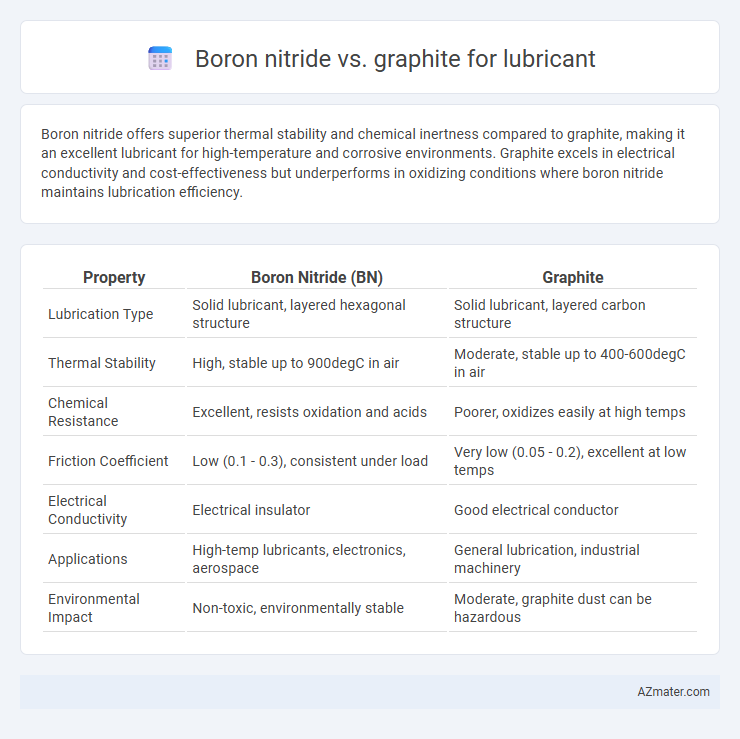
Boron nitride offers superior thermal stability and chemical inertness compared to graphite, making it an excellent lubricant for high-temperature and corrosive environments. Graphite excels in electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but underperforms in oxidizing conditions where boron nitride maintains lubrication efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Boron Nitride (BN) | Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Lubrication Type | Solid lubricant, layered hexagonal structure | Solid lubricant, layered carbon structure |
| Thermal Stability | High, stable up to 900degC in air | Moderate, stable up to 400-600degC in air |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists oxidation and acids | Poorer, oxidizes easily at high temps |
| Friction Coefficient | Low (0.1 - 0.3), consistent under load | Very low (0.05 - 0.2), excellent at low temps |
| Electrical Conductivity | Electrical insulator | Good electrical conductor |
| Applications | High-temp lubricants, electronics, aerospace | General lubrication, industrial machinery |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, environmentally stable | Moderate, graphite dust can be hazardous |
Introduction to Lubricant Materials
Boron nitride and graphite are prominent solid lubricant materials used to reduce friction and wear in high-temperature and extreme environments. Graphite's layered structure enables easy shear between planes, making it an effective lubricant especially in the presence of moisture, while boron nitride, with its hexagonal crystalline form, offers superior thermal stability and oxidization resistance. Both materials excel in enhancing surface protection, but boron nitride is preferred for applications requiring higher temperature endurance and chemical inertness compared to graphite.
Overview of Boron Nitride as a Lubricant
Boron nitride, particularly in its hexagonal form (h-BN), is a highly effective lubricant known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical inertness, and low friction coefficient. Unlike graphite, boron nitride maintains consistent lubricating properties in extreme temperatures and aggressive chemical environments, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and electronics. Its unique crystalline structure provides excellent resistance to oxidation, ensuring durability and enhanced performance where traditional lubricants may fail.
Graphite: Properties and Lubrication Mechanism
Graphite exhibits excellent lubrication properties due to its layered crystal structure, where weak van der Waals forces between graphene sheets allow easy shear under friction. Its high thermal conductivity and chemical stability enhance performance in extreme temperature environments. Graphite's ability to form a robust, lubricating film reduces wear and friction in mechanical systems, making it a preferred solid lubricant in various industrial applications compared to boron nitride.
Thermal Stability: Boron Nitride vs Graphite
Boron nitride exhibits superior thermal stability compared to graphite, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures above 1000degC in oxidative environments, whereas graphite oxidizes and degrades around 400-500degC. Hexagonal boron nitride's ability to withstand extreme heat without significant chemical breakdown makes it ideal for high-temperature lubrication applications. Graphite, while effective at moderate temperatures, cannot match boron nitride's performance in sustained high-heat conditions due to its lower oxidation resistance.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Boron nitride exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to graphite, maintaining stability in aggressive environments such as strong acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents. Graphite tends to degrade or oxidize when exposed to harsh chemicals, limiting its effectiveness in corrosive conditions. Consequently, boron nitride is preferred in lubrication applications requiring enhanced chemical inertness and durability under extreme chemical exposure.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Boron nitride exhibits superior thermal stability and chemical inertness compared to graphite, making it highly effective as a lubricant in extreme temperature and pressure conditions. Its hexagonal structure allows it to maintain low friction coefficients even in oxidizing environments where graphite tends to degrade. Graphite performs well in standard conditions but loses efficacy under high humidity and oxidative stress, limiting its use in harsh industrial applications.
Friction and Wear Characteristics
Boron nitride exhibits superior lubrication properties compared to graphite due to its low friction coefficient and excellent thermal stability, minimizing wear under high-temperature conditions. Graphite provides effective lubrication primarily in the presence of moisture but tends to have higher friction and wear rates in dry or oxidative environments. The lamellar structure of boron nitride allows for consistent surface protection and reduced material degradation, making it more durable for prolonged mechanical use.
Applications in Industry
Boron nitride offers superior thermal stability and chemical inertness compared to graphite, making it ideal for high-temperature lubrication in aerospace and electronics industries. Graphite excels in environments with low oxygen levels, commonly used in steel manufacturing and heavy machinery due to its excellent lubricating properties under extreme pressure. Industrial applications favor boron nitride for precision components where contamination must be minimized, while graphite remains preferred for large-scale mechanical operations requiring effective, low-cost lubrication.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Boron nitride, especially in its hexagonal form, offers superior environmental safety compared to graphite due to its chemically inert nature and non-toxicity, reducing risks of harmful emissions and residues during lubrication. Graphite, while effective as a lubricant, can release fine particulate matter and pose respiratory hazards, necessitating careful handling and disposal to mitigate environmental contamination. Both materials present distinct safety profiles, with boron nitride favored in applications prioritizing eco-friendly and non-toxic lubrication solutions.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Boron nitride offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to graphite, but comes at a higher cost and limited availability due to complex manufacturing processes. Graphite remains more widely available and cost-effective, benefiting from extensive natural deposits and established extraction methods. For applications prioritizing budget and supply chain reliability, graphite is often preferred despite its lower performance under extreme conditions.
Infographic: Boron nitride vs Graphite for Lubricant
 azmater.com
azmater.com