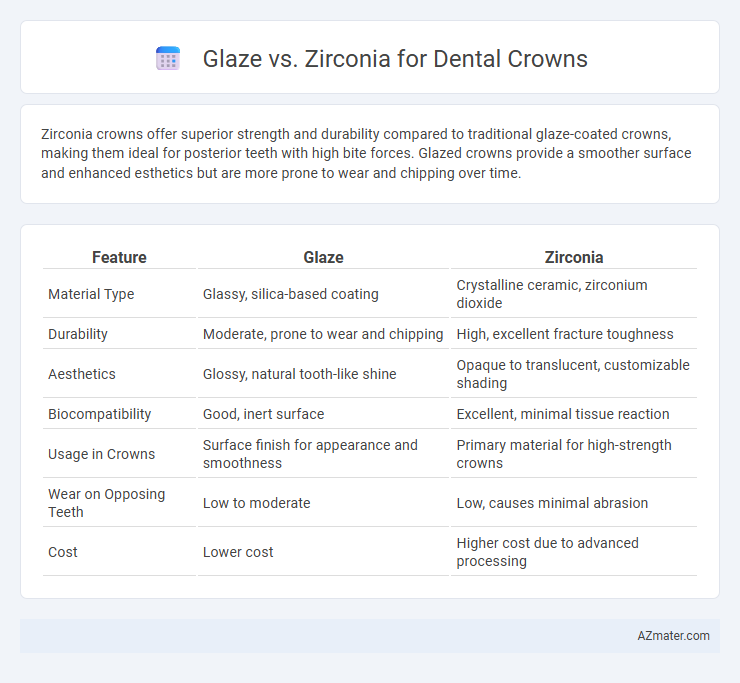
Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional glaze-coated crowns, making them ideal for posterior teeth with high bite forces. Glazed crowns provide a smoother surface and enhanced esthetics but are more prone to wear and chipping over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glaze | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glassy, silica-based coating | Crystalline ceramic, zirconium dioxide |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear and chipping | High, excellent fracture toughness |
| Aesthetics | Glossy, natural tooth-like shine | Opaque to translucent, customizable shading |
| Biocompatibility | Good, inert surface | Excellent, minimal tissue reaction |
| Usage in Crowns | Surface finish for appearance and smoothness | Primary material for high-strength crowns |
| Wear on Opposing Teeth | Low to moderate | Low, causes minimal abrasion |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Dental Crowns
Dental crowns are vital restorations designed to cover and protect damaged or weakened teeth, restoring both function and aesthetics. Zirconia crowns offer exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for posterior teeth subjected to heavy biting forces. In contrast, glazed crowns provide a smooth, polished surface that enhances esthetic appeal and reduces plaque accumulation, often favored for visible front teeth.
What is Glazed Porcelain in Dental Crowns?
Glazed porcelain in dental crowns refers to a smooth, glass-like coating applied to the crown surface, enhancing its aesthetic appeal and providing a natural shine that mimics real teeth. This glaze not only improves the crown's translucency and color but also reduces plaque accumulation and enhances resistance to wear and staining. Compared to zirconia crowns, glazed porcelain offers superior cosmetic results but may have lower durability and fracture resistance.
Understanding Zirconia Dental Crowns
Zirconia dental crowns offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional glaze finishes, making them ideal for long-lasting dental restorations. Their biocompatibility and resistance to wear and fracture provide optimal comfort and functionality for patients. Advanced computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology enhances the precision and fit of zirconia crowns, ensuring improved aesthetics and patient satisfaction.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior strength and durability compared to glazed dental crowns, with a flexural strength typically ranging from 900 to 1,200 MPa, making them highly resistant to fracture. Glazed crowns often use porcelain materials that, while offering enhanced aesthetic qualities, generally possess lower strength, averaging around 70-100 MPa flexural strength. Zirconia's toughness and wear resistance make it ideal for long-term dental restorations in high-stress areas like molars, whereas glazed crowns may be more suitable for anterior teeth where aesthetics are prioritized over maximum structural performance.
Aesthetics: Glaze vs Zirconia Appearance
Glazed dental crowns feature a smooth, glass-like surface that enhances light reflection, giving a natural shine and lifelike translucency similar to enamel. Zirconia crowns, while highly durable, typically possess a more opaque appearance, which can limit their ability to mimic the natural translucency and gloss of teeth. Advances in multi-layered and high-translucency zirconia formulations have improved their aesthetics, but glazed porcelain remains superior for achieving the most realistic dental crown appearance.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility due to their inert composition, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or gum irritation compared to glazed porcelain. The durable, non-porous surface of zirconia minimizes bacterial adhesion, enhancing patient safety by lowering the likelihood of plaque accumulation and subsequent periodontal issues. Glaze coatings can wear off over time, potentially exposing underlying materials that may compromise tissue compatibility, whereas zirconia maintains its integrity and biocompatibility long-term.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Zirconia crowns demonstrate superior longevity and wear resistance compared to glazed dental crowns due to their high fracture toughness and ability to withstand occlusal forces without significant degradation. Glazed crowns, while aesthetically pleasing, can experience surface wear and glaze chipping over time, compromising their durability. Clinical studies show zirconia maintains structural integrity and resists abrasion for 10-15 years, making it a preferred choice for long-term dental restorations.
Cost Differences Between Glaze and Zirconia
Glazed dental crowns typically cost less than zirconia crowns due to lower material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes. Zirconia crowns are more expensive, reflecting their superior strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal, often ranging from $1,000 to $2,500 per crown compared to $800 to $1,500 for glazed options. The cost difference also accounts for the advanced technology and labor-intensive production required for high-quality zirconia restorations.
Indications and Best Use Cases
Glaze dental crowns are ideal for patients seeking enhanced aesthetics and smooth surfaces to reduce plaque accumulation, commonly used in front teeth restorations where translucency is critical. Zirconia crowns offer superior strength and durability, making them best suited for molars and posterior teeth that endure higher chewing forces, especially in patients with bruxism or heavy occlusion. Indications for glaze include cases prioritizing cosmetic appeal, while zirconia is preferred for functional longevity and resistance to fracture.
Choosing the Right Dental Crown Material
Selecting between glaze and zirconia for dental crown material hinges on durability, aesthetics, and biocompatibility. Zirconia crowns offer exceptional strength and long-lasting wear, making them ideal for molars, while glazed crowns provide a smoother, more natural appearance suited for front teeth. Evaluating patient-specific factors such as bite pressure, aesthetic preferences, and potential allergies ensures optimal crown performance and longevity.
Infographic: Glaze vs Zirconia for Dental Crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com