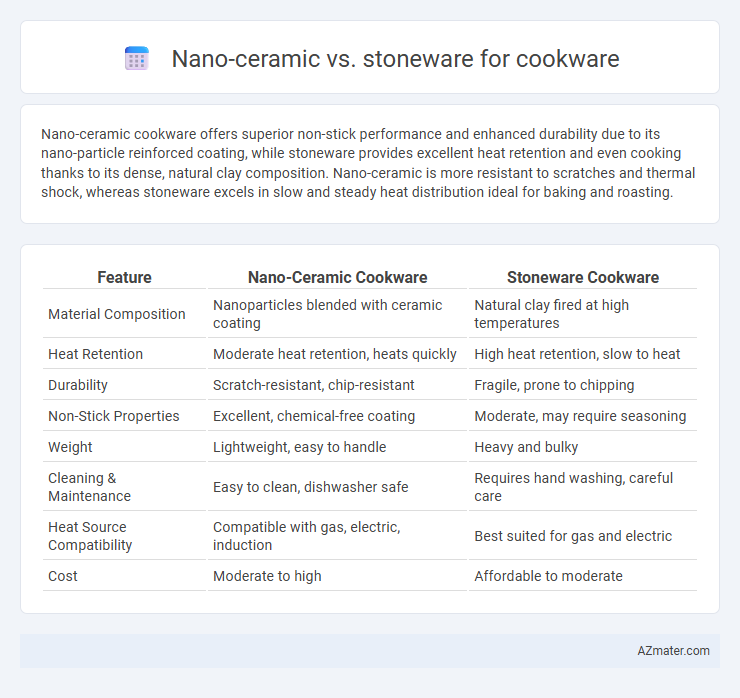
Nano-ceramic cookware offers superior non-stick performance and enhanced durability due to its nano-particle reinforced coating, while stoneware provides excellent heat retention and even cooking thanks to its dense, natural clay composition. Nano-ceramic is more resistant to scratches and thermal shock, whereas stoneware excels in slow and steady heat distribution ideal for baking and roasting.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nano-Ceramic Cookware | Stoneware Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Nanoparticles blended with ceramic coating | Natural clay fired at high temperatures |
| Heat Retention | Moderate heat retention, heats quickly | High heat retention, slow to heat |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant, chip-resistant | Fragile, prone to chipping |
| Non-Stick Properties | Excellent, chemical-free coating | Moderate, may require seasoning |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavy and bulky |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires hand washing, careful care |
| Heat Source Compatibility | Compatible with gas, electric, induction | Best suited for gas and electric |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable to moderate |
Introduction to Nano-Ceramic and Stoneware Cookware
Nano-ceramic cookware utilizes advanced nanotechnology to create a non-stick, durable surface that resists scratching and promotes even heat distribution, making it highly efficient for cooking. Stoneware cookware is crafted from natural clay, baked at high temperatures to develop excellent heat retention and even cooking, ideal for slow-cooked meals and baking. Both materials offer non-toxic, chemical-free alternatives to traditional coatings, with nano-ceramic emphasizing modern technology and stoneware highlighting natural, artisanal qualities.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Nano-ceramic cookware features a coating infused with nanoparticles, enhancing durability, heat resistance, and non-stick properties through a sol-gel process that bonds ceramic and titanium dioxide at the molecular level. Stoneware, made from natural clay fired at high temperatures, undergoes vitrification, creating a dense, heat-retentive surface with a porous structure that can absorb and evenly distribute heat. The manufacturing process of nano-ceramic involves advanced nanotechnology for a thin, smooth layer, while stoneware relies on traditional kiln-firing techniques to achieve its robust, oven-safe composition.
Heat Distribution and Retention Properties
Nano-ceramic cookware offers superior heat distribution due to its advanced nano-particle coating, which ensures even cooking and reduces hot spots. Stoneware excels in heat retention, maintaining consistent temperatures for longer periods, making it ideal for slow-cooking and baking. Both materials provide distinct advantages, with nano-ceramic promoting rapid, uniform heating and stoneware delivering prolonged heat preservation.
Durability and Resistance to Wear
Nano-ceramic cookware features an advanced coating made from nanoparticles that enhances scratch resistance and prolongs its lifespan compared to traditional stoneware. Stoneware, composed of natural clay fired at high temperatures, offers excellent durability but is more susceptible to surface chipping and wear with frequent use. The nano-ceramic coating provides superior non-stick properties and greater resilience to abrasion, making it a more wear-resistant choice for long-term cookware performance.
Non-Stick Performance and Cooking Experience
Nano-ceramic cookware offers superior non-stick performance due to its advanced nanoparticle coating, which ensures even heat distribution and effortless food release without synthetic chemicals. Stoneware provides a naturally non-stick surface that improves over time with proper seasoning, delivering excellent heat retention and slow, even cooking ideal for baking and roasting. Nano-ceramic is best for quick, low-oil cooking with easy cleanup, while stoneware excels in durability and flavor enhancement through gradual heat buildup.
Health and Safety Concerns
Nano-ceramic cookware offers a non-toxic, PFOA and PTFE-free surface, reducing the risk of harmful chemical leaching during cooking, unlike some traditional stoneware glazes that may contain lead or cadmium if not properly manufactured. Stoneware is generally safe for high-heat cooking but can crack or chip, potentially harboring bacteria if the glaze is compromised. Both materials require appropriate care to maintain their non-reactive, food-safe surfaces, with nano-ceramic being favored for its enhanced durability and resistance to scratching and staining.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Nano-ceramic cookware features a non-porous surface that resists stains and prevents food from sticking, making it easier to clean with just mild soap and water. Stoneware, while durable, requires more careful maintenance to avoid cracks or chips and often needs hand washing to preserve its finish and prevent residue buildup. Both materials benefit from avoiding abrasive cleaners, but nano-ceramic typically offers a lower-maintenance option due to its enhanced surface technology.
Compatibility with Cooking Surfaces
Nano-ceramic cookware offers excellent compatibility with a wide range of cooking surfaces, including induction, gas, electric, and ceramic stovetops, due to its smooth and non-reactive coating. Stoneware, typically used in ovens, is less suitable for direct stovetop use because it can crack under uneven heat and is not compatible with induction cooktops. Choosing nano-ceramic cookware ensures versatility across multiple heat sources, while stoneware is ideal for baking and slow roasting applications.
Price Range and Cost-Effectiveness
Nano-ceramic cookware typically ranges from $40 to $150, offering a modern, non-toxic alternative with superior heat distribution that often justifies its higher price point. Stoneware is generally more affordable, priced between $20 and $80, providing durable, heat-retentive qualities ideal for slow cooking but may lack the advanced non-stick properties of nano-ceramic. Evaluating cost-effectiveness, nano-ceramic cookware delivers long-term savings through durability and energy efficiency, while stoneware is budget-friendly upfront but may require more cautious handling to prevent chipping or cracking.
Choosing the Right Cookware: Nano-Ceramic vs Stoneware
Nano-ceramic cookware offers superior non-stick properties and exceptional heat distribution, making it ideal for low-fat cooking and easy cleanup. Stoneware provides excellent heat retention and even cooking, perfect for baking and slow-cooking dishes that benefit from steady, consistent heat. Choosing between nano-ceramic and stoneware depends on your cooking style: opt for nano-ceramic for versatility and health-conscious meals, or stoneware for durability and traditional, oven-based recipes.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Stoneware for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com