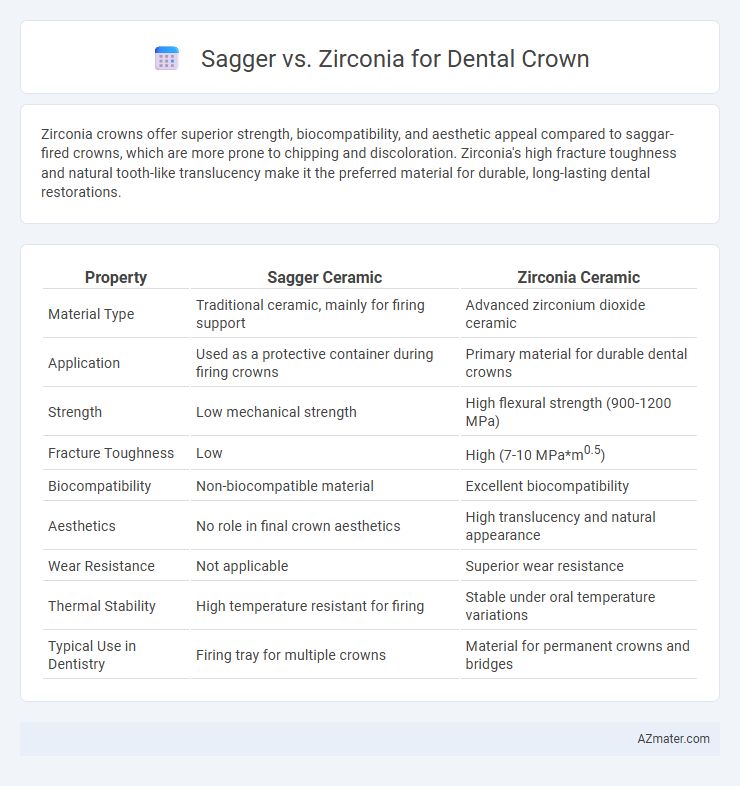
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength, biocompatibility, and aesthetic appeal compared to saggar-fired crowns, which are more prone to chipping and discoloration. Zirconia's high fracture toughness and natural tooth-like translucency make it the preferred material for durable, long-lasting dental restorations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger Ceramic | Zirconia Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Traditional ceramic, mainly for firing support | Advanced zirconium dioxide ceramic |
| Application | Used as a protective container during firing crowns | Primary material for durable dental crowns |
| Strength | Low mechanical strength | High flexural strength (900-1200 MPa) |
| Fracture Toughness | Low | High (7-10 MPa*m0.5) |
| Biocompatibility | Non-biocompatible material | Excellent biocompatibility |
| Aesthetics | No role in final crown aesthetics | High translucency and natural appearance |
| Wear Resistance | Not applicable | Superior wear resistance |
| Thermal Stability | High temperature resistant for firing | Stable under oral temperature variations |
| Typical Use in Dentistry | Firing tray for multiple crowns | Material for permanent crowns and bridges |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crown materials primarily include Sagger and Zirconia, each offering distinct advantages in durability and aesthetics. Zirconia crowns provide exceptional strength, biocompatibility, and a natural tooth-like appearance, making them ideal for both anterior and posterior restorations. Sagger crowns, often made from metal alloys or porcelain-fused-to-metal, are valued for their cost-effectiveness and traditional reliability in dental prosthetics.
What is Sagger in Dentistry?
Sagger in dentistry refers to a specialized container used during the sintering process to hold dental crowns, such as zirconia, protecting them from contamination and deformation at high temperatures. It ensures uniform heat distribution, preserving the structural integrity and surface quality of zirconia crowns. Saggers are essential for achieving optimal strength and translucency in ceramic dental restorations.
Understanding Zirconia Dental Crowns
Zirconia dental crowns are made from zirconium dioxide, a highly durable ceramic material known for its strength and biocompatibility, making it an ideal choice for long-lasting restorations. Compared to traditional Sagger crowns, zirconia crowns offer superior resistance to chipping and wear, while also providing excellent aesthetic results due to their natural translucency. These crowns are also less likely to cause allergic reactions and require minimal tooth reduction, enhancing patient comfort and overall treatment outcomes.
Physical Properties: Sagger vs Zirconia
Sagger for dental crowns primarily serves as a protective container during the firing process, composed of refractory materials with high thermal resistance and insulation properties. Zirconia, a crystalline dioxide of zirconium, exhibits superior physical properties such as high flexural strength (900-1200 MPa), fracture toughness (7-10 MPa*m^0.5), and excellent biocompatibility, making it ideal for durable and aesthetic dental crowns. Unlike saggers, zirconia's dense microstructure contributes to its hardness and wear resistance, enabling long-lasting restoration performance.
Aesthetic Comparison: Sagger vs Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns offer superior aesthetics compared to Sagger crowns due to their translucency and natural tooth-like appearance, allowing for better light reflection and color matching. Sagger crowns, typically made from metal or metal-ceramic composites, often lack the lifelike translucency and may appear opaque or metallic at the margins. Patients seeking highly aesthetic restorations in anterior teeth frequently prefer zirconia crowns for their ability to blend seamlessly with surrounding natural teeth.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior strength and durability compared to Sagger crowns, with compressive strength values often exceeding 1200 MPa, making them ideal for high-stress dental restorations. Sagger crowns, typically made from less dense ceramic materials, demonstrate lower fracture toughness and are more prone to chipping under occlusal forces. Long-term clinical studies confirm that zirconia offers enhanced wear resistance and maintains structural integrity better than Sagger crowns, ensuring extended lifespan in demanding oral environments.
Biocompatibility: Sagger vs Zirconia
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility due to their inert nature, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and promoting better gum tissue response. In contrast, Sagger materials, often ceramic-based but less pure, may provoke mild inflammatory responses in some patients. The high stability and non-toxic properties of Zirconia make it the preferred choice for patients with metal sensitivities or those requiring long-term dental restorations.
Cost Efficiency of Sagger and Zirconia Crowns
Sagger crowns offer a cost-efficient solution for dental restorations, primarily due to their lower material and manufacturing costs compared to zirconia crowns. Zirconia crowns, while more expensive, provide superior durability and aesthetic appeal that can reduce long-term replacement expenses. Patients seeking budget-friendly options may prefer sagger crowns, whereas those prioritizing longevity and appearance might consider the higher initial investment in zirconia crowns as more cost-effective over time.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Sagger crowns, typically made from metal-ceramic materials, offer strong clinical performance with excellent fracture resistance and durability, but may show slight translucency limitations compared to zirconia. Zirconia crowns provide superior biocompatibility, high fracture toughness, and enhanced esthetics due to their translucency and color stability, making them increasingly preferred for long-term restorations. Studies indicate zirconia crowns demonstrate greater longevity in posterior restorations, with lower rates of chipping and wear over time compared to traditional Sagger crowns.
Choosing the Best Material: Sagger or Zirconia?
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal compared to Sagger, which is less commonly used and primarily refers to a ceramic firing container rather than a crown material. Choosing zirconia ensures biocompatibility, high fracture resistance, and natural translucency suitable for both anterior and posterior restorations. Dentists favor zirconia for its long-term performance and minimal tooth preparation, making it the optimal choice for dental crowns.
Infographic: Sagger vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com