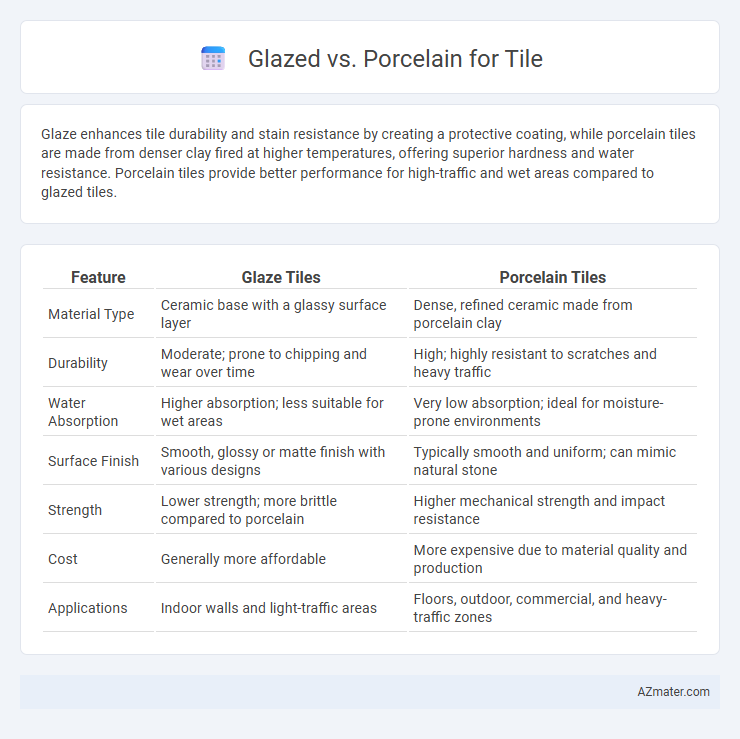
Glaze enhances tile durability and stain resistance by creating a protective coating, while porcelain tiles are made from denser clay fired at higher temperatures, offering superior hardness and water resistance. Porcelain tiles provide better performance for high-traffic and wet areas compared to glazed tiles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glaze Tiles | Porcelain Tiles |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic base with a glassy surface layer | Dense, refined ceramic made from porcelain clay |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping and wear over time | High; highly resistant to scratches and heavy traffic |
| Water Absorption | Higher absorption; less suitable for wet areas | Very low absorption; ideal for moisture-prone environments |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, glossy or matte finish with various designs | Typically smooth and uniform; can mimic natural stone |
| Strength | Lower strength; more brittle compared to porcelain | Higher mechanical strength and impact resistance |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | More expensive due to material quality and production |
| Applications | Indoor walls and light-traffic areas | Floors, outdoor, commercial, and heavy-traffic zones |
Introduction to Glazed and Porcelain Tiles
Glazed tiles feature a glass-like coating that enhances color variety and provides extra protection against stains and scratches, making them ideal for indoor use. Porcelain tiles are a subtype of ceramic made from denser, finer clay and are fired at higher temperatures, resulting in increased strength, durability, and water resistance suitable for heavy-traffic and outdoor areas. Both tile types offer versatile design options, but porcelain's low porosity makes it superior for moisture-prone environments.
Material Composition: Glaze vs Porcelain
Porcelain tiles are made from a dense, refined clay mixed with other natural materials, fired at higher temperatures to achieve durability and low porosity. Glazed tiles feature a layer of liquid glass-like coating applied to the surface of the base tile, which can be ceramic or porcelain, providing color, texture, and enhanced water resistance. The key difference lies in porcelain's inherently dense composition versus the glaze's surface treatment that adds protection and design versatility.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Glaze and porcelain tiles differ significantly in their manufacturing processes; porcelain tiles are made by firing a dense mixture of fine clay at very high temperatures, resulting in a non-porous, durable surface without the need for a glaze. Glazed tiles undergo an additional step where a liquid glass coating is applied before firing, creating a decorative, water-resistant surface on a less dense ceramic body. This difference in firing temperatures and material composition impacts the tile's durability, water absorption, and aesthetic qualities.
Appearance and Design Options
Glaze tiles offer a wide variety of colors, patterns, and finishes, allowing for highly customizable and vibrant designs that mimic natural stone, wood, or intricate patterns. Porcelain tiles provide a dense, durable surface with subtle, natural aesthetics, often featuring muted tones and a smooth finish suitable for minimalist or modern designs. Both options vary in texture and sheen, but glazed tiles excel in bold, decorative styles while porcelain tiles emphasize sleek, uniform appearances.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Porcelain tiles are denser and harder than glazed tiles, offering superior durability and resistance to wear, scratches, and stains. Glazed tiles feature a protective coating that can chip or crack under heavy impact, making them less resistant to long-term damage compared to porcelain. The inherent strength of porcelain makes it ideal for high-traffic areas and environments requiring robust tile performance.
Water Resistance and Porosity
Glaze significantly enhances a tile's water resistance by creating a glass-like surface that prevents moisture absorption, making glazed tiles less porous compared to unglazed porcelain. Porcelain tiles, known for their dense and low-porosity composition, inherently offer superior water resistance even without a glaze, making them ideal for wet environments. The combination of porcelain's natural density and optional glaze ensures optimal protection against water infiltration and staining.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Glazed tiles feature a protective layer that resists stains and moisture, making them easier to clean with mild detergents and regular sweeping. Porcelain tiles, known for their dense, non-porous composition, require minimal maintenance and resist water absorption, reducing mold and mildew risks. Both options benefit from routine cleaning, but porcelain's durability and low porosity offer superior longevity with less upkeep.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Glazed tiles typically cost less than porcelain tiles due to their manufacturing process and material composition, making them a budget-friendly option for large projects. Porcelain tiles, known for their durability and density, often come at a higher price point but offer long-term value through increased lifespan and lower maintenance costs. When budgeting, consider not only the initial tile cost but also installation complexity and potential future repairs, where porcelain may provide better overall savings despite the upfront expense.
Best Applications: Where to Use Each Tile
Glazed tiles are ideal for interior walls, backsplashes, and low-traffic areas due to their moisture resistance and vibrant color options. Porcelain tiles excel in high-traffic floors, outdoor patios, and wet environments like bathrooms because of their density, durability, and low water absorption rate. Selecting the right tile depends on balancing aesthetic appeal with functional requirements specific to residential or commercial applications.
Choosing the Right Tile: Glaze or Porcelain?
Porcelain tiles offer superior durability and water resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas, while glazed tiles provide a wide range of colors and finishes due to their ceramic surface coating. Porcelain is denser and less porous, resulting in higher stain resistance and longevity compared to glazed tiles, which may chip or wear over time. When choosing between glazed and porcelain tiles, consider the installation environment, maintenance needs, and desired aesthetic to ensure the most suitable tile performance and appearance.
Infographic: Glaze vs Porcelain for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com