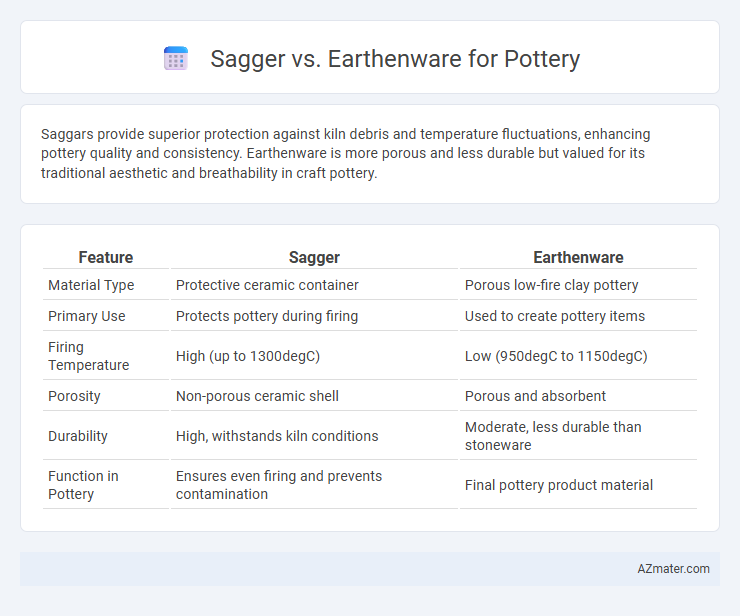
Saggars provide superior protection against kiln debris and temperature fluctuations, enhancing pottery quality and consistency. Earthenware is more porous and less durable but valued for its traditional aesthetic and breathability in craft pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sagger | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Protective ceramic container | Porous low-fire clay pottery |
| Primary Use | Protects pottery during firing | Used to create pottery items |
| Firing Temperature | High (up to 1300degC) | Low (950degC to 1150degC) |
| Porosity | Non-porous ceramic shell | Porous and absorbent |
| Durability | High, withstands kiln conditions | Moderate, less durable than stoneware |
| Function in Pottery | Ensures even firing and prevents contamination | Final pottery product material |
Introduction to Sagger and Earthenware Pottery
Sagger is a protective container used in pottery to shield clay pieces from direct flame and ash during kiln firing, enhancing the firing quality by preventing surface damage. Earthenware pottery, made from porous clay fired at low temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, is characterized by its rich, earthy colors and is often finished with a glaze to improve durability. Understanding the role of a sagger in the firing process is crucial for achieving optimal results with earthenware, as it helps maintain delicate textures and details.
What is Sagger Pottery?
Sagger pottery involves firing ceramic pieces inside a protective container called a sagger, which shields the pottery from direct flame and ash during kiln firing, resulting in unique surface effects and color variations. This technique contrasts with earthenware, which refers to pottery made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures without such protective measures, often yielding a more rustic and less durable finish. Saggers enable potters to experiment with controlled atmospheres and materials, enhancing creativity and the quality of the ceramic surface.
What is Earthenware Pottery?
Earthenware pottery is a type of ceramic made from porous clay fired at relatively low temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a sturdy yet slightly porous final product. Unlike saggars, which are protective containers used during firing to shield pottery from direct flames and debris, earthenware pieces are often decorative and functional items such as bowls, plates, and flower pots. The low firing temperature gives earthenware its characteristic warmth in color and texture but requires glazing to make it watertight and durable.
Key Differences Between Sagger and Earthenware
Sagger is a protective container made from refractory material used in kilns to shield pottery from direct flame and ash, enhancing surface quality during firing, while earthenware refers to a porous, low-fired clay pottery that typically matures at temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC. The key difference lies in function and material: saggars serve as kiln accessories made from fireclay or similar heat-resistant compounds, whereas earthenware is a finished ceramic product used for functional and decorative purposes. Saggars enable controlled firing environments, improving the appearance and durability of earthenware but are not part of the final ceramic object.
Materials Used in Sagger vs Earthenware
Saggers are protective containers made primarily from refractory clay, fireclay, or chamotte, designed to shield pottery from direct flame and contaminants in kilns, whereas earthenware consists of porous clay bodies composed mainly of iron-rich clays, kaolin, and silica, fired at lower temperatures typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC. The refractory materials in saggers provide high thermal resistance and durability, enabling them to withstand repeated high-temperature firings without cracking, while earthenware's natural clay composition results in a more porous and less durable ceramic body that requires glazing for waterproofing. Chemical additives like grog or crushed fired clay in saggers enhance their thermal shock resistance, contrasting with earthenware's focus on organic impurities and fine particle size for workability and aesthetic qualities.
Firing Techniques: Sagger vs Earthenware
Sagger firing involves placing pottery inside a protective container called a sagger, which shields the pieces from direct flame and ash, ensuring cleaner surfaces and controlled atmospheres during firing. Earthenware firing typically occurs in an oxidizing or reducing atmosphere within a kiln, where the porous nature of earthenware demands lower firing temperatures, usually between 1,000degC and 1,150degC. The sagger technique allows for more precise environmental control, reducing defects and enhancing design clarity compared to traditional earthenware firing.
Durability and Longevity of Each Type
Sagger pottery offers enhanced durability by providing a protective barrier during firing, reducing surface defects and thermal shock, which ensures longer-lasting pieces compared to standard earthenware. Earthenware, made from porous clay and fired at lower temperatures, tends to be more fragile and susceptible to chipping and moisture absorption, limiting its longevity. Consequently, saggers extend the lifespan of pottery by maintaining structural integrity under higher temperatures, while traditional earthenware requires careful handling to preserve its durability.
Artistic Possibilities and Surface Effects
Sagger pottery offers intensified artistic possibilities by allowing precise control over atmosphere and temperature, resulting in unique surface textures and color variations often unattainable with earthenware. Earthenware provides a porous and earthy surface that enhances rustic finishes and absorbs glazes differently, enabling diverse visual and tactile effects. Both techniques influence the ceramic's aesthetic, with sagger firing expanding the palette of surface outcomes through smoke and ash patterns, while earthenware emphasizes organic and matte qualities inherent to its clay body.
Practical Uses: Sagger vs Earthenware Pottery
Saggers provide practical protection for delicate pottery during firing, enabling higher temperature tolerance and preventing surface damage or warping, ideal for fine ceramics and glazes. Earthenware pottery, made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, is widely used for functional items like terracotta pots, dishes, and tiles, valued for its rustic appearance and affordability. While saggers enhance kiln firing precision and produce high-quality finishes, earthenware remains popular for everyday, decorative, and artisanal pottery due to its ease of handling and versatility.
Choosing the Right Pottery Method for Your Project
Sagger firing provides enhanced protection for delicate glazes and intricate decorations by shielding pottery from direct flame and ash, making it ideal for high-temperature stoneware and porcelain projects requiring precise finishes. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, is more porous and less durable but offers vibrant color options and faster firing cycles perfect for decorative or functional pieces with a rustic aesthetic. Choosing between sagger and earthenware depends on the desired durability, firing temperature, glaze sensitivity, and final appearance of your pottery project.
Infographic: Sagger vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com