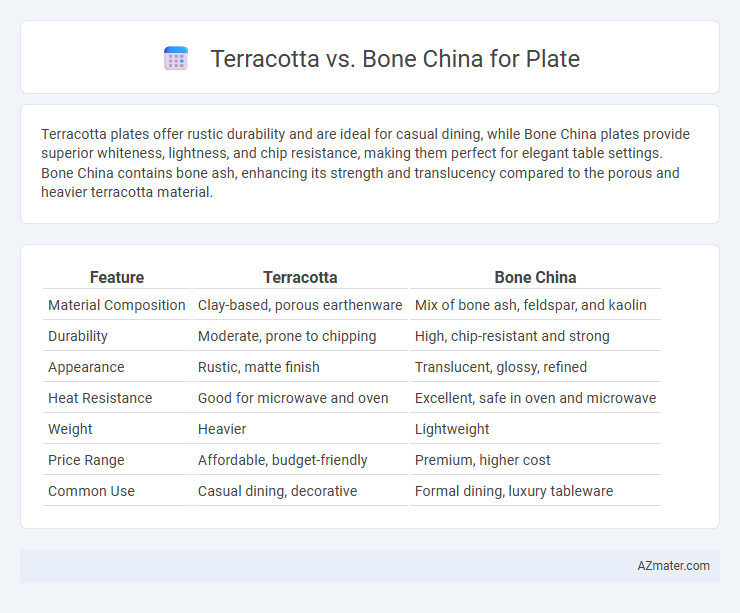
Terracotta plates offer rustic durability and are ideal for casual dining, while Bone China plates provide superior whiteness, lightness, and chip resistance, making them perfect for elegant table settings. Bone China contains bone ash, enhancing its strength and translucency compared to the porous and heavier terracotta material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Terracotta | Bone China |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-based, porous earthenware | Mix of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | High, chip-resistant and strong |
| Appearance | Rustic, matte finish | Translucent, glossy, refined |
| Heat Resistance | Good for microwave and oven | Excellent, safe in oven and microwave |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Price Range | Affordable, budget-friendly | Premium, higher cost |
| Common Use | Casual dining, decorative | Formal dining, luxury tableware |
Introduction: Terracotta vs Bone China Plates
Terracotta plates, crafted from natural clay, offer rustic charm with their porous texture and earthy tones, making them ideal for casual dining and outdoor settings. Bone China plates, composed of fine bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, provide superior strength, translucency, and a delicate, polished finish suited for formal occasions. Differences in durability, aesthetic appeal, and fragility highlight the distinct uses of Terracotta versus Bone China in tableware.
Material Composition Overview
Terracotta plates are made from coarse, porous clay that is fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a rustic, earthy texture ideal for casual dining. Bone china plates consist of refined clay mixed with bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, fired at high temperatures to achieve a delicate yet durable, translucent finish favored for formal settings. The high bone ash content in bone china enhances its strength and whiteness compared to the porous and less durable terracotta material.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Terracotta plates are crafted from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and earthy texture, while bone china involves blending bone ash, feldspathic material, and kaolin fired at higher temperatures to achieve a strong, translucent finish. The terracotta manufacturing process is simpler, relying on hand molding and fewer refining steps, whereas bone china requires precision mixing, multiple firing stages, and glazing to enhance durability and whiteness. These manufacturing differences directly impact the strength, finish, and aesthetic qualities of each plate type.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Terracotta plates exhibit moderate durability but are more porous and prone to chipping or cracking under heavy impact compared to bone china. Bone china is renowned for its exceptional strength and resilience due to its high calcium phosphate content, making it less likely to break or chip during everyday use. The vitrified finish on bone china enhances its toughness, providing superior resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress relative to terracotta plates.
Aesthetic and Design Variation
Terracotta plates exhibit a rustic, earthy aesthetic with natural hues and handcrafted textures that emphasize artisanal appeal and traditional craftsmanship. Bone china offers a refined, translucent finish with delicate patterns and intricate designs, ideal for elegant table settings and sophisticated decor. The design variation in bone china is broader, ranging from classic floral motifs to modern minimalist styles, whereas terracotta remains rooted in organic and folk-inspired aesthetics.
Heat Retention and Performance
Terracotta plates excel in heat retention due to their thick, porous structure, keeping food warm longer but requiring careful handling to avoid cracks from thermal shock. Bone china offers superior performance with its lightweight, non-porous composition that resists chipping and rapidly recovers its temperature, making it ideal for both casual and formal dining. While terracotta enhances heat maintenance during serving, bone china combines durability and elegant presentation with moderate heat retention.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Terracotta plates are porous and may absorb liquids and odors, posing potential hygiene concerns unless properly glazed; their natural composition is free from harmful chemicals, making them food-safe when sealed correctly. Bone china offers superior non-porous surfaces, reducing bacterial retention and making it highly safe and compatible with all types of food, including acidic dishes. Both materials can be microwave and dishwasher safe, but bone china generally provides enhanced durability and safer food contact due to its vitrified, non-porous nature.
Maintenance and Care
Terracotta plates require gentle hand washing and should be thoroughly dried to prevent cracking or mold growth due to their porous nature. Bone china demands careful handling to avoid chipping and is dishwasher-safe but best washed with mild detergents to maintain its translucency and fine glaze. Both materials benefit from avoiding sudden temperature changes to preserve their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Terracotta plates are crafted from natural clay with minimal processing, resulting in a lower carbon footprint and better biodegradability compared to bone china. Bone china requires significant energy for production and relies on animal bone ash, raising ethical and sustainability concerns. Choosing terracotta supports eco-friendly dining by reducing resource consumption and promoting biodegradable waste.
Cost and Value Analysis
Terracotta plates offer an affordable option with a rustic aesthetic, costing significantly less than bone china, which is priced higher due to its refined materials and manufacturing process. Bone china provides superior durability, chip resistance, and a translucent, elegant appearance that increases its value over time despite the initial expense. For budget-conscious buyers prioritizing cost-effectiveness, terracotta is ideal, while collectors or formal settings benefit from investing in the long-lasting quality and prestige of bone china.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Bone China for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com