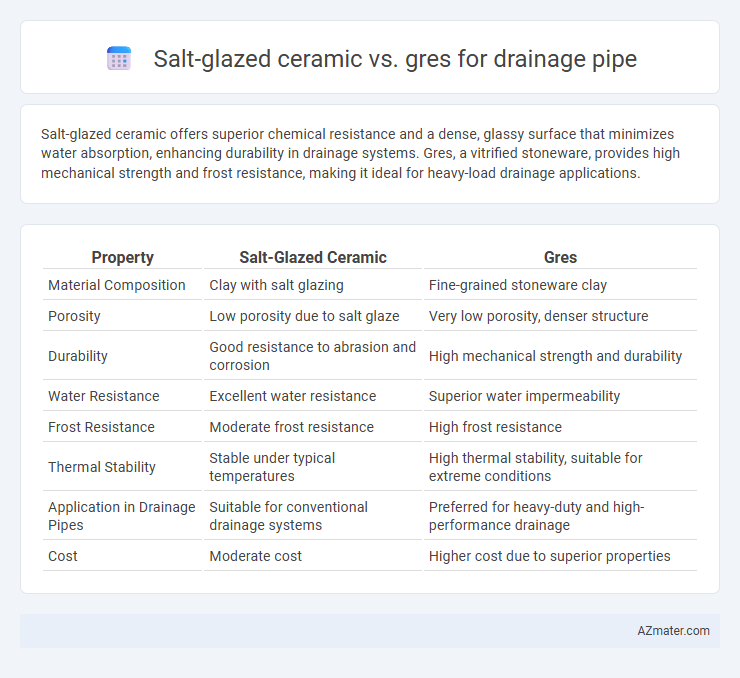
Salt-glazed ceramic offers superior chemical resistance and a dense, glassy surface that minimizes water absorption, enhancing durability in drainage systems. Gres, a vitrified stoneware, provides high mechanical strength and frost resistance, making it ideal for heavy-load drainage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Gres |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay with salt glazing | Fine-grained stoneware clay |
| Porosity | Low porosity due to salt glaze | Very low porosity, denser structure |
| Durability | Good resistance to abrasion and corrosion | High mechanical strength and durability |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water resistance | Superior water impermeability |
| Frost Resistance | Moderate frost resistance | High frost resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Stable under typical temperatures | High thermal stability, suitable for extreme conditions |
| Application in Drainage Pipes | Suitable for conventional drainage systems | Preferred for heavy-duty and high-performance drainage |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
Overview of Salt-Glazed Ceramic and Gres Drainage Pipes
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes feature a glossy, smooth surface formed by salt vapor reacting with the clay during firing, resulting in enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion and root penetration. Gres drainage pipes, also known as vitrified clay pipes, are manufactured from highly refined clay fired at high temperatures to create a dense, non-porous structure resistant to chemical attack and mechanical wear. Both materials offer long service life and excellent environmental compatibility, but salt-glazed ceramics provide superior surface protection, while gres pipes are valued for their cost-effectiveness and structural robustness.
Historical Development of Drainage Materials
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes emerged in the 19th century, valued for their durable, non-porous surface created by a sodium chloride firing process that enhanced resistance to water and soil chemicals. Gres, a type of stoneware clay fired at high temperatures, gained popularity for drainage applications due to its superior strength, minimal porosity, and resistance to frost damage, becoming a standard in the 20th century. Both materials reflect evolving technological advances in ceramic manufacturing aimed at improving the longevity and efficiency of urban drainage systems.
Manufacturing Processes: Salt-Glazed Ceramic vs Gres
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes are manufactured by applying common salt during high-temperature firing, which reacts with the silica in the clay to form a durable, glossy sodium-aluminosilicate glaze on the surface. In contrast, gres pipes are produced through dry-pressing fine, highly purified clays followed by high-temperature firing without additional glazing, resulting in a dense, vitrified structure with inherent water resistance. The salt-glazing process enhances surface smoothness and resistance to chemical attack, while gres manufacturing emphasizes material compactness and structural strength for superior durability in drainage applications.
Material Composition and Properties Comparison
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes feature a unique outer layer formed by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, creating a glassy, corrosion-resistant surface that enhances durability and reduces roughness. Gres pipes, made from finely ground natural clays sintered at high temperatures, exhibit high mechanical strength, low porosity, and excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for aggressive drainage environments. While salt-glazed ceramics offer a distinctive glaze that improves surface hardness and water repellency, gres pipes provide superior structural integrity and consistent performance under heavy load and thermal variations.
Durability and Longevity in Drainage Applications
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes exhibit a highly durable, impervious surface resistant to chemical corrosion and abrasion, ensuring a lifespan exceeding 50 years in wastewater applications. Gres pipes, crafted from vitrified clay, offer exceptional mechanical strength and resistance to soil acidity, providing reliable service for over 70 years in drainage systems. Both materials deliver superior longevity, but gres's enhanced structural integrity and lower porosity often result in extended performance under aggressive environmental conditions.
Resistance to Chemical and Environmental Factors
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes exhibit exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion due to their dense, vitrified surface created during high-temperature salt glazing, making them highly durable against acids, alkalis, and other aggressive substances in wastewater. Gres pipes, composed of vitrified clay, also offer strong chemical resistance but may be more susceptible to abrasion and long-term environmental degradation in highly acidic or alkaline conditions. Both materials provide robust performance in drainage systems, but salt-glazed ceramics typically deliver superior protection against environmental factors such as soil acidity and groundwater contaminants.
Installation Methods and Practical Considerations
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes require careful handling during installation due to their brittleness and heavy weight, often necessitating mechanical joint systems and precise bedding to prevent damage. Gres pipes, made from vitrified clay, offer greater durability and ease of jointing with flexible couplings, allowing faster and more adaptable installations in various soil conditions. Practical considerations include the preference for gres pipes in aggressive environments due to their chemical resistance and lower maintenance needs, while salt-glazed ceramics demand regular inspections to avoid glaze surface wear impacting pipe longevity.
Cost Analysis: Salt-Glazed Ceramic vs Gres
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes typically have higher upfront costs due to their specialized glazing process, which enhances durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for long-term use in harsh environments. Gres pipes, made from vitrified clay, generally offer a more cost-effective solution with lower initial expenses, yet they may involve higher maintenance costs over time due to potential fragility under heavy loads or chemical exposure. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals salt-glazed ceramic pipes provide better value in demanding drainage applications, while gres pipes remain an economical choice for less intense conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Salt-glazed ceramic drainage pipes offer enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental waste. Gres pipes, made from natural clay and fired at high temperatures, are highly recyclable and biodegradable, contributing positively to sustainability goals. Both materials have low carbon footprints compared to plastic alternatives, but gres pipes often have a slight edge due to their simpler production process and natural composition.
Choosing the Best Drainage Pipe: Key Factors to Consider
Salt-glazed ceramic pipes offer superior chemical resistance and smoother interior surfaces, minimizing friction and sediment buildup, making them ideal for drainage systems exposed to harsh environments. Gres pipes, known for their high mechanical strength and durability, excel in high-load applications and provide excellent resistance to abrasion and corrosion. When choosing the best drainage pipe, factors such as environmental conditions, load requirements, chemical exposure, and installation longevity should be carefully evaluated to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Gres for Drainage Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com