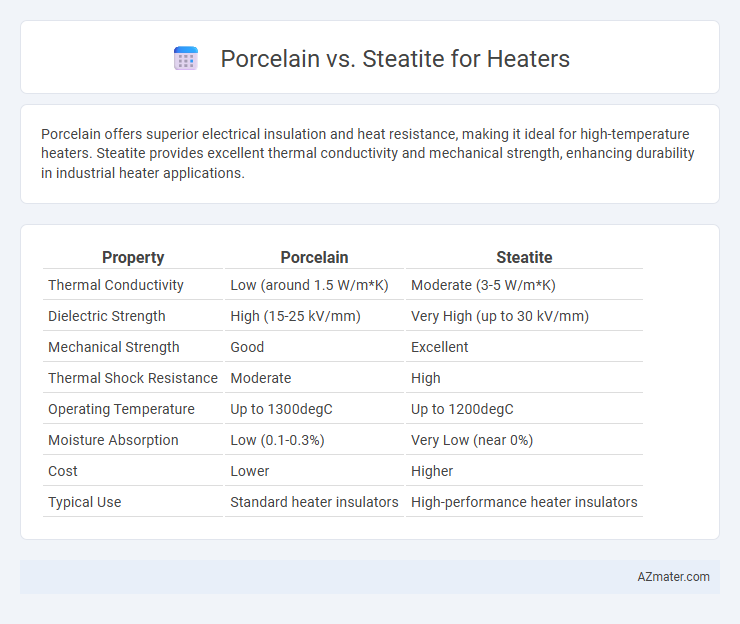
Porcelain offers superior electrical insulation and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature heaters. Steatite provides excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, enhancing durability in industrial heater applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (around 1.5 W/m*K) | Moderate (3-5 W/m*K) |
| Dielectric Strength | High (15-25 kV/mm) | Very High (up to 30 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Excellent |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1300degC | Up to 1200degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.1-0.3%) | Very Low (near 0%) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Use | Standard heater insulators | High-performance heater insulators |
Introduction to Heater Insulation Materials
Porcelain and steatite are two common materials used for heater insulation, each offering unique thermal and electrical properties. Porcelain is renowned for its high dielectric strength and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for electrical insulation in heating elements. Steatite, a type of dense ceramic, provides excellent heat resistance and mechanical durability, ensuring reliable performance under high temperatures and mechanical stress.
What is Porcelain? Properties and Uses
Porcelain is a dense, non-porous ceramic material fired at high temperatures, known for its excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for heater components. Its smooth surface and durability ensure efficient heat distribution and long-lasting performance in electric heaters, especially in heating elements and insulators. Common uses include insulator housings, heating element supports, and protective covers in industrial and domestic heating applications.
What is Steatite? Properties and Uses
Steatite, also known as soapstone, is a dense, heat-resistant mineral primarily composed of talc that offers excellent thermal insulation and high dielectric strength, making it ideal for electrical heating elements. Its high thermal shock resistance and ability to withstand temperatures up to 1000degC allow it to be used extensively in electrical insulators, heating elements, and industrial applications where stable heat conduction is critical. Compared to porcelain, steatite provides superior mechanical strength and better resistance to cracking under thermal stress, enhancing the durability and efficiency of heaters.
Thermal Conductivity: Porcelain vs Steatite
Porcelain exhibits lower thermal conductivity, typically around 1.5 W/m*K, which results in slower heat transfer compared to steatite. Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, has a higher thermal conductivity of approximately 3 W/m*K, enabling more efficient heat dissipation and faster thermal response in heaters. This difference makes steatite preferable for applications requiring rapid heating and cooling cycles, while porcelain is suited for insulating components in electrical heaters.
Electrical Insulation Comparison
Porcelain offers superior electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to high voltage breakdown, making it ideal for high-temperature heating elements. Steatite, known for its good insulating capabilities, provides better mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance but generally exhibits lower dielectric strength compared to porcelain. When selecting materials for heater insulation, porcelain's enhanced electrical insulation performance ensures safer and more efficient operation in demanding electrical environments.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Porcelain heaters exhibit high durability and excellent mechanical strength due to their dense, vitrified ceramic structure, making them resistant to thermal shock and wear. Steatite heaters, composed mainly of talc, offer superior resistance to high temperatures and mechanical stress, providing long-lasting performance in industrial applications. Porcelain is preferred for environments demanding exceptional toughness, while steatite is favored for its thermal stability and resilience under heavy mechanical loads.
Temperature Resistance and Stability
Porcelain offers high temperature resistance, typically withstanding up to 1200degC, making it ideal for consistent thermal stability in heater elements. Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, provides excellent mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance but generally handles temperatures around 1000degC. Both materials ensure stability under heat, yet porcelain's superior temperature tolerance makes it preferable for high-temperature heating applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Porcelain and steatite heaters differ significantly in cost-effectiveness and availability, with porcelain models typically being more affordable due to widespread manufacturing and materials. Steatite heaters, though often pricier, offer superior durability and heat retention, making them cost-effective over the long term despite higher initial investment. Availability of porcelain heaters is broader in consumer markets, whereas steatite heaters are more specialized, sometimes requiring sourcing from niche suppliers.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Porcelain heaters excel in high-temperature applications due to their excellent electrical insulation and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for industrial heating elements. Steatite heaters offer superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance, suitable for environments with harsh conditions or where durability is critical. Selecting the right material depends on the specific operational demands, such as temperature range, exposure to moisture, and mechanical stress, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion: Which is Better for Heater Insulation?
Steatite offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher mechanical strength compared to porcelain, making it more durable for heater insulation in high-stress environments. Porcelain, while cost-effective and electrically insulating, is more brittle and prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. For optimal heater insulation performance, steatite is generally the better choice due to its enhanced durability and heat resistance.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Steatite for Heater
 azmater.com
azmater.com