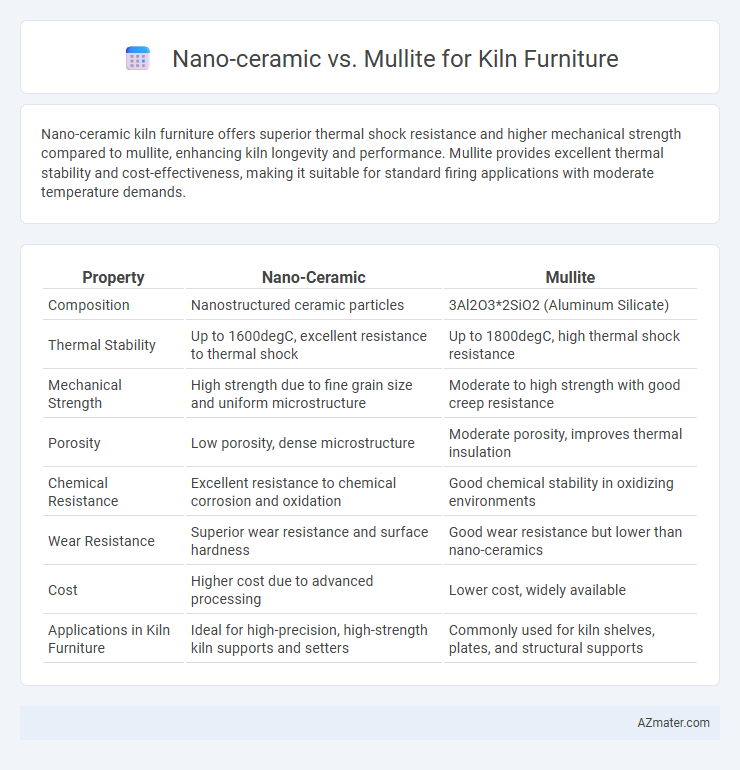
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher mechanical strength compared to mullite, enhancing kiln longevity and performance. Mullite provides excellent thermal stability and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for standard firing applications with moderate temperature demands.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nanostructured ceramic particles | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Aluminum Silicate) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1600degC, excellent resistance to thermal shock | Up to 1800degC, high thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength due to fine grain size and uniform microstructure | Moderate to high strength with good creep resistance |
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense microstructure | Moderate porosity, improves thermal insulation |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and oxidation | Good chemical stability in oxidizing environments |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear resistance and surface hardness | Good wear resistance but lower than nano-ceramics |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications in Kiln Furniture | Ideal for high-precision, high-strength kiln supports and setters | Commonly used for kiln shelves, plates, and structural supports |
Introduction: Kiln Furniture Material Choices
Nano-ceramic and mullite are prominent materials used for kiln furniture due to their excellent thermal stability and resistance to high-temperature corrosion. Nano-ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and enhanced mechanical strength because of its fine-grained microstructure, making it ideal for rapid heating and cooling cycles. Mullite's high refractoriness, low thermal expansion, and good resistance to chemical attack ensure durability and dimensional stability during prolonged high-temperature firings.
What is Nano-Ceramic for Kiln Furniture?
Nano-ceramic for kiln furniture consists of materials engineered at the nanoscale to enhance properties such as thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. Unlike traditional mullite, nano-ceramics offer improved durability and reduced sintering shrinkage, leading to longer service life in high-temperature kiln environments. These advanced properties make nano-ceramic an optimal choice for applications requiring precise thermal management and mechanical performance in kiln furniture components.
Overview of Mullite as Kiln Furniture Material
Mullite, a crystalline aluminosilicate mineral with a high melting point of approximately 1840degC, offers exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for kiln furniture applications. Its low thermal expansion and excellent resistance to thermal shock enhance the longevity and reliability of kiln shelves and supports during repeated high-temperature firing cycles. Mullite's chemical inertness also prevents contamination of ceramic ware, ensuring purity and quality throughout the kiln firing process.
Thermal Performance: Nano-Ceramic vs Mullite
Nano-ceramic materials exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and faster heat recovery compared to mullite, making them ideal for high-temperature kiln applications requiring rapid temperature changes. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, provides reliable performance at sustained high temperatures but typically has lower thermal conductivity than nano-ceramics. The enhanced thermal performance of nano-ceramics contributes to improved kiln efficiency and extended furniture lifespan in demanding firing cycles.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to mullite, with higher fracture toughness and enhanced resistance to thermal shock, enabling prolonged durability under extreme kiln temperatures exceeding 1600degC. Mullite, while offering good mechanical stability and lower thermal expansion, typically shows lower flexural strength and increased susceptibility to microcracking under rapid temperature fluctuations. The nano-ceramic's refined microstructure and nano-scale grain size contribute to its improved load-bearing capacity and fracture resistance, making it preferable for high-stress and high-temperature kiln applications.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture offers superior lightweight properties compared to traditional mullite, reducing overall kiln load and enhancing energy efficiency. The nanostructured composition allows for more intricate and customizable shapes, providing greater design flexibility to accommodate complex kiln configurations. Mullite, while durable and thermally stable, is heavier and less adaptable in form, limiting its use in advanced, lightweight kiln furniture applications.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Retention
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture offers superior energy efficiency due to its enhanced thermal insulation and lower heat capacity, reducing fuel consumption during firing cycles. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and durability, provides high heat retention but typically requires longer heating times, impacting overall energy use. Selecting nano-ceramic materials can optimize kiln performance by minimizing heat loss and accelerating temperature recovery, leading to significant energy savings in industrial ceramic production.
Longevity and Durability
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture offers superior longevity due to its enhanced grain refinement, resulting in increased resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress compared to mullite. Mullite, a highly refractory material with excellent thermal stability, provides good durability but tends to degrade faster under rapid temperature cycling or prolonged high-temperature exposure. The nano-ceramic's improved microstructure enables longer service life in demanding kiln environments, reducing replacement frequency and operational costs.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture typically demands a higher upfront investment due to advanced manufacturing processes and material costs compared to mullite, which is more affordable initially. Over the long term, nano-ceramic offers enhanced durability, thermal shock resistance, and reduced maintenance frequency, potentially lowering overall lifecycle expenses relative to mullite's higher susceptibility to cracking and replacement costs. Cost analysis reveals that while mullite may suit budget-conscious operations with lower firing cycles, nano-ceramic proves more cost-effective in high-volume or high-temperature applications where longevity and performance drive savings.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Kiln
Nano-ceramic kiln furniture offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher mechanical strength compared to traditional mullite, making it ideal for demanding firing cycles in ceramic production. Mullite provides excellent thermal stability and chemical inertness at a lower cost, suitable for general kiln use where extreme durability is not critical. Selecting between nano-ceramic and mullite depends on the specific firing temperature, load capacity, and budget constraints to optimize kiln performance and longevity.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Mullite for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com