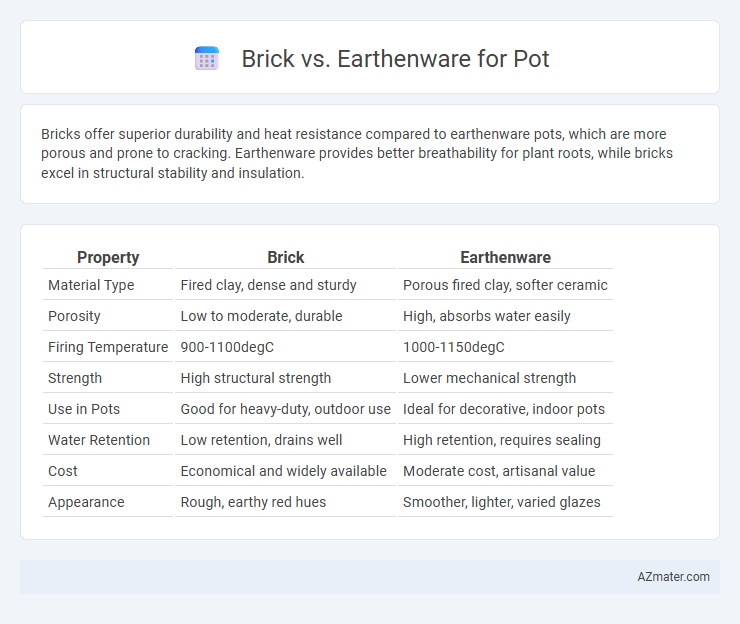
Bricks offer superior durability and heat resistance compared to earthenware pots, which are more porous and prone to cracking. Earthenware provides better breathability for plant roots, while bricks excel in structural stability and insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fired clay, dense and sturdy | Porous fired clay, softer ceramic |
| Porosity | Low to moderate, durable | High, absorbs water easily |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC | 1000-1150degC |
| Strength | High structural strength | Lower mechanical strength |
| Use in Pots | Good for heavy-duty, outdoor use | Ideal for decorative, indoor pots |
| Water Retention | Low retention, drains well | High retention, requires sealing |
| Cost | Economical and widely available | Moderate cost, artisanal value |
| Appearance | Rough, earthy red hues | Smoother, lighter, varied glazes |
Introduction to Pottery Materials
Brick and earthenware are fundamental pottery materials distinguished by their composition, firing temperature, and porosity. Brick, made from dense clay fired at high temperatures, offers strength and durability suitable for construction and heavy-duty applications. Earthenware, produced by firing porous clay at lower temperatures, is ideal for decorative pots and functional vessels that require a porous, breathable structure.
Overview of Brick Pots
Brick pots offer exceptional durability and heat retention, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor planting. Their porous structure allows for excellent aeration and moisture regulation, promoting healthy root development. Commonly used in traditional gardening and construction, brick pots provide a sturdy and long-lasting alternative to earthenware.
Overview of Earthenware Pots
Earthenware pots are crafted from natural clay and fired at lower temperatures, resulting in porous, breathable containers ideal for plants requiring good drainage and aeration. Unlike bricks, earthenware offers a lighter, more porous structure that helps regulate soil moisture but can be more fragile and prone to chipping. These pots are widely favored in gardening due to their ability to enhance root health by allowing excess water to evaporate naturally.
Key Differences Between Brick and Earthenware Pots
Brick pots offer superior durability and heat retention due to their dense, fired clay composition, making them ideal for outdoor planting and long-term use. Earthenware pots, characterized by their porous and unglazed surfaces, provide excellent breathability for plant roots but require careful handling due to their fragility. The primary difference lies in brick pots' robustness and thermal insulation versus earthenware's moisture regulation and aesthetic variety.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Brick pots exhibit superior durability due to their dense, fired clay composition, which resists cracking and weathering over time. Earthenware pots, while aesthetically appealing with their porous nature, tend to absorb moisture, making them prone to chipping and degradation under freezing or wet conditions. For long-term outdoor use, brick pots provide enhanced longevity and withstand harsh environmental factors better than traditional earthenware counterparts.
Porosity and Water Retention
Brick pots exhibit higher porosity compared to earthenware, allowing for better air circulation and moderate water retention beneficial for plant roots. Earthenware, with its denser composition, has lower porosity, leading to reduced water permeability and increased moisture retention over time. This difference in material structure directly impacts irrigation frequency and soil moisture management in potted plants.
Weight and Portability
Brick pots are considerably heavier due to their dense, fired clay composition, making them less portable and more suited for permanent installations. Earthenware pots, crafted from lighter, porous clay, offer enhanced portability ideal for seasonal use or rearranging indoor and outdoor spaces. The weight difference significantly impacts ease of handling, with earthenware favored for tasks requiring frequent movement.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Brick pots offer a rustic, industrial aesthetic with a sturdy, textured surface ideal for urban and contemporary designs, while earthenware pots provide a warm, natural look characterized by their smooth finish and earthy tones that complement traditional and bohemian styles. Brick materials allow for varied shapes and modular stacking designs, making them suitable for modern, geometric arrangements, whereas earthenware pots excel in hand-painted patterns and organic forms, enhancing artisanal and vintage decor. The choice between brick and earthenware pots hinges on the desired visual impact and compatibility with the overall interior or garden theme.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brick pots are typically made from fired clay, requiring high energy consumption and emitting significant CO2 during production, which impacts their environmental footprint. Earthenware pots are also clay-based but fired at lower temperatures, resulting in less energy use and reduced emissions, enhancing sustainability. Both materials are biodegradable and reusable, but earthenware's lower firing temperature makes it a more environmentally friendly choice.
Choosing the Right Pot for Your Needs
Choosing between brick and earthenware pots hinges on durability, breathability, and usage. Brick pots offer sturdy, weather-resistant qualities suitable for outdoor plants and heavy use, while earthenware pots provide superior breathability that helps regulate moisture, ideal for delicate indoor plants or succulents. Assessing factors like plant type, watering frequency, and aesthetic preference guides selecting the right pot to enhance plant health and growth.
Infographic: Brick vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com