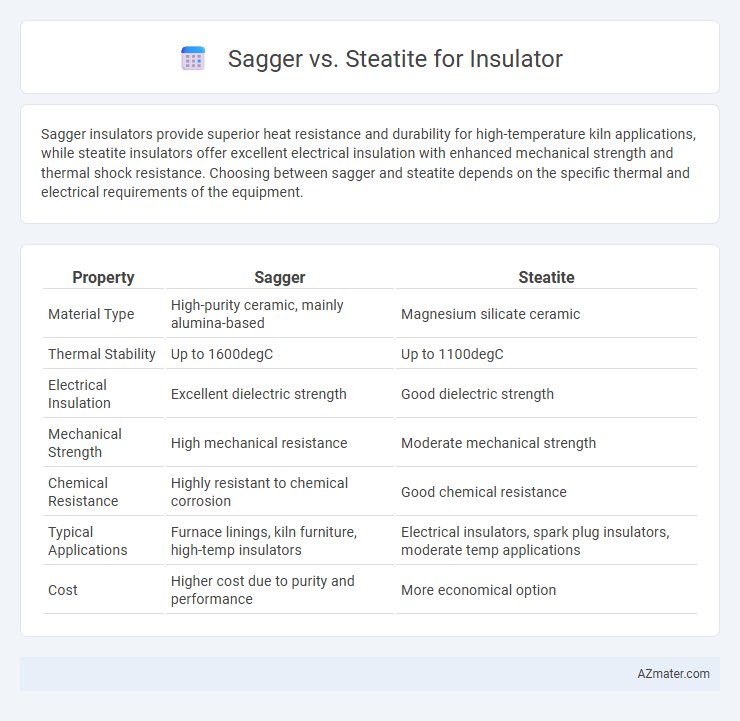
Sagger insulators provide superior heat resistance and durability for high-temperature kiln applications, while steatite insulators offer excellent electrical insulation with enhanced mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. Choosing between sagger and steatite depends on the specific thermal and electrical requirements of the equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-purity ceramic, mainly alumina-based | Magnesium silicate ceramic |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1600degC | Up to 1100degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength | Good dielectric strength |
| Mechanical Strength | High mechanical resistance | Moderate mechanical strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to chemical corrosion | Good chemical resistance |
| Typical Applications | Furnace linings, kiln furniture, high-temp insulators | Electrical insulators, spark plug insulators, moderate temp applications |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and performance | More economical option |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Sagger and steatite are critical materials used as electrical insulators due to their high dielectric strength and thermal stability. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, offers excellent mechanical strength and moisture resistance, making it ideal for high-voltage insulation applications. Sagger, often used in kiln environments to protect components, provides insulating properties along with thermal protection, though it is less commonly applied in electrical contexts compared to steatite.
Understanding Sagger Material Properties
Sagger insulators are typically made from high-purity alumina or porcelain, offering excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, which make them suitable for high-temperature applications in kilns and furnaces. Steatite insulators, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, provide superior dielectric strength and mechanical robustness while maintaining good thermal shock resistance, ideal for electrical insulation in demanding environments. Understanding these material properties is crucial for selecting the appropriate insulator, balancing factors such as thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and mechanical durability.
Overview of Steatite as an Insulator
Steatite, a ceramic material composed mainly of talc, offers excellent electrical insulation properties characterized by high dielectric strength and low loss tangent, making it suitable for high-frequency and high-voltage applications. Its superior thermal stability and mechanical strength allow it to maintain insulating performance under harsh environmental conditions, including high temperatures and mechanical stress. Compared to sagger, steatite provides improved durability, better moisture resistance, and consistent insulating behavior, making it a preferred choice in electronic and electrical components.
Mechanical Strength: Sagger vs Steatite
Steatite insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to saggers, making them ideal for applications requiring high durability under mechanical stress. Steatite's dense ceramic composition provides enhanced resistance to cracking and wear, whereas saggers, typically made from more porous materials, have lower fracture toughness. The robustness of steatite insulators ensures longer service life and reliability in demanding electrical environments.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Sagger insulators, typically made from high-purity alumina or silicon carbide, offer superior thermal resistance due to their dense microstructure and ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 1700degC. Steatite insulators, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, exhibit lower thermal resistance, generally tolerating temperatures up to 1000degC with moderate thermal conductivity. The choice between Sagger and Steatite hinges on application-specific thermal resistance requirements, where Sagger provides enhanced performance under high-temperature and thermal shock conditions.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Sagger and steatite insulators differ significantly in electrical insulation performance, with steatite exhibiting superior dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity due to its dense, high-purity ceramic composition. Steatite's stable resistance to high voltages and thermal shocks makes it ideal for high-frequency and high-temperature applications, whereas sagger insulators, often made from less dense ceramic materials, offer moderate insulation but are more prone to microcracks and leakage currents. The enhanced electrical insulation properties of steatite contribute to its widespread use in advanced electrical components and devices requiring reliable dielectric performance.
Durability and Longevity
Sagger insulators, made from dense ceramic materials, exhibit exceptional resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, ensuring long-term durability in high-temperature environments. Steatite insulators, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offer superior mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance, extending their service life in industrial applications. Both materials provide reliable insulation performance, but saggers generally excel in extreme thermal conditions while steatite is favored for its robustness under mechanical stress.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Steatite insulators offer superior cost-effectiveness compared to Sagger insulators due to their lower production costs and enhanced durability under high-temperature conditions. Sagger insulators, made from specialized clay, have higher manufacturing expenses and shorter lifespan, increasing replacement frequency. Investing in steatite ensures reduced maintenance and overall expenditure in industrial applications, maximizing long-term savings.
Typical Applications in Industry
Sagger insulators are commonly used in high-temperature kiln and furnace applications due to their excellent thermal shock resistance and chemical stability, making them ideal for ceramics and metallurgy industries. Steatite insulators, known for their high mechanical strength and electrical insulating properties, are frequently applied in electrical and electronic components, including insulators for high-voltage equipment and capacitors. Both materials serve critical roles in industrial insulation but are selected based on specific temperature tolerances and mechanical requirements.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
When choosing between sagger and steatite for insulators, consider factors such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties. Steatite offers excellent dielectric strength and is highly resistant to thermal shock, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Saggers, typically made from refractory ceramics, provide robust thermal insulation and chemical resistance but may lack the mechanical durability found in steatite insulators.
Infographic: Sagger vs Steatite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com