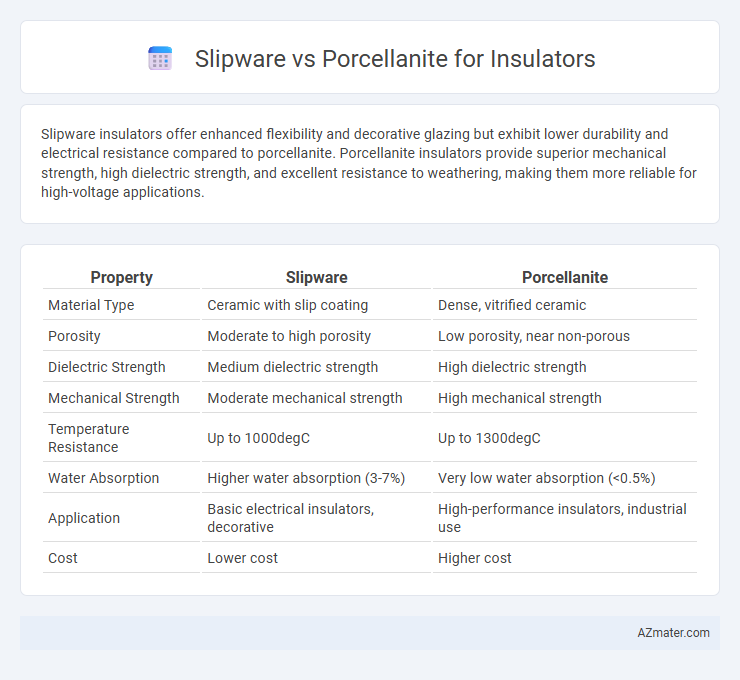
Slipware insulators offer enhanced flexibility and decorative glazing but exhibit lower durability and electrical resistance compared to porcellanite. Porcellanite insulators provide superior mechanical strength, high dielectric strength, and excellent resistance to weathering, making them more reliable for high-voltage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Slipware | Porcellanite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic with slip coating | Dense, vitrified ceramic |
| Porosity | Moderate to high porosity | Low porosity, near non-porous |
| Dielectric Strength | Medium dielectric strength | High dielectric strength |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | High mechanical strength |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1300degC |
| Water Absorption | Higher water absorption (3-7%) | Very low water absorption (<0.5%) |
| Application | Basic electrical insulators, decorative | High-performance insulators, industrial use |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Insulator Materials
Insulator materials like slipware and porcellanite are essential in preventing electrical conduction by providing high resistance. Slipware, a ceramic made from refined clays and slip coatings, offers durability with moderate electrical insulation properties, suitable for less demanding applications. Porcellanite, a dense and vitrified ceramic, delivers superior dielectric strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-voltage insulators and harsh environments.
What is Slipware?
Slipware is a technique involving the application of liquid clay slip to pottery surfaces before firing, enhancing both aesthetics and texture. In insulator manufacturing, slipware provides a smooth, uniform coating that improves dielectric properties and durability. Unlike porcellanite, a dense, vitrified ceramic, slipware insulators emphasize decorative finishes and surface treatments without compromising electrical insulation.
Defining Porcellanite in Insulation
Porcellanite in insulation refers to a dense, vitrified ceramic material known for its superior electrical resistance and mechanical strength compared to slipware, a more porous, earthenware-type ceramic. Porcellanite's low porosity and high dielectric strength make it ideal for high-voltage insulators, preventing electrical leakage and withstand harsh environmental conditions. Slipware, although more affordable, lacks the durability and insulating properties required for demanding electrical applications.
Key Material Properties Compared
Slipware exhibits high porosity and moderate dielectric strength, making it suitable for insulators requiring some flexibility and moisture absorption control. Porcellanite offers superior density, low water absorption, and exceptional electrical insulation properties, resulting in higher mechanical strength and longer durability under electrical stress. The critical comparison hinges on porcellanite's enhanced resistance to thermal shock and environmental degradation compared to the more porous and less mechanically robust slipware.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Slipware insulators typically exhibit lower electrical insulation performance due to higher porosity and moisture absorption, which can lead to reduced dielectric strength and increased leakage currents. Porcellanite insulators offer superior electrical insulation properties, characterized by dense, vitrified materials with minimal porosity that provide enhanced resistance to electrical breakdown and improved longevity under high-voltage stresses. The low water absorption and high dielectric strength of porcellanite make it the preferred choice for high-performance insulators in demanding electrical applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Slipware insulators exhibit moderate mechanical strength due to their porous, slip-cast ceramic composition, making them less resistant to impact and heavy mechanical stress. Porcellanite insulators, characterized by their dense, vitrified structure, offer superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability against wear, fractures, and environmental factors. The high durability of porcellanite ensures longer service life and reliability in high-voltage applications compared to slipware.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Slipware insulators exhibit moderate thermal resistance and stability, often suitable for applications with less extreme temperature variations. Porcellanite insulators, characterized by higher thermal resistance and superior stability, perform efficiently under severe thermal stress and fluctuating environments. The dense, vitrified structure of porcellanite enhances its capacity to withstand thermal shock and maintain insulating properties over prolonged periods.
Manufacturing Processes: Slipware vs Porcellanite
Slipware insulators are produced through the slip casting process, where liquid clay slip is poured into molds and then dried and fired to form durable, porous ceramic structures. Porcellanite insulators undergo manufacturing involving high-temperature firing of refined clay mixtures, resulting in a dense, vitrified material with superior mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties. The key difference lies in slipware's molded, layered makeup versus porcellanite's compact, glass-like composition achieved through intense vitrification.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Slipware insulators typically offer lower production costs due to simpler raw materials and traditional manufacturing methods, making them more affordable for bulk applications. Porcellanite insulators, composed of high-density ceramic materials, involve higher production expenses but provide superior durability and insulation properties. Availability of slipware is widespread in local markets, whereas porcellanite requires specialized suppliers, impacting lead times and overall procurement costs.
Best Applications for Each Material
Slipware insulators excel in applications requiring high electrical resistance and durability in humid or corrosive environments, such as outdoor power distribution and telecommunication lines. Porcellanite insulators, characterized by their superior mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, are ideal for high-voltage transmission systems and heavy industrial settings where physical impact and extreme weather conditions are common. Selecting slipware ensures cost-effective performance in moderate load conditions, while porcellanite is preferred for critical infrastructure demanding long-term reliability under intense stress.
Infographic: Slipware vs Porcellanite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com