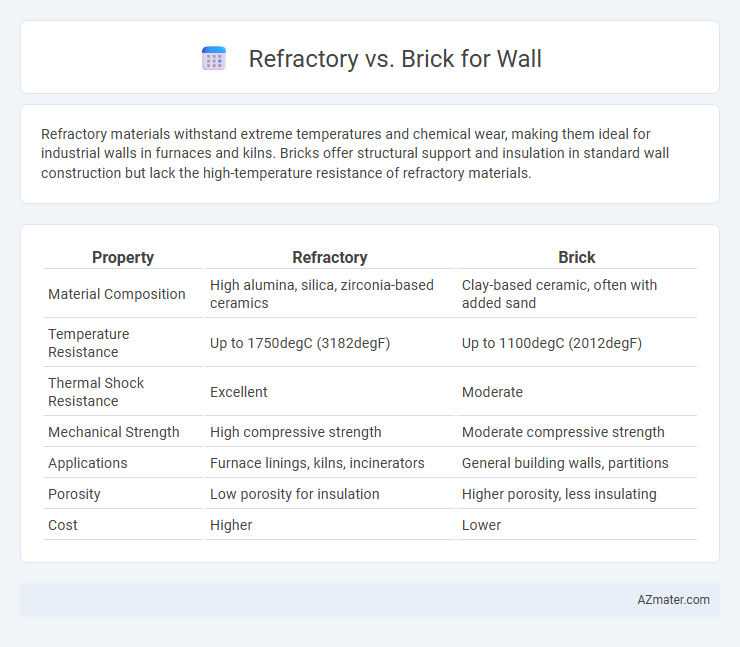
Refractory materials withstand extreme temperatures and chemical wear, making them ideal for industrial walls in furnaces and kilns. Bricks offer structural support and insulation in standard wall construction but lack the high-temperature resistance of refractory materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High alumina, silica, zirconia-based ceramics | Clay-based ceramic, often with added sand |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1750degC (3182degF) | Up to 1100degC (2012degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength | Moderate compressive strength |
| Applications | Furnace linings, kilns, incinerators | General building walls, partitions |
| Porosity | Low porosity for insulation | Higher porosity, less insulating |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Understanding Refractory and Brick Walls
Refractory walls are specifically designed to withstand extreme temperatures, making them ideal for industrial furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces, where heat resistance and durability are critical. Brick walls, typically made from clay or concrete, are primarily used in building construction for their structural support and aesthetic appeal, but they lack the high thermal tolerance of refractory materials. Understanding the key difference lies in the thermal properties: refractory bricks have high alumina and silica content, providing superior heat insulation and resistance, whereas standard bricks prioritize strength and weather resistance for general architectural use.
Key Differences Between Refractory and Regular Bricks
Refractory bricks, also known as fire bricks, are specifically designed to withstand extremely high temperatures and thermal shock, making them ideal for furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces, whereas regular bricks are primarily used for general construction and have lower heat resistance. Key differences include refractory bricks' composition of silica, alumina, and other heat-resistant materials, which provide superior thermal insulation and durability compared to regular bricks made from clay or shale. Additionally, refractory bricks maintain structural integrity at temperatures above 1500degC, while regular bricks typically withstand temperatures only up to about 1000degC.
Material Composition: Refractory vs Standard Brick
Refractory bricks are composed primarily of alumina and silica, designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock, making them ideal for furnaces and kilns. Standard bricks, typically made from clay and shale, offer good structural integrity but lack the heat resistance necessary for extreme environments. The high alumina content in refractory bricks enhances their durability under intense heat compared to the porous structure of standard bricks.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Refractory materials exhibit superior thermal resistance and heat tolerance compared to conventional bricks, withstanding temperatures above 1600degC without degrading. Common bricks typically tolerate heat up to 1000degC, making refractory bricks essential for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnaces and kilns. The dense microstructure of refractory bricks minimizes thermal conductivity, enhancing insulation and maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat conditions.
Structural Strength and Durability
Refractory bricks are engineered to withstand high temperatures and thermal stress, making them ideal for industrial applications such as furnaces and kilns due to their superior structural strength and durability under extreme heat. Standard bricks used in wall construction provide adequate structural integrity for residential and commercial buildings but lack the heat resistance and longevity of refractory bricks when exposed to severe thermal conditions. Choosing refractory bricks for walls enhances durability in high-temperature environments, while regular bricks suit conventional load-bearing walls with less thermal demand.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Refractory materials are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion, making them essential for lining furnaces, kilns, and reactors in industries such as steel manufacturing and glass production. Bricks, typically made from clay or concrete, are primarily used for structural walls, facades, and load-bearing applications in residential and commercial construction. While refractory bricks provide thermal insulation and durability under high heat, standard bricks offer strength and aesthetic appeal for general construction needs.
Cost Comparison: Refractory Wall vs Brick Wall
Refractory walls typically incur higher initial costs due to specialized heat-resistant materials and installation processes, making them more expensive than traditional brick walls. Brick walls offer a cost-effective solution with lower material and labor expenses but lack the high-temperature durability of refractory walls. Over time, refractory walls can reduce maintenance costs in industrial settings due to their enhanced thermal resistance and longevity.
Installation Process and Maintenance Requirements
Refractory walls require specialized installation involving high-temperature resistant mortar and precise curing to withstand extreme heat conditions, whereas brick walls use standard masonry techniques with cement-based mortar. Maintenance for refractory walls includes routine inspections for cracks and periodic replacement of damaged refractory materials to ensure thermal efficiency, while brick walls primarily need regular repointing and weatherproofing to prevent moisture intrusion and structural degradation. Installation complexity and ongoing maintenance costs are higher for refractory walls due to their heat-resistant properties compared to the more straightforward process and upkeep of traditional brick walls.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Refractory materials and bricks differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with refractory bricks often requiring higher energy consumption during production due to their specialized compositions designed to withstand extreme temperatures. Standard clay bricks generally have a lower carbon footprint and can be made from abundant natural materials, although their durability may be less compared to refractory options. Sustainable practices in brick production include using recycled materials and alternative fuels, while refractory materials demand innovation in energy-efficient manufacturing to reduce ecological footprints.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Wall
Refractory materials are designed to withstand high temperatures and are ideal for walls exposed to intense heat, such as in furnaces or fireplaces, while traditional bricks offer durability and insulation suited for standard construction walls. Choosing the right material depends on the wall's function, where refractory bricks provide superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, enhancing safety in high-heat environments. Consider factors like temperature exposure, structural requirements, and cost-effectiveness to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your wall.
Infographic: Refractory vs Brick for Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com