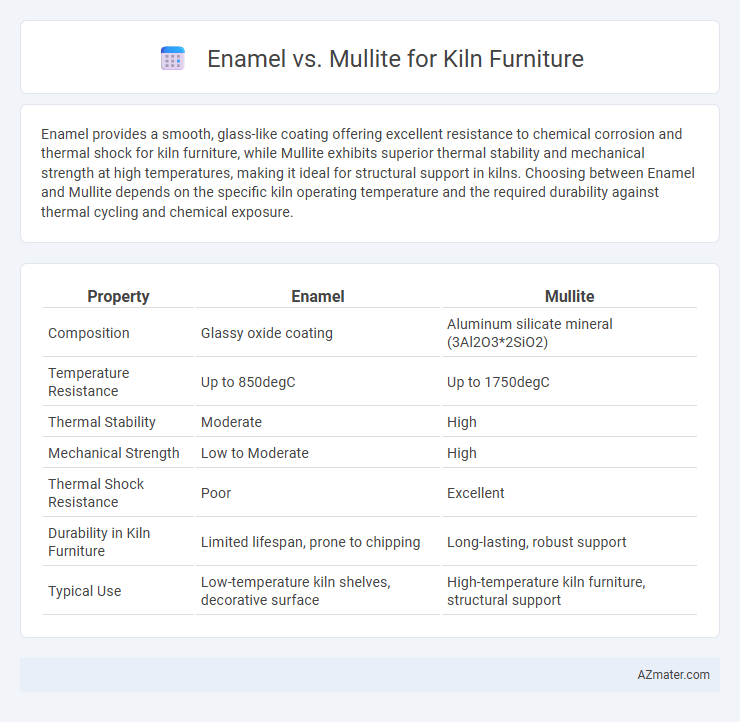
Enamel provides a smooth, glass-like coating offering excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock for kiln furniture, while Mullite exhibits superior thermal stability and mechanical strength at high temperatures, making it ideal for structural support in kilns. Choosing between Enamel and Mullite depends on the specific kiln operating temperature and the required durability against thermal cycling and chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glassy oxide coating | Aluminum silicate mineral (3Al2O3*2SiO2) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 850degC | Up to 1750degC |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to Moderate | High |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Durability in Kiln Furniture | Limited lifespan, prone to chipping | Long-lasting, robust support |
| Typical Use | Low-temperature kiln shelves, decorative surface | High-temperature kiln furniture, structural support |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Kiln furniture materials such as enamel and mullite play a crucial role in high-temperature industrial processes by providing support and thermal resistance. Enamel coatings offer excellent protection against chemical corrosion and thermal shock, making them ideal for certain kiln applications. Mullite, a silicate mineral with superior high-temperature stability and mechanical strength, is widely used for kiln furniture due to its ability to withstand extreme firing environments and reduce deformation.
Overview of Enamel and Mullite
Enamel is a glassy coating applied to kiln furniture that offers excellent chemical resistance and smooth surface properties, enhancing durability under thermal cycling conditions. Mullite, a crystalline aluminum silicate mineral, provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength at high temperatures, making it ideal for structural components in kiln furniture. Both materials are crucial for kiln efficiency, with enamel focusing on surface protection and mullite on heat resistance and structural integrity.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Enamel and mullite differ significantly in chemical composition, influencing their suitability for kiln furniture. Enamel primarily consists of a glassy matrix containing silica (SiO2), boron oxide (B2O3), and various metal oxides such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and calcium oxide (CaO), providing a smooth, non-porous surface resistant to thermal shock. Mullite is an aluminosilicate mineral with a stoichiometric ratio of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, offering high refractoriness, excellent thermal stability, and low thermal expansion due to its crystalline structure, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Mullite offers superior thermal stability for kiln furniture, enduring temperatures up to 1750degC without deformation, making it ideal for high-temperature firing processes. Enamel coatings, while providing corrosion resistance and surface smoothness, typically degrade above 900degC, limiting their thermal performance in extreme kiln environments. Mullite's crystalline structure ensures enhanced thermal shock resistance and longevity, outperforming enamel in consistent high-heat applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Enamel-coated kiln furniture offers enhanced mechanical strength through its protective, wear-resistant surface that resists thermal shock and abrasion, extending service life in high-temperature environments. Mullite, a ceramic material composed primarily of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, exhibits exceptional durability due to its high melting point (~1840degC), low thermal expansion, and excellent resistance to mechanical stress and chemical corrosion. For applications demanding prolonged thermal cycling and mechanical load endurance, mullite kiln furniture provides superior performance compared to enamel-coated alternatives, ensuring structural integrity and reduced maintenance costs.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Mullite kiln furniture exhibits superior resistance to thermal shock due to its high thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for rapid heating and cooling cycles in kilns. Enamel-coated kiln furniture, while offering a smooth surface and chemical resistance, generally has lower thermal shock resistance and is more prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes. Choosing mullite ensures enhanced durability and lifespan in high-temperature applications with frequent thermal cycling.
Weight and Density Considerations
Enamel kiln furniture typically exhibits higher density values ranging from 3.5 to 4.0 g/cm3, contributing to increased weight and thermal mass compared to mullite, which has a lower density around 2.7 to 3.0 g/cm3. The lighter mullite reduces overall kiln load, enhancing energy efficiency and ease of handling during firing cycles. Weight considerations impact kiln furniture selection as heavier enamel pieces may provide better structural rigidity but can increase thermal inertia and energy consumption.
Cost-Effectiveness for Industrial Use
Mullite kiln furniture offers superior cost-effectiveness for industrial use due to its high thermal stability and resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. Enamel-coated kiln furniture, while initially less expensive, tends to deteriorate faster under extreme kiln conditions, leading to higher long-term expenses and potential productivity losses. Industrial manufacturers prioritize mullite for its durability, energy efficiency, and lower total cost of ownership in high-temperature firing applications.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Enamel kiln furniture offers easy maintenance due to its smooth, non-porous surface that resists glaze sticking and simplifies cleaning, but it may chip or wear over time, affecting durability. Mullite kiln furniture provides exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength, resulting in a longer lifespan and lower maintenance frequency despite occasional surface deposits that require careful removal. Choosing between enamel and mullite depends on balancing ease of upkeep with durability needs in high-temperature kiln environments.
Selecting the Right Material for Kiln Furniture
Selecting the right material for kiln furniture depends on the specific firing temperature and thermal stability requirements. Enamel-coated kiln furniture offers excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and a smooth surface finish, ideal for lower to mid-temperature firings. Mullite kiln furniture provides superior thermal shock resistance and structural strength at high temperatures, making it suitable for extended use in high-temperature kilns.
Infographic: Enamel vs Mullite for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com