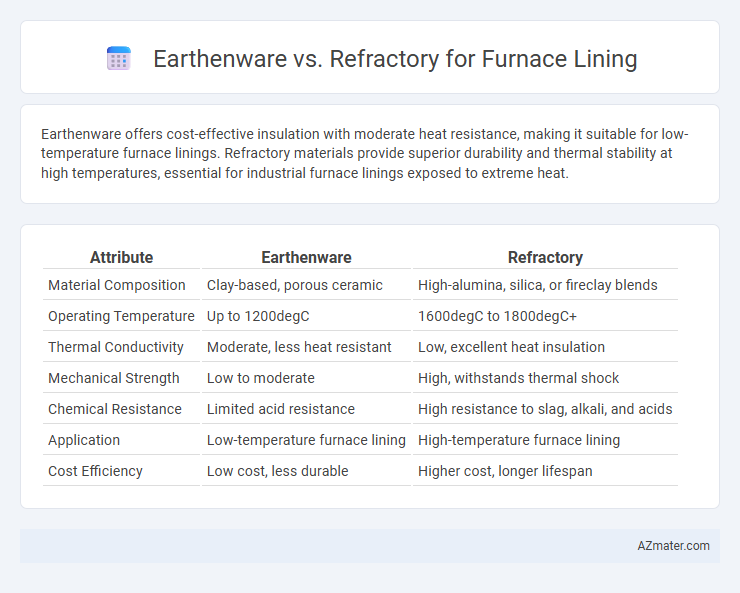
Earthenware offers cost-effective insulation with moderate heat resistance, making it suitable for low-temperature furnace linings. Refractory materials provide superior durability and thermal stability at high temperatures, essential for industrial furnace linings exposed to extreme heat.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Earthenware | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-based, porous ceramic | High-alumina, silica, or fireclay blends |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1200degC | 1600degC to 1800degC+ |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate, less heat resistant | Low, excellent heat insulation |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High, withstands thermal shock |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited acid resistance | High resistance to slag, alkali, and acids |
| Application | Low-temperature furnace lining | High-temperature furnace lining |
| Cost Efficiency | Low cost, less durable | Higher cost, longer lifespan |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials are crucial for thermal insulation and structural integrity in high-temperature environments. Earthenware offers cost-effective, moderate heat resistance suitable for lower-temperature applications, while refractory materials provide superior durability and insulation at extreme temperatures exceeding 1400degC. Selecting the appropriate lining depends on factors such as thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance to optimize furnace performance and longevity.
What is Earthenware?
Earthenware is a porous, non-vitreous ceramic material made from natural clay, commonly used for decorative and functional pottery due to its ease of shaping and firing at relatively low temperatures. It differs from refractory materials, which are engineered to withstand high heat and thermal shock, making them suitable for furnace lining applications. While earthenware offers aesthetic value and moderate heat resistance, it lacks the durability and insulation properties essential for high-temperature environments like industrial furnaces.
What are Refractory Materials?
Refractory materials are specially designed substances capable of withstanding extremely high temperatures without melting or degrading, making them ideal for furnace linings. These materials include fireclay, alumina, silica, and zirconia, each offering different thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties tailored to specific industrial applications. Unlike earthenware, which has limited heat resistance and durability, refractory materials ensure efficient insulation, structural integrity, and prolonged service life in high-temperature environments.
Key Properties: Earthenware vs Refractory
Earthenware offers moderate thermal insulation and is relatively porous, making it less suitable for high-temperature furnace linings compared to refractory materials. Refractory linings provide superior heat resistance, low thermal conductivity, and high mechanical strength essential for withstanding extreme conditions in industrial furnaces. Key properties such as refractoriness, thermal shock resistance, and chemical stability distinguish refractory materials as the preferred choice over earthenware in high-temperature applications.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Earthenware offers moderate thermal resistance suitable for low-temperature furnace linings up to approximately 1100degC, while refractory materials provide superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures exceeding 1600degC, essential for high-temperature industrial applications. Refractories maintain structural integrity and insulating properties under extreme thermal stress and repeated heating cycles better than earthenware. Selecting refractory lining enhances furnace longevity and efficiency by minimizing heat loss and preventing material degradation at elevated temperatures.
Durability and Lifespan
Earthenware furnace linings offer moderate durability, suitable for low to medium temperature applications but tend to degrade faster under extreme thermal cycling compared to refractory linings. Refractory materials, composed of alumina, silica, and fireclay, withstand higher temperatures exceeding 1700degC and exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear. This results in a significantly longer lifespan and reduced maintenance frequency, making refractory linings the preferred choice for industrial furnaces operating under harsh conditions.
Cost and Availability
Earthenware is generally more affordable and widely available due to its natural clay composition and simpler manufacturing process, making it a cost-effective option for furnace linings. Refractory materials, while more expensive, offer superior heat resistance and durability, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Availability of refractory bricks or castables may be limited in some regions, requiring specialized suppliers, whereas earthenware can often be sourced locally.
Applications in Furnace Lining
Earthenware is commonly used in low-temperature furnace linings due to its affordability and moderate thermal resistance, making it suitable for applications such as pottery kilns and small-scale heat treatment furnaces. Refractory materials excel in high-temperature furnace linings, offering superior thermal stability, chemical inertness, and resistance to thermal shock, essential for industrial furnaces used in steelmaking, glass production, and metal smelting. The choice between earthenware and refractory lining hinges on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress within the furnace environment.
Pros and Cons: Earthenware and Refractory
Earthenware offers cost-effective insulation and ease of shaping but lacks high-temperature resistance, making it less durable for intense furnace conditions. Refractory materials provide superior thermal stability and durability at extreme temperatures, ensuring longer furnace lifespan and efficient heat retention, though they require higher initial investment and specialized installation. Choosing between earthenware and refractory depends on the specific furnace operating temperature and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Furnace
Earthenware and refractory materials serve distinct roles in furnace lining; earthenware is less heat-resistant and suitable for low-temperature applications, while refractory materials withstand extreme temperatures above 1500degF, offering superior durability and thermal efficiency. Selecting the right furnace lining depends on factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, and thermal shock resistance requirements, with refractory linings preferred for industrial furnaces and kilns. Proper material choice enhances furnace longevity, energy efficiency, and safety in high-heat environments.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Refractory for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com