Celadon features a translucent, jade-like glaze prized for its subtle green hues and smooth texture, making it ideal for refined decorative objects. Faience showcases vibrant, opaque tin-glazed surfaces often decorated with intricate patterns, offering bold visual appeal in ornamental ceramics.
Table of Comparison
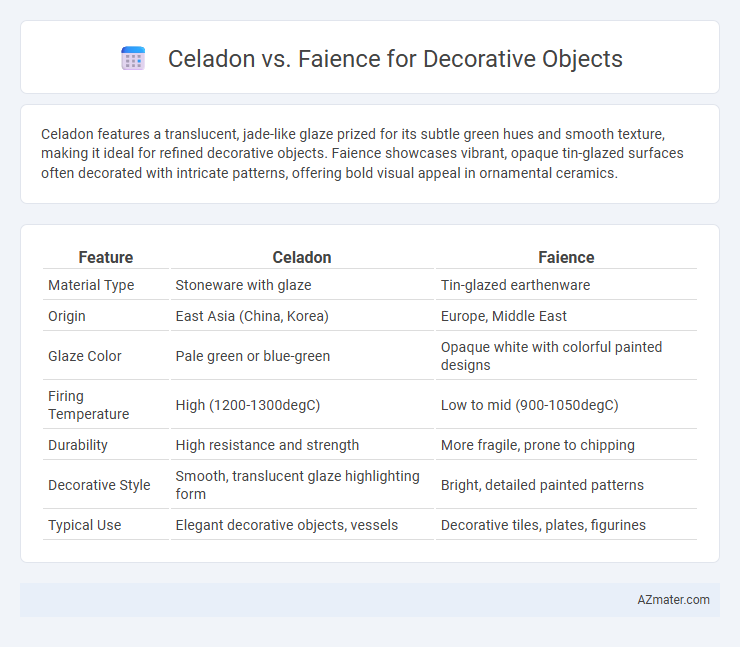
| Feature | Celadon | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Stoneware with glaze | Tin-glazed earthenware |
| Origin | East Asia (China, Korea) | Europe, Middle East |
| Glaze Color | Pale green or blue-green | Opaque white with colorful painted designs |
| Firing Temperature | High (1200-1300degC) | Low to mid (900-1050degC) |
| Durability | High resistance and strength | More fragile, prone to chipping |
| Decorative Style | Smooth, translucent glaze highlighting form | Bright, detailed painted patterns |
| Typical Use | Elegant decorative objects, vessels | Decorative tiles, plates, figurines |
Introduction to Celadon and Faience
Celadon is a type of ceramic glaze known for its delicate jade-green finish, originating from ancient China and highly prized for its smooth, translucent surface that enhances decorative objects. Faience refers to tin-glazed pottery that produces a bright, opaque white base, often decorated with colorful motifs, and has historical roots in the Middle East and Europe. Both Celadon and Faience offer distinct aesthetic qualities and cultural significance, making them popular choices for artistic and decorative ceramics.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Celadon originated during the Eastern Han Dynasty in China, known for its jade-like green glaze achieved through iron oxide in a reduction kiln atmosphere, evolving through the Song and Yuan Dynasties with refined translucency and intricate designs. Faience dates back to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, characterized by its opaque glaze made from crushed quartz and alkaline salts, often decorated with symbolic motifs, and later adapted in Islamic and European ceramics during the medieval period. The evolution of Celadon emphasized subtle color variation and texture, while Faience focused on vibrant colors and detailed pictorial patterns, reflecting distinct cultural and technological trajectories in decorative arts.
Material Composition and Production Techniques
Celadon features a high-fired stoneware or porcelain body coated with a distinctive jade-green glaze achieved through iron oxide reduction during kiln firing, resulting in a smooth, glassy surface. Faience, in contrast, is a tin-glazed earthenware made from a porous clay body covered with an opaque white glaze that serves as a canvas for colorful painted designs, produced at lower firing temperatures. The difference in material composition--high-fired stoneware versus low-fired earthenware--and glazing methods define their durability, texture, and aesthetic appeal in decorative objects.
Color Palette and Visual Appeal
Celadon features a translucent pale green to bluish-green glaze that enhances intricate carved or incised designs, offering a serene and elegant color palette ideal for subtle decorative objects. Faience showcases a vibrant range of opaque colors, including bright blues, yellows, and greens, often with glossy finishes that emphasize bold, eye-catching patterns and motifs. The visual appeal of Celadon lies in its smooth, muted tones and refined texture, while Faience captivates with its rich, saturated hues and ornamental versatility.
Durability and Functional Qualities
Celadon offers superior durability due to its dense, high-fired stoneware composition, making it resistant to chipping and cracking, whereas faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, is more porous and fragile. Functional qualities of celadon include better moisture resistance and suitability for everyday use, while faience is primarily decorative and prone to wear under heavy handling. The glaze of celadon also provides a smoother surface that enhances stain resistance, unlike faience's matte and often more absorbent finish.
Cultural Significance and Symbolism
Celadon ceramics, originating from ancient China, are prized for their jade-like glaze symbolizing purity, harmony, and nobility, often linked to Confucian ideals and imperial prestige. Faience, rooted in Egyptian and Mediterranean cultures, features vibrant tin-glazed pottery representing fertility, protection, and religious devotion, frequently adorned with symbolic motifs like lotus flowers and scarabs. The cultural significance of celadon emphasizes refined elegance and spiritual balance, while faience embodies vibrant storytelling and ritualistic symbolism in decorative objects.
Common Decorative Applications
Celadon glaze, prized for its translucent pale green hues, is commonly applied to vases, bowls, and tiles, offering a serene, classical aesthetic in decorative objects. Faience, characterized by its bright, opaque colors and tin-glazed surface, is frequently used for ornate plates, figurines, and tiled murals, lending a vibrant, intricate charm to decorative collections. Both celadon and faience serve distinct stylistic purposes, with celadon emphasizing subtle elegance and faience showcasing colorful, elaborate designs.
Collectibility and Market Value
Celadon ceramics, prized for their translucent green glaze and smooth texture, often command higher collectibility and market value due to their historical significance and rarity. Faience, characterized by its tin-glazed earthenware with vibrant painted designs, tends to attract collectors interested in decorative diversity but usually holds a moderate market price compared to celadon. Market trends indicate that authentic celadon pieces from renowned dynasties consistently outperform faience in auction results and private sales, highlighting their superior investment potential.
Contemporary Trends in Design
Celadon and faience ceramics both showcase rich historical craftsmanship but differ significantly in style and contemporary appeal. Celadon's smooth, jade-like glaze with subtle green hues aligns well with minimalist and Asian-inspired modern interiors, emphasizing tranquility and elegance. Faience's vibrant, tin-glazed surface with intricate patterns suits eclectic and bohemian designs, adding bold color and texture that complement contemporary maximalist trends.
Choosing Between Celadon and Faience for Décor
Celadon offers a translucent glaze with subtle greenish hues, ideal for elegant, understated decorative objects that evoke traditional Asian aesthetics. Faience provides vibrant, glossy finishes with intricate painted designs, making it perfect for bold, colorful decor that highlights Mediterranean or Middle Eastern influences. Choosing between celadon and faience depends on whether the goal is to achieve a minimalist, serene ambiance or a lively, ornate visual impact in the space.
Infographic: Celadon vs Faience for Decorative object
 azmater.com
azmater.com