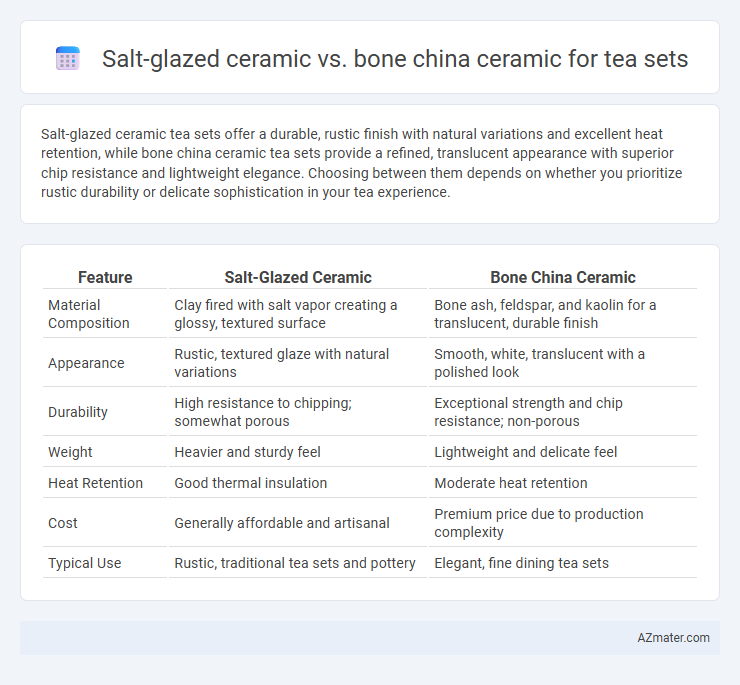
Salt-glazed ceramic tea sets offer a durable, rustic finish with natural variations and excellent heat retention, while bone china ceramic tea sets provide a refined, translucent appearance with superior chip resistance and lightweight elegance. Choosing between them depends on whether you prioritize rustic durability or delicate sophistication in your tea experience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Bone China Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay fired with salt vapor creating a glossy, textured surface | Bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin for a translucent, durable finish |
| Appearance | Rustic, textured glaze with natural variations | Smooth, white, translucent with a polished look |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping; somewhat porous | Exceptional strength and chip resistance; non-porous |
| Weight | Heavier and sturdy feel | Lightweight and delicate feel |
| Heat Retention | Good thermal insulation | Moderate heat retention |
| Cost | Generally affordable and artisanal | Premium price due to production complexity |
| Typical Use | Rustic, traditional tea sets and pottery | Elegant, fine dining tea sets |
Overview of Salt-glazed and Bone China Ceramics
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit a distinctive glossy, textured surface achieved by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, producing durable, non-porous stoneware ideal for rustic tea sets. Bone china ceramics, composed of bone ash, feldspathic material, and kaolin, deliver renowned translucency, high whiteness, and remarkable strength, making them a premium choice for elegant and refined tea sets. Both materials cater to different aesthetic and functional preferences, with salt-glazed emphasizing robustness and earthy appeal, while bone china prioritizes delicate beauty and fine craftsmanship.
Historical Background: Salt-glazed vs Bone China
Salt-glazed ceramics originated in 15th-century Germany, where artisans introduced salt into the kiln atmosphere to create a distinctive glossy, textured surface ideal for functional pottery like tea sets. Bone china, developed in 18th-century England by Josiah Spode, revolutionized ceramic tea ware with its blend of bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, producing translucent, strong, and delicate porcelain highly prized for fine tea sets. The historical progression from utilitarian salt-glazed stoneware to refined bone china reflects evolving tastes and technological advancements in ceramic production for tea service.
Visual Differences in Tea Sets
Salt-glazed ceramic tea sets exhibit a distinctive textured surface with a glossy, slightly mottled finish that enhances rustic and artisanal aesthetics. Bone china tea sets feature a smooth, translucent surface with a delicate, pure white color and often display intricate painted patterns or gold accents. The visual difference lies in the salt-glazed ceramic's earthy and robust appeal contrasted with bone china's refined and elegant appearance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Salt-glazed ceramic tea sets exhibit high durability due to their dense, vitreous surface, resisting chipping and scratching better than many other ceramics. Bone china tea sets, while more delicate, offer excellent longevity when handled carefully, featuring high resistance to thermal shock and maintaining their translucency over time. Salt-glazed ceramics are typically more robust for everyday use, whereas bone china excels in preserving aesthetic quality with moderate use.
Weight and Handling: User Experience
Salt-glazed ceramic tea sets are significantly heavier and provide a sturdy, rustic feel that enhances grip and durability during use. Bone china tea sets offer a lightweight and delicate handling experience, making them ideal for prolonged tea sessions where ease of movement and elegance matter. Users often prefer bone china for its smooth, thin walls that contribute to superior thermal insulation and refined tactile comfort compared to the thicker, denser salt-glazed ceramic.
Porosity and Stain Resistance
Salt-glazed ceramic exhibits low porosity due to its dense, vitrified surface created by salt vapor during firing, making it highly resistant to stains and ideal for long-term tea use. Bone china ceramic, although less porous than many other porcelains, has a finer, smoother composition with moderate porosity that can absorb slight stains over time if not carefully maintained. For tea sets requiring superior stain resistance and durability, salt-glazed ceramics offer enhanced protection against liquid absorption compared to bone china.
Heat Retention and Tea Flavor
Salt-glazed ceramic tea sets offer superior heat retention due to their dense, vitrified surface, keeping tea warm longer without rapid cooling. Bone china ceramic, while less dense, provides a smoother surface that does not affect the tea flavor, allowing the natural aroma and taste to remain pure. Salt-glazed ceramics may slightly enhance flavors by maintaining stable temperatures, whereas bone china emphasizes a neutral, clean tasting experience.
Suitability for Everyday Use
Salt-glazed ceramic offers exceptional durability and resistance to chipping, making it highly suitable for everyday use in tea sets, especially for those seeking a rustic aesthetic with easy maintenance. Bone china ceramic, renowned for its delicate translucency and lightweight feel, provides a refined drinking experience but requires careful handling due to its fragile nature. For daily tea rituals, salt-glazed ceramics balance practicality and robustness, whereas bone china suits occasions where elegance is prioritized over durability.
Price and Collectibility
Salt-glazed ceramic tea sets typically have a lower price point due to their rustic finish and simpler production process, making them accessible for everyday use. Bone china tea sets command higher prices, valued for their translucency, delicate craftsmanship, and durability, attracting serious collectors and connoisseurs. Collectibility of bone china is elevated by brand reputation and limited editions, whereas salt-glazed ceramics gain appeal through artisanal uniqueness and regional styles.
Eco-Friendliness and Production Methods
Salt-glazed ceramics use a traditional kiln process that produces a durable, glossy surface by vaporizing salt at high temperatures, resulting in minimal chemical additives and lower environmental impact compared to bone china, which involves bone ash and intensive processing. Bone china requires animal-sourced bone ash and higher energy consumption during production, raising concerns about sustainability and eco-friendliness. Choosing salt-glazed ceramic tea sets supports a more natural, less resource-intensive manufacturing method with reduced carbon footprint in the ceramic industry.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Bone china ceramic for Tea set
 azmater.com
azmater.com