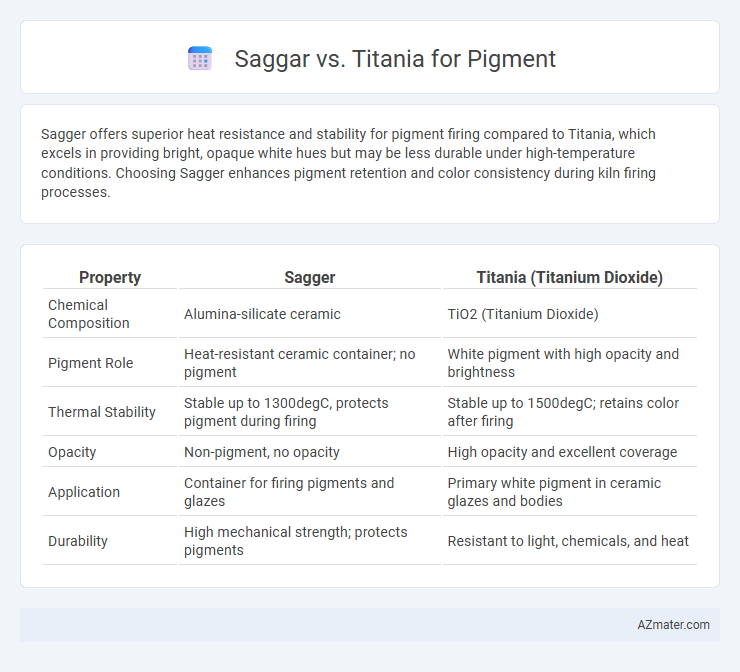
Sagger offers superior heat resistance and stability for pigment firing compared to Titania, which excels in providing bright, opaque white hues but may be less durable under high-temperature conditions. Choosing Sagger enhances pigment retention and color consistency during kiln firing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Titania (Titanium Dioxide) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Alumina-silicate ceramic | TiO2 (Titanium Dioxide) |
| Pigment Role | Heat-resistant ceramic container; no pigment | White pigment with high opacity and brightness |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 1300degC, protects pigment during firing | Stable up to 1500degC; retains color after firing |
| Opacity | Non-pigment, no opacity | High opacity and excellent coverage |
| Application | Container for firing pigments and glazes | Primary white pigment in ceramic glazes and bodies |
| Durability | High mechanical strength; protects pigments | Resistant to light, chemicals, and heat |
Introduction to Sagger and Titania in Pigment Production
Sagger and Titania serve distinct roles in pigment production, with Sagger acting as a protective ceramic container used during the firing process to prevent pigment contamination and preserve color integrity. Titania, or titanium dioxide, is a widely used white pigment renowned for its exceptional brightness, opacity, and stability in diverse applications such as paints, coatings, and plastics. Optimizing the use of Sagger in kiln firing ensures the quality and consistency of Titania-based pigments by shielding them from impurities and thermal degradation.
Overview of Pigment Manufacturing Processes
Sagger and Titania represent critical components in pigment manufacturing, with Sagger referring to protective containers used during firing processes to prevent contamination and maintain pigment purity. Titania, or titanium dioxide, is a widely used white pigment produced through the sulfate or chloride process, involving calcination to achieve desired particle size and crystallinity. Manufacturing efficiency depends on precise control of temperature and raw material quality, impacting the brightness, opacity, and durability of the final pigment product.
What is Sagger? Roles and Applications in Pigment Creation
Sagger is a protective ceramic container used in high-temperature firing processes to shield pigments and glazes from direct flame and contamination, ensuring color consistency and preventing oxidation or reduction effects. It plays a crucial role in pigment creation by maintaining a controlled atmosphere around the pigment materials, which influences the final hue and intensity of the color. Saggers are commonly employed in the production of ceramic pigments, allowing for precise heat treatment and stable pigment development before comparison with alternatives like Titania-based pigments.
Titania (Titanium Dioxide): Key Functions in Pigment Industry
Titania, primarily composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), serves as a crucial pigment due to its exceptional brightness and high refractive index, providing superior whiteness and opacity in paints, coatings, and plastics. Its chemical stability and non-toxic nature enhance durability and safety, making it a preferred choice over alternatives like Sagger-based pigments. Titania's ability to scatter light efficiently leads to excellent coverage and vibrant color retention in various industrial applications.
Comparative Performance: Sagger vs. Titania in Pigment Quality
Sagger and Titania pigments exhibit distinct performance characteristics influencing pigment quality, with Sagger providing superior thermal stability and enhanced color vibrancy suited for high-temperature applications. Titania offers excellent opacity and brightness, making it ideal for coatings requiring strong light reflectance and durability. Comparative analysis reveals Sagger excels in retaining pigment integrity under intense heat, while Titania leads in achieving maximum whiteness and opacity in various industrial uses.
Thermal Stability and Resistance Analysis
Sagger and Titania pigments exhibit distinct thermal stability profiles critical for high-temperature applications, with Sagger demonstrating superior resistance to thermal degradation up to 1200degC compared to Titania's limit near 900degC. Resistance analysis reveals Sagger's enhanced chemical inertness against oxidation and sulfur compounds, making it ideal for harsh firing conditions in ceramics and metallurgy. Titania, while offering excellent brightness and opacity, tends to suffer phase transformations and reduced durability under prolonged thermal stress, limiting its use in extreme environments.
Effects on Color Consistency and Opacity
Sagger and Titania pigments differ significantly in their impact on color consistency and opacity. Sagger pigments typically provide more uniform color dispersion, resulting in consistent hues across various mediums, while Titania pigments, known for high refractive indices, enhance opacity but may cause slight color shifts due to light scattering. Selecting between Sagger and Titania depends on the desired balance between maintaining precise color fidelity and achieving optimal coverage and opacity in the final product.
Cost Efficiency: Sagger vs. Titania
Sagger offers higher cost efficiency compared to Titania due to its lower raw material expenses and reduced processing times, resulting in decreased overall production costs. Titania provides superior pigment quality but at a significantly higher price point, making Sagger a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Evaluating the balance between cost and performance is crucial when selecting between Sagger and Titania for pigment manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Sagger and Titania pigments differ significantly in their environmental impact and sustainability profiles, with Titania (titanium dioxide) often scrutinized for energy-intensive production and potential nanoparticle dispersion concerns. Sagger, typically a clay-based pigment derived as a byproduct of kiln processes, offers a more sustainable alternative due to lower resource consumption and biodegradability. Lifecycle assessments highlight Titania's high carbon footprint compared to Sagger's minimal ecological disruption, making Sagger preferable in eco-conscious applications.
Conclusion: Selecting the Ideal Material for Pigment Production
Sagger offers superior thermal stability and enhanced refillability, making it ideal for high-temperature firing processes in pigment production. Titania (titanium dioxide) provides exceptional brightness and opacity, contributing to vibrant and durable pigments widely used in coatings. Choosing between Sagger and Titania depends on the desired pigment application--Sagger suits ceramic glaze pigments requiring thermal resistance, while Titania excels in paints and plastics demanding high whiteness and coverage.
Infographic: Sagger vs Titania for Pigment
 azmater.com
azmater.com