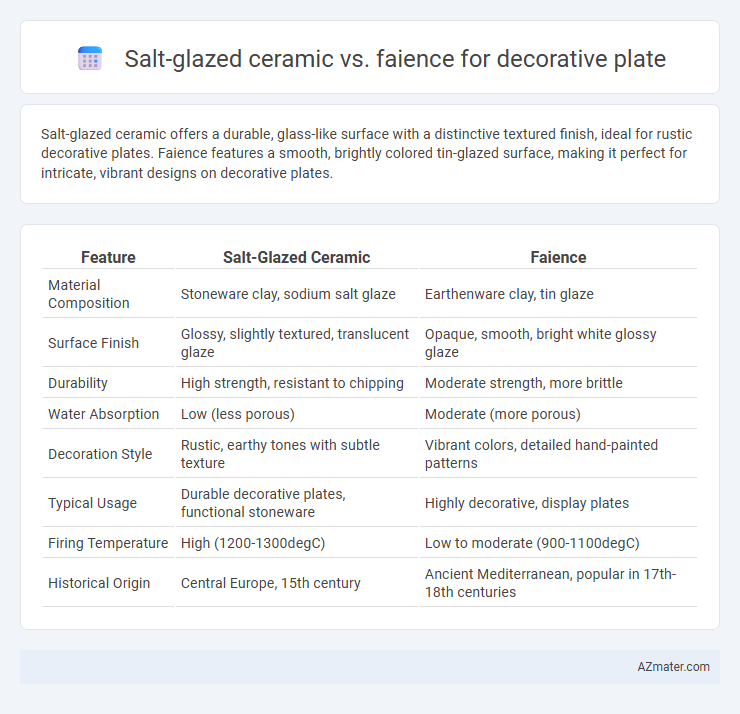
Salt-glazed ceramic offers a durable, glass-like surface with a distinctive textured finish, ideal for rustic decorative plates. Faience features a smooth, brightly colored tin-glazed surface, making it perfect for intricate, vibrant designs on decorative plates.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Stoneware clay, sodium salt glaze | Earthenware clay, tin glaze |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, slightly textured, translucent glaze | Opaque, smooth, bright white glossy glaze |
| Durability | High strength, resistant to chipping | Moderate strength, more brittle |
| Water Absorption | Low (less porous) | Moderate (more porous) |
| Decoration Style | Rustic, earthy tones with subtle texture | Vibrant colors, detailed hand-painted patterns |
| Typical Usage | Durable decorative plates, functional stoneware | Highly decorative, display plates |
| Firing Temperature | High (1200-1300degC) | Low to moderate (900-1100degC) |
| Historical Origin | Central Europe, 15th century | Ancient Mediterranean, popular in 17th-18th centuries |
Introduction to Decorative Ceramic Plates
Decorative ceramic plates showcase diverse glazing techniques such as salt-glazed ceramic and faience, each offering unique aesthetic and textural qualities. Salt-glazed ceramics possess a distinctive glossy, orange-peel surface achieved by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, enhancing durability and rustic charm. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, features a smooth, opaque white surface ideal for intricate painted designs, providing vivid color contrasts and refined elegance on decorative plates.
What is Salt-Glazed Ceramic?
Salt-glazed ceramic is a type of pottery finished by introducing salt into a hot kiln, creating a distinctive glossy, textured surface with a slightly orange-peel effect. This technique enhances durability and offers a unique, rustic aesthetic ideal for decorative plates, contrasting with the smooth, brightly painted surfaces typical of faience. Unlike faience, which is tin-glazed and often features intricate painted designs, salt-glazed ceramics emphasize natural colors and organic textures.
Understanding Faience: An Overview
Faience ceramics are characterized by a tin-glazed, opaque white surface that provides a brilliant canvas for vibrant painted designs, making them highly prized in decorative plates. This glaze technique originates from ancient Egypt and the Middle East, involving a quartz-based body coated with an alkaline glaze enriched with tin oxide to achieve its distinctive brightness and smooth texture. Compared to salt-glazed ceramics, which feature a rougher, glossy surface created through high-temperature salt vapor treatment, faience stands out for its delicate, colorful artistry and historical significance in decorative arts.
Key Differences: Salt-Glazed Ceramic vs Faience
Salt-glazed ceramics are characterized by a glossy, textured surface created by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, producing a durable and slightly translucent glaze primarily used in stoneware. Faience, on the other hand, is a tin-glazed earthenware known for its opaque, bright white glaze that serves as a smooth canvas for colorful, intricate painted designs, commonly associated with decorative plates. The key differences lie in their composition and finish: salt-glazed pieces emphasize durability and a rustic texture, while faience highlights decorative artistry with vivid, opaque surfaces.
Historical Significance and Origins
Salt-glazed ceramics originated in Germany during the 15th century and are characterized by a glossy, textured surface achieved through the vaporization of salt in the kiln, which historically signified durability and utilitarian artistry. Faience, with roots tracing back to the Italian Renaissance town of Faenza, is known for its tin-glazed, bright, and colorful decorative plates that reflect European artistic influences and the spread of ceramic technology across the continent. Both techniques reveal distinct historical narratives: salt-glazing emphasizes rustic craftsmanship and functional ware, while faience represents a shift toward elaborate decoration and cultural expression in ceramics.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finishes
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit a distinctive glossy, textured surface with subtle variations in color due to the vaporized salt reacting with the clay body, creating an earthy, rustic aesthetic ideal for traditional and artisanal decorative plates. Faience, characterized by its smooth, opaque tin-glazed finish, offers vibrant and crisp painted designs with a bright, reflective surface that enhances intricate patterns and detailed artwork, making it perfect for decorative plates featuring colorful motifs. The choice between salt-glazed ceramic and faience largely depends on desired visual impact--rustic natural appeal versus vivid, polished elegance.
Durability and Functional Benefits
Salt-glazed ceramics offer superior durability due to their vitrified, glass-like surface created through the salt-firing process, making them highly resistant to moisture and wear. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, provides vibrant, colorful finishes but is more porous and prone to chipping over time, reducing functional longevity. For decorative plates intended for frequent handling or display in humid environments, salt-glazed ceramics deliver enhanced strength and moisture resistance compared to faience.
Design Applications in Modern Decor
Salt-glazed ceramic offers a textured, rustic finish ideal for contemporary rustic or industrial-themed decor, enhancing natural and organic design elements. Faience provides a smooth, glossy surface with vibrant, intricate patterns perfect for adding a touch of classic elegance or Mediterranean flair in modern interiors. Both materials serve distinct design applications, with salt-glazed ceramics emphasizing tactile depth and faience highlighting colorful, detailed artistry for decorative plates.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Salt-glazed ceramic decorative plates feature a durable, glass-like surface that resists stains and scratches, requiring only gentle wiping with a damp cloth for maintenance. Faience plates, made from tin-glazed earthenware, have a more porous and delicate finish that necessitates careful handling and avoidance of abrasive cleaners to prevent surface damage. Proper care extends the longevity of both materials, but salt-glazed ceramics offer easier upkeep compared to the more sensitive faience.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Decorative Plate
Salt-glazed ceramic offers a durable, glossy finish created through a high-temperature firing process that fuses salt vapors with the clay surface, providing excellent resistance to scratches and moisture. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, is prized for its vibrant colors and intricate designs but is typically more fragile and less water-resistant than salt-glazed ceramics. Choosing the right material depends on whether durability and moisture resistance or vivid artistic expression and traditional aesthetics are your priority for the decorative plate.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Faience for Decorative Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com