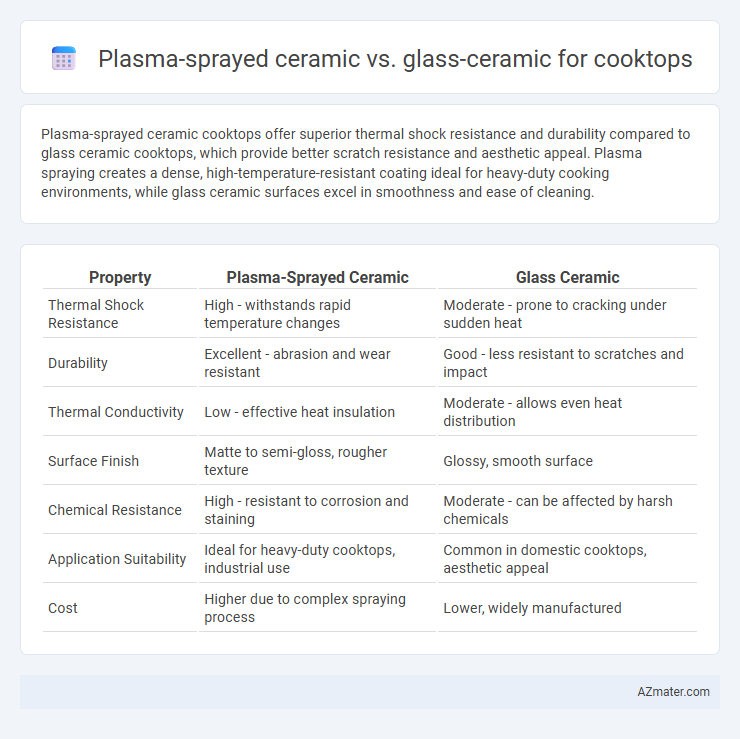
Plasma-sprayed ceramic cooktops offer superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to glass ceramic cooktops, which provide better scratch resistance and aesthetic appeal. Plasma spraying creates a dense, high-temperature-resistant coating ideal for heavy-duty cooking environments, while glass ceramic surfaces excel in smoothness and ease of cleaning.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High - withstands rapid temperature changes | Moderate - prone to cracking under sudden heat |
| Durability | Excellent - abrasion and wear resistant | Good - less resistant to scratches and impact |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low - effective heat insulation | Moderate - allows even heat distribution |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-gloss, rougher texture | Glossy, smooth surface |
| Chemical Resistance | High - resistant to corrosion and staining | Moderate - can be affected by harsh chemicals |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for heavy-duty cooktops, industrial use | Common in domestic cooktops, aesthetic appeal |
| Cost | Higher due to complex spraying process | Lower, widely manufactured |
Introduction to Cooktop Surface Materials
Plasma-sprayed ceramic offers a highly durable and heat-resistant surface for cooktops, providing excellent thermal insulation and scratch resistance compared to traditional glass ceramic materials. Glass ceramic cooktops are favored for their smooth, sleek appearance and ease of cleaning, with strong resistance to thermal shock but less durability against mechanical impacts. Choosing between plasma-sprayed ceramic and glass ceramic surfaces hinges on prioritizing either long-term durability and heat efficiency or aesthetic appeal and surface smoothness in kitchen technology.
What is Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic?
Plasma-sprayed ceramic is a coating process where ceramic materials are melted using a high-temperature plasma jet and then rapidly sprayed onto a surface, creating a durable, heat-resistant layer ideal for cooktops. This technique offers superior thermal insulation, abrasion resistance, and enhanced durability compared to glass ceramics. Plasma-sprayed ceramic surfaces provide improved heat retention and resistance to thermal shock, making them a high-performance choice for advanced cooking appliances.
Understanding Glass Ceramic Cooktops
Glass ceramic cooktops provide excellent thermal shock resistance and smooth surface durability, making them highly suitable for modern kitchen appliances. Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings often enhance heat distribution but can lack the seamless, easy-to-clean finish that glass ceramics offer. Understanding glass ceramic cooktops means recognizing their superior ability to withstand rapid temperature changes while maintaining a sleek, scratch-resistant cooking surface.
Thermal Performance: Heat Distribution and Retention
Plasma-sprayed ceramic cooktops exhibit superior thermal performance with rapid heat distribution and high heat retention due to their dense microstructure and enhanced bonding layers. Glass ceramic cooktops provide even heat spreading but have slower heat-up times and lower heat retention, resulting in less efficient energy use during cooking. The plasma-sprayed ceramic's ability to maintain consistent surface temperatures enhances cooking precision and reduces energy consumption compared to traditional glass ceramic surfaces.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Plasma-sprayed ceramic cooktops exhibit superior durability and scratch resistance compared to glass ceramic surfaces due to their dense ceramic coating applied at high temperatures, which enhances hardness and wear resistance. Glass ceramic cooktops, while offering smooth aesthetics and thermal shock resistance, are more prone to visible scratches and surface damage under heavy kitchen use. The advanced plasma-sprayed ceramic layer significantly extends the lifespan and maintains the pristine appearance of cooktops in demanding cooking environments.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock due to their dense microstructure and strong adhesion to the substrate, making them ideal for high-temperature cooktop applications. Glass ceramics, while offering excellent thermal stability and resistance to cracking under rapid temperature changes, generally have lower tolerance to thermal shock compared to plasma-sprayed ceramics. The enhanced durability of plasma-sprayed ceramics reduces the risk of surface damage and deformation during abrupt temperature fluctuations in cooking environments.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Plasma-sprayed ceramic cooktops offer enhanced durability and resistance to scratches but require careful cleaning with non-abrasive materials to avoid damage to the coating. Glass ceramic cooktops are easier to clean due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces but can be more prone to scratches and stains if abrasive cleaners or sharp utensils are used. Both materials benefit from regular wiping with specialized cooktop cleaners to maintain their appearance and performance over time.
Aesthetic Differences Between the Two Materials
Plasma-sprayed ceramic cooktops exhibit a distinctive textured surface with a matte finish, providing a rugged and industrial aesthetic that resists visible scratches and wear. In contrast, glass ceramic cooktops feature a smooth, glossy surface with a sleek, modern appearance that enhances kitchen elegance and allows for vibrant color options. The reflective quality of glass ceramic surfaces contributes to a brighter countertop area, while plasma-sprayed ceramics offer a more muted, understated look ideal for rustic or industrial kitchen designs.
Cost Analysis: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic vs Glass Ceramic
Plasma-sprayed ceramic cooktops generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing techniques and specialized equipment compared to glass ceramic cooktops, which benefit from mass production efficiencies. Maintenance expenses for plasma-sprayed ceramics may be lower over time due to superior scratch resistance and thermal stability, reducing replacement frequency. Glass ceramic cooktops often require more frequent repairs or replacements, impacting long-term cost-effectiveness despite their lower upfront price.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cooktop Material
Plasma-sprayed ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-heat cooking environments, while glass ceramic provides excellent heat distribution and aesthetic appeal with easier cleaning. For users prioritizing longevity and heat tolerance, plasma-sprayed ceramic is the best choice, whereas those valuing smooth surfaces and uniform heating may prefer glass ceramic. Selecting the right cooktop material depends on balancing factors like thermal performance, maintenance, and overall cooking needs.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com