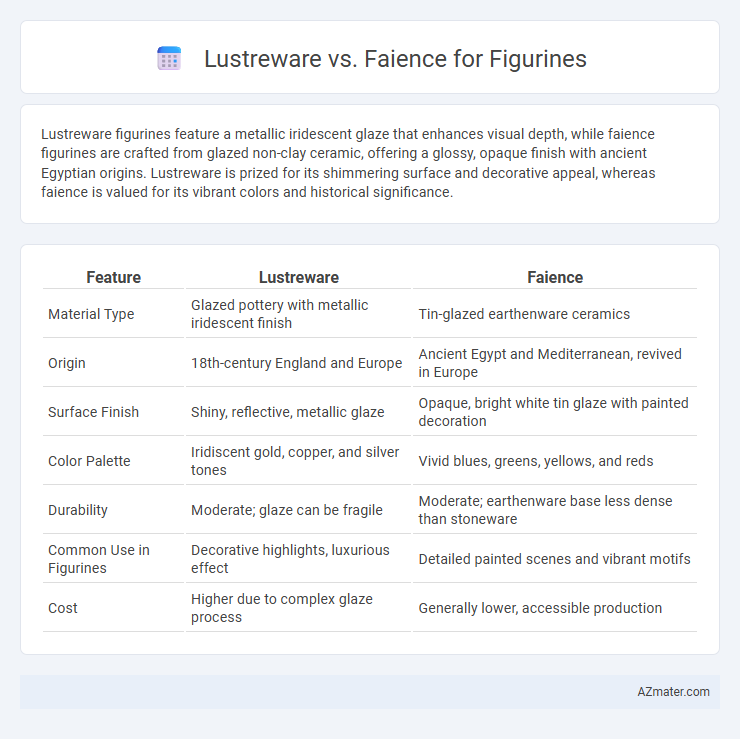
Lustreware figurines feature a metallic iridescent glaze that enhances visual depth, while faience figurines are crafted from glazed non-clay ceramic, offering a glossy, opaque finish with ancient Egyptian origins. Lustreware is prized for its shimmering surface and decorative appeal, whereas faience is valued for its vibrant colors and historical significance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lustreware | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed pottery with metallic iridescent finish | Tin-glazed earthenware ceramics |
| Origin | 18th-century England and Europe | Ancient Egypt and Mediterranean, revived in Europe |
| Surface Finish | Shiny, reflective, metallic glaze | Opaque, bright white tin glaze with painted decoration |
| Color Palette | Iridiscent gold, copper, and silver tones | Vivid blues, greens, yellows, and reds |
| Durability | Moderate; glaze can be fragile | Moderate; earthenware base less dense than stoneware |
| Common Use in Figurines | Decorative highlights, luxurious effect | Detailed painted scenes and vibrant motifs |
| Cost | Higher due to complex glaze process | Generally lower, accessible production |
Introduction to Lustreware and Faience Figurines
Lustreware figurines are characterized by their iridescent, metallic glaze achieved through a complex firing process involving metallic oxides, creating a shimmering surface that enhances decorative appeal. Faience figurines, traditionally made from tin-glazed earthenware, feature a bright, opaque glaze with vibrant colors, emphasizing detailed painted designs and a glossy finish. Both Lustreware and Faience hold significant historical and artistic value in ceramic art, with Lustreware prized for its unique reflective quality and Faience for its vivid color palette and intricate patterns.
Historical Origins and Development
Lustreware and faience figurines both originated from distinct historical and cultural contexts, with lustreware emerging in the Middle East during the 9th century as a technique involving metallic glaze to produce iridescent effects, while faience dates back to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, characterized by a tin-glazing method that creates a bright, opaque surface. Lustreware's development evolved through Islamic pottery traditions and later influenced European ceramics in the 19th century, whereas faience maintained its prominence mainly in ancient and early modern decorative arts, especially within Mediterranean cultures. The contrasting glazing techniques and regional influences highlight the unique aesthetic and material qualities that define lustreware and faience figurine production over centuries.
Key Characteristics of Lustreware Figurines
Lustreware figurines are characterized by their distinctive iridescent metallic glaze, created through the application of metal oxides in a reduction kiln atmosphere, resulting in a shimmering, reflective surface that enhances intricate details. These figurines often exhibit vibrant hues ranging from gold to copper and rose, contributing to their unique visual appeal compared to the matte or glossy finishes of faience. The delicate, thin layers of lustre glaze require careful handling, making lustreware figurines prized collectibles known for their artistic craftsmanship and luminous finish.
Distinctive Features of Faience Figurines
Faience figurines are characterized by their bright, glossy finish achieved through a tin-glazed earthenware technique that produces vibrant blues, greens, and whites, distinguishing them from the metallic sheen of lustreware. These figurines often feature intricate hand-painted details and a smooth, opaque surface that emphasizes fine artistry and cultural motifs typical of ancient Egyptian and Mediterranean craftsmanship. The porous body beneath the glaze allows faience to have a distinct weight and texture, setting it apart from the denser, reflective qualities of lustreware ceramics.
Material Composition and Production Techniques
Lustreware figurines are created using a ceramic base coated with metallic oxides that produce an iridescent glaze through a firing process in a reduction atmosphere, enhancing their reflective and shimmering appearance. In contrast, faience figurines are made from fine tin-glazed earthenware, characterized by a white opaque glaze adhered to a clay body, often decorated with vivid painted designs under the glaze. Lustreware involves complex chemical reactions during firing to achieve its metallic sheen, whereas faience relies on the use of tin oxide in its glaze to achieve an opaque, bright surface suitable for detailed polychrome decoration.
Color Palette and Surface Decoration
Lustreware figurines exhibit a distinctive metallic sheen achieved through a special glaze, often showcasing iridescent tones like gold, copper, and ruby that create a shimmering surface decoration. Faience figurines, in contrast, are known for their bright, opaque glazes in a vibrant color palette including blues, greens, yellows, and whites, emphasizing flat, glossy finishes without metallic effects. The surface decoration of Lustreware prioritizes reflective brilliance and depth, whereas Faience emphasizes bold, solid colors with intricate painted or molded details.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Lustreware figurines, characterized by their metallic glaze, offer moderate durability but require careful maintenance to prevent tarnishing and surface wear. Faience figurines, made from glazed earthenware, tend to be more porous and fragile, demanding gentle handling and avoidance of harsh cleaning agents to preserve their finish. Selecting between Lustreware and Faience involves balancing the metallic sheen and relative resilience of Lustreware against the delicate, matte-glazed aesthetic and sensitivity of Faience to environmental factors.
Artistic Styles and Iconic Motifs
Lustreware figurines exhibit a distinctive iridescent glaze that enhances artistic styles with shimmering surface effects, often depicting intricate floral patterns and mythological scenes emblematic of Art Nouveau and Victorian aesthetics. Faience figurines are known for their matte glaze and vibrant, opaque colors, featuring iconic motifs such as pastoral scenes, classical figures, and folkloric themes rooted in European and Mediterranean ceramic traditions. The contrasting finishes between lustreware's glossy, reflective sheen and faience's earthy, matte texture highlight different artistic intentions and cultural symbolism in figurine design.
Collectibility and Market Value Comparison
Lustreware figurines, characterized by their iridescent glaze developed in the late 19th century, typically hold higher collectibility due to their unique finish and rarity compared to faience, a tin-glazed pottery known for its opaque, colorful surface and historical prominence in European ceramics. Market value of lustreware figurines often exceeds that of faience because collectors prize the metallic sheen and the complex glazing process, which adds to their aesthetic appeal and exclusive nature. While faience figurines attract enthusiasts interested in traditional craftsmanship and historical motifs, lustreware's limited production periods and visually striking appearance command premium prices at auctions and specialty markets.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Lustreware and Faience for Figurine Collectors
Choosing between lustreware and faience for figurine collectors hinges on personal preference for finish and historical value, as lustreware offers iridescent glaze and vibrant colors popular in Art Deco designs, while faience showcases tin-glazed earthenware with origins in ancient Egyptian and Mediterranean pottery. Collectors valuing intricate glaze techniques and a shimmering effect may lean toward lustreware, whereas those who appreciate classical, matte finishes and cultural heritage often prefer faience. Both materials hold distinct aesthetic and collectible appeal, making the decision dependent on desired visual impact and period representation.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Faience for Figurine
 azmater.com
azmater.com