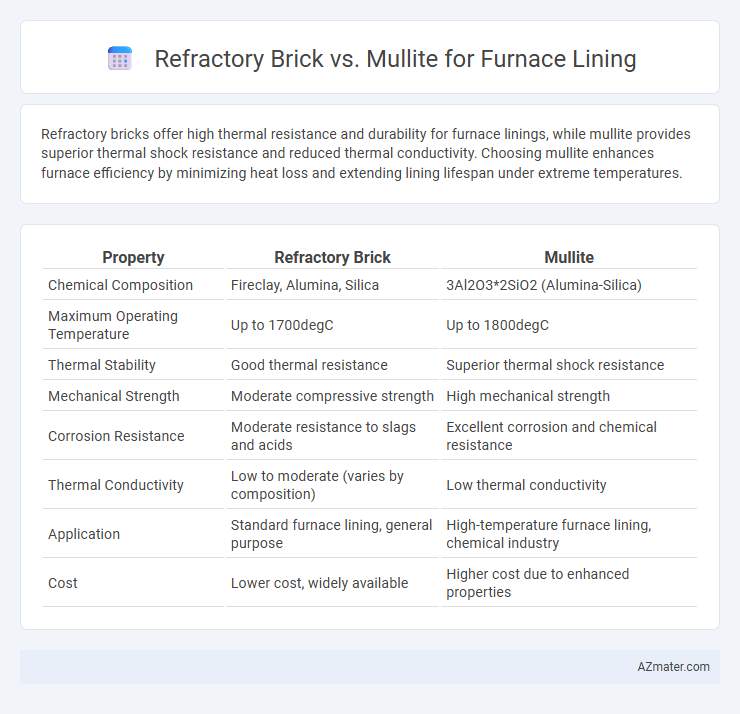
Refractory bricks offer high thermal resistance and durability for furnace linings, while mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance and reduced thermal conductivity. Choosing mullite enhances furnace efficiency by minimizing heat loss and extending lining lifespan under extreme temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory Brick | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Fireclay, Alumina, Silica | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumina-Silica) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1700degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal resistance | Superior thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate compressive strength | High mechanical strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate resistance to slags and acids | Excellent corrosion and chemical resistance |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate (varies by composition) | Low thermal conductivity |
| Application | Standard furnace lining, general purpose | High-temperature furnace lining, chemical industry |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials play a crucial role in industrial high-temperature applications, with refractory bricks and mullite being prominent choices due to their thermal stability and resistance properties. Refractory bricks offer excellent mechanical strength and durability under extreme heat, making them suitable for heavy-duty furnace environments. Mullite, a synthetic mineral, provides superior thermal shock resistance and low thermal conductivity, enhancing furnace efficiency and lifespan.
Understanding Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion, making them essential for furnace lining applications. These bricks are typically composed of alumina, silica, fireclay, or magnesia, providing high thermal stability and insulating properties. Understanding the composition and thermal resistance of refractory bricks is crucial when comparing them to mullite bricks, as it directly impacts furnace efficiency and longevity.
What is Mullite?
Mullite is a high-temperature ceramic material composed primarily of aluminum silicate (3Al2O3*2SiO2), known for its excellent thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for furnace linings. Unlike traditional refractory bricks made from fireclay or silica, mullite bricks exhibit superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, enhancing furnace durability and performance. Its unique microstructure and high melting point above 1840degC ensure effective insulation and prolonged service life in demanding industrial environments.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Refractory bricks offer high thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for rapid heating and cooling cycles in furnace linings. Mullite bricks provide superior thermal insulation and stability at temperatures above 1500degC, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in high-temperature environments. Choosing between refractory brick and mullite depends on the required thermal performance, with mullite favored for long-term insulation and refractory brick preferred for structural durability under thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength Differences
Refractory bricks typically exhibit higher compressive strength, making them suitable for withstanding heavy mechanical loads in furnace linings. Mullite bricks, characterized by their excellent thermal shock resistance and moderate mechanical strength, provide greater durability under fluctuating temperature conditions but may have lower load-bearing capacity compared to conventional refractory bricks. Selecting between refractory brick and mullite for furnace lining depends on balancing mechanical strength requirements with thermal performance demands.
Chemical Resistance: Refractory Brick vs Mullite
Refractory bricks exhibit strong chemical resistance against acidic slags and molten metals, maintaining stability in environments with high alumina and silica content. Mullite offers superior resistance to alkali attacks and thermal shock due to its unique 3Al2O3*2SiO2 crystalline structure, making it ideal for harsh furnace conditions. Both materials ensure longevity, but mullite's enhanced chemical resilience extends furnace lining life in aggressive chemical environments.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Refractory brick offers straightforward installation with modular shapes that fit precisely, reducing downtime during furnace lining repair, while mullite refractory requires specialized handling due to its brittle nature and precise firing conditions. Maintenance of refractory bricks involves routine inspection for cracks and spalling, enabling targeted replacements, whereas mullite linings demand careful monitoring of thermal gradients to prevent catastrophic failure caused by its lower mechanical toughness. Choosing between refractory brick and mullite depends on balancing ease of installation with long-term durability under specific thermal and mechanical stresses in furnace operations.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Refractory bricks generally offer lower initial costs compared to mullite, making them attractive for budget-sensitive projects; however, mullite bricks provide superior thermal stability and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Mullite's enhanced resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion results in lower downtime costs, contributing to a favorable cost-per-year metric despite higher upfront investment. For furnace linings subjected to extreme temperatures and aggressive environments, mullite bricks deliver better long-term value by minimizing operational disruptions and extending furnace lifespan.
Applications and Suitability
Refractory bricks offer excellent resistance to high temperatures and thermal shock, making them ideal for general furnace lining applications such as in steel, glass, and cement industries. Mullite bricks, composed mainly of alumina and silica, provide superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance, particularly suitable for environments with extreme temperature fluctuations and chemical exposure. Choosing between refractory brick and mullite depends on the specific furnace operating conditions, including temperature range, chemical aggressiveness, and mechanical stress tolerance.
Choosing the Optimal Material for Your Furnace
Choosing the optimal material for your furnace lining involves comparing refractory bricks and mullite based on their thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Refractory bricks offer excellent durability at high temperatures up to 1700degC, making them suitable for general-purpose furnace linings, while mullite provides superior performance with high alumina content, better thermal shock resistance, and lower thermal expansion, ideal for specialized high-temperature applications. Prioritizing furnace operating conditions, such as maximum temperature, atmosphere, and abrasion levels, ensures the selection of the best lining material to enhance furnace longevity and efficiency.
Infographic: Refractory Brick vs Mullite for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com