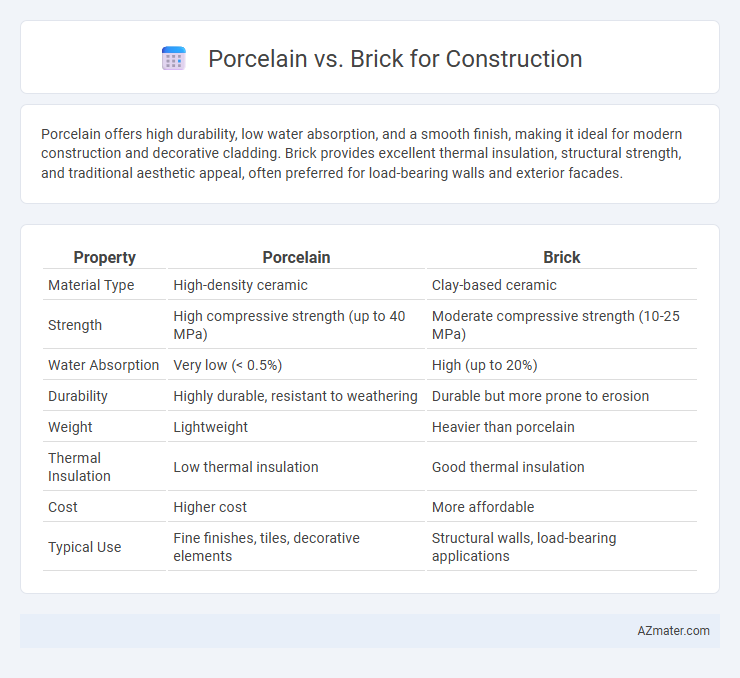
Porcelain offers high durability, low water absorption, and a smooth finish, making it ideal for modern construction and decorative cladding. Brick provides excellent thermal insulation, structural strength, and traditional aesthetic appeal, often preferred for load-bearing walls and exterior facades.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-density ceramic | Clay-based ceramic |
| Strength | High compressive strength (up to 40 MPa) | Moderate compressive strength (10-25 MPa) |
| Water Absorption | Very low (< 0.5%) | High (up to 20%) |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to weathering | Durable but more prone to erosion |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than porcelain |
| Thermal Insulation | Low thermal insulation | Good thermal insulation |
| Cost | Higher cost | More affordable |
| Typical Use | Fine finishes, tiles, decorative elements | Structural walls, load-bearing applications |
Introduction to Porcelain and Brick in Construction
Porcelain and brick are widely used materials in construction, valued for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Porcelain is a ceramic product made by firing kaolin at high temperatures, resulting in a dense, waterproof, and low-maintenance surface ideal for flooring and wall cladding. Brick, typically made from clay or shale, offers excellent thermal insulation, structural strength, and a timeless appearance, making it a staple for both load-bearing walls and decorative facades.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Porcelain is made from a refined clay mixture combined with kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, fired at extremely high temperatures around 1200 to 1400degC, resulting in a dense, non-porous, and durable material ideal for precise architectural finishes. Brick consists primarily of natural clay or shale, shaped and then fired at lower temperatures ranging from 900 to 1100degC, producing a porous and robust material commonly used for load-bearing walls and exterior facades. The higher firing temperature and fine particle composition give porcelain superior strength, water resistance, and smoothness compared to the more textured, breathable, and traditional aesthetic of brick.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Porcelain offers high resistance to moisture, stains, and wear, making it suitable for areas with heavy use and exposure to harsh conditions, while bricks provide exceptional strength and thermal insulation due to their dense composition. Both materials demonstrate excellent durability, but brick structures often boast longer lifespans exceeding 100 years with proper maintenance, whereas porcelain's longevity depends on installation quality and environmental factors. Choosing between porcelain and brick hinges on specific project requirements, balancing porcelain's resistance to surface damage and brick's robust structural integrity over time.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Porcelain tiles have lower thermal conductivity, enhancing insulation by maintaining indoor temperatures and reducing heating and cooling costs in construction. Brick, with its higher thermal mass, absorbs and slowly releases heat, providing natural temperature regulation and energy savings in varying climates. Choosing between porcelain and brick depends on specific insulation needs, with porcelain offering superior resistance to thermal transfer and brick excelling in thermal mass benefits for energy efficiency.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design Options
Porcelain offers superior aesthetic versatility with a wide range of colors, patterns, and finishes that mimic natural stone, wood, or concrete, allowing for seamless integration into modern and contemporary designs. Brick, known for its classic and timeless appeal, provides a rich texture and warm color palette but is generally limited to traditional red, brown, and earth tones. Porcelain's adaptability to various shapes and sizes enables intricate design patterns and creative layouts that brick cannot easily replicate.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Porcelain tiles possess high compressive strength but are primarily designed for surface finishes, lacking the load-bearing capacity required for structural elements in construction. Bricks, especially clay or concrete variants, exhibit superior structural strength and durability due to their denser composition and ability to withstand significant compressive loads. For load-bearing walls and foundational structures, bricks provide reliable support, whereas porcelain is unsuitable for these applications despite its hardness and resistance to wear.
Weather Resistance and Environmental Adaptability
Porcelain offers superior weather resistance due to its low porosity, making it highly resistant to frost, moisture, and UV radiation, which ensures long-term durability in harsh climates. Brick, while durable, tends to absorb more water, potentially leading to frost damage and requiring more maintenance in extreme weather conditions. Porcelain's environmental adaptability allows it to perform well in both humid and arid environments without compromising structural integrity, whereas brick may suffer from efflorescence and erosion when exposed to persistent moisture fluctuations.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Porcelain tiles demand minimal maintenance due to their non-porous surface, resisting stains, moisture, and scratches, which extends their lifespan up to 50 years or more when properly installed. Brick, while durable with a lifespan exceeding 100 years, requires regular upkeep such as repointing mortar joints and occasional sealing to prevent water infiltration and spalling. Choosing porcelain reduces routine maintenance efforts, whereas brick offers longevity with consistent care to preserve structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Porcelain vs Brick
Porcelain tiles generally offer a higher upfront cost compared to traditional brick, with prices varying between $5 to $15 per square foot, while bricks typically range from $3 to $8 per square foot. Installation costs for porcelain can be elevated due to the need for skilled labor and specialized tools, whereas brick installation is often more labor-intensive but benefits from widespread availability of experienced masons. Over time, porcelain's durability and low maintenance requirements can result in lower overall expenses, making it a cost-effective option despite higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Construction Project
Porcelain tiles offer exceptional durability, low maintenance, and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for areas requiring a sleek, modern finish, while brick provides superior thermal insulation, timeless aesthetics, and structural strength suitable for load-bearing walls. When choosing between porcelain and brick, consider the specific requirements of your construction project, such as climate, load-bearing needs, design preferences, and budget constraints. Evaluating factors like installation complexity, long-term maintenance costs, and environmental impact will help determine the most efficient and sustainable material for your build.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Brick for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com