Tiles offer high durability and water resistance, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor pot surfaces. Earthenware pots provide natural breathability and a rustic aesthetic but are more porous and less durable than tiled alternatives.
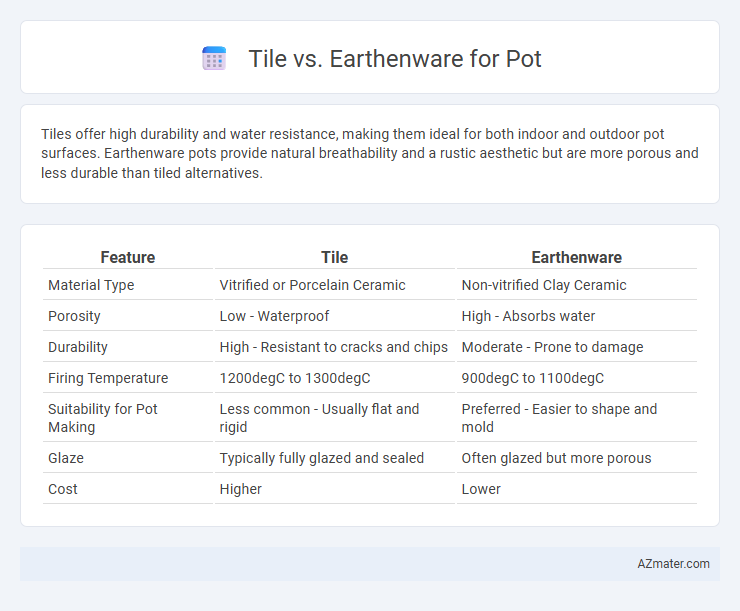
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tile | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vitrified or Porcelain Ceramic | Non-vitrified Clay Ceramic |
| Porosity | Low - Waterproof | High - Absorbs water |
| Durability | High - Resistant to cracks and chips | Moderate - Prone to damage |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC to 1300degC | 900degC to 1100degC |
| Suitability for Pot Making | Less common - Usually flat and rigid | Preferred - Easier to shape and mold |
| Glaze | Typically fully glazed and sealed | Often glazed but more porous |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction: Tile vs Earthenware Pots
Tile pots offer superior durability and moisture resistance compared to earthenware pots, making them ideal for outdoor gardening and long-term plant health. Earthenware pots, made from natural clay, provide excellent breathability, promoting better aeration for roots but requiring more careful maintenance to prevent cracking and water loss. Choosing between tile and earthenware depends on factors such as environmental exposure, plant type, and desired aesthetic, with tile pots favored for longevity and earthenware for traditional, natural appeal.
Material Composition and Differences
Tile pots are typically made from glazed ceramic or porcelain, offering a dense, non-porous surface that provides superior water resistance and durability. Earthenware pots consist of natural clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous material that allows for better breathability and moisture regulation but requires sealing to prevent water absorption. The key differences lie in the firing temperature and porosity, with tile pots offering enhanced strength and chemical resistance, while earthenware delivers a rustic, breathable quality ideal for plant health.
Durability and Longevity
Tiles made from ceramic or porcelain exhibit higher durability and longevity compared to earthenware pots due to their dense, vitrified structure that resists chipping, cracking, and moisture absorption. Earthenware pots, being porous and fired at lower temperatures, are more susceptible to damage from freezing temperatures and prolonged water exposure, leading to shorter lifespan. Investing in tile-based pots ensures enhanced resilience against environmental wear and maintains aesthetic appeal over extended use.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Tile pots typically offer superior heat retention due to their dense, glazed surfaces, which prevent rapid temperature loss during cooking. Earthenware pots, made from porous clay, provide excellent heat distribution by slowly and evenly transferring heat throughout the pot, ideal for simmering and slow-cooking recipes. While tile pots maintain consistent heat for longer periods, earthenware allows for gentle, uniform warmth that prevents hotspots and enhances flavor development.
Weight and Handling
Earthenware pots are generally heavier than tile pots, making them more stable but less portable for frequent handling. Tile pots are lighter due to their thinner material, facilitating easier movement and rearrangement in gardening or indoor settings. The weight difference impacts usability, with earthenware providing durability and insulation, while tile offers convenience and flexibility in handling.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Tiles offer a sleek, modern aesthetic with a wide range of colors, patterns, and finishes, making them ideal for creating bold and contemporary pot designs. Earthenware provides a more rustic, handcrafted look with natural textures and warm, earthy tones that add charm and organic appeal to pots. Both materials accommodate diverse design preferences, but tiles excel in precision and vibrant customization, while earthenware shines in unique, artisanal character.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Tile pots require regular cleaning to prevent grout discoloration and mold buildup, typically needing mild detergent and a soft brush to maintain their polished surface. Earthenware pots demand gentle handling due to their porous nature, often cleaned with water alone to avoid damaging the clay and preserving breathability. Both materials benefit from thorough drying after cleaning to prevent moisture retention and potential deterioration.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Tile pots, often made from glazed ceramic or porcelain, provide excellent durability and water resistance, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments as they can withstand moisture and varying temperatures. Earthenware pots, crafted from porous clay, are ideal for indoor use due to their breathability, which aids plant root health, but they require careful protection from outdoor elements to prevent cracking and weather damage. For outdoor applications, glazed tile pots offer superior longevity and minimal maintenance, whereas earthenware pots need strategic placement in sheltered areas to ensure durability.
Cost Comparison
Tile pots typically cost more than earthenware due to the manufacturing process and materials involved, with prices ranging from $20 to $100 depending on design and size. Earthenware pots are generally more affordable, often priced between $10 and $40, making them a budget-friendly option for gardeners. The durability and aesthetic value of tile can justify the higher expense, while earthenware offers cost-efficiency with decent performance for everyday planting needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pot for Your Needs
Tile pots offer durability and a sleek finish suitable for outdoor landscaping, while earthenware pots provide porous material that enhances soil aeration and moisture regulation, ideal for indoor plants. Consider environmental factors and plant species when selecting a pot, as tile withstands harsh weather better and earthenware supports healthy root development. Prioritize your specific gardening requirements to ensure optimal plant growth and longevity.
Infographic: Tile vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com