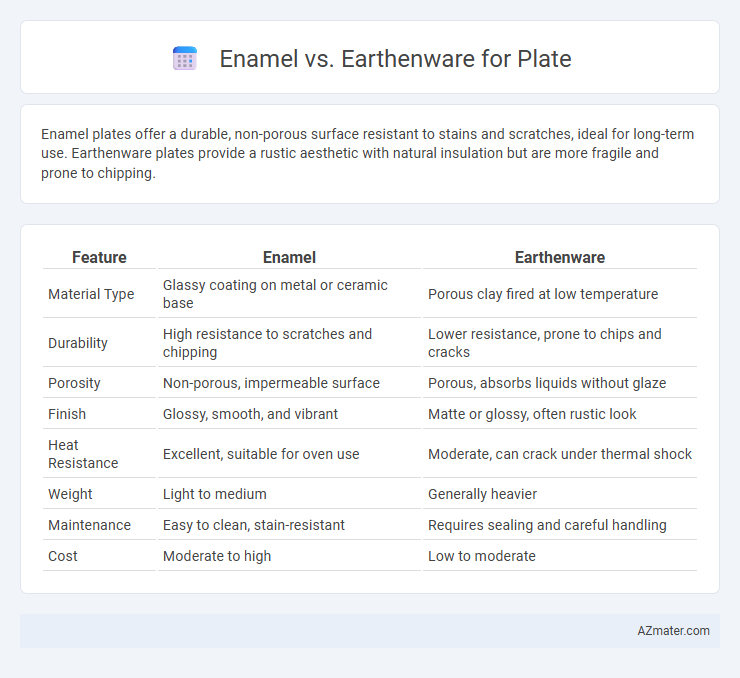
Enamel plates offer a durable, non-porous surface resistant to stains and scratches, ideal for long-term use. Earthenware plates provide a rustic aesthetic with natural insulation but are more fragile and prone to chipping.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enamel | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glassy coating on metal or ceramic base | Porous clay fired at low temperature |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and chipping | Lower resistance, prone to chips and cracks |
| Porosity | Non-porous, impermeable surface | Porous, absorbs liquids without glaze |
| Finish | Glossy, smooth, and vibrant | Matte or glossy, often rustic look |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, suitable for oven use | Moderate, can crack under thermal shock |
| Weight | Light to medium | Generally heavier |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, stain-resistant | Requires sealing and careful handling |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction: Understanding Plate Materials
Enamel plates feature a durable, non-porous surface made from powdered glass fused to metal, offering resistance to scratches and stains. Earthenware plates, crafted from clay fired at lower temperatures, provide a porous, rustic finish that may require glazing for durability. Understanding these material properties helps determine their suitability for everyday use or decorative purposes.
What is Enamel Plate?
Enamel plates are made by fusing powdered glass to a metal base, typically steel or cast iron, through high-temperature firing, creating a durable, smooth surface that resists stains and scratches. These plates combine the strength of metal with a glossy, non-porous coating that is dishwasher-safe and ideal for outdoor use due to its lightweight and chip-resistant properties. Compared to earthenware, enamel plates offer enhanced durability and heat distribution, making them a practical choice for both everyday dining and camping.
What is Earthenware Plate?
Earthenware plates are crafted from natural clay fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC to 1,150degC, resulting in a porous and slightly rough texture that requires glazing to be food-safe and water-resistant. This type of ceramic is heavier and more fragile compared to other dinnerware materials like stoneware or porcelain but offers a rustic, handcrafted aesthetic that is popular in artisanal tableware. The glaze not only seals the porous surface but also allows for vibrant colors and decorative finishes, making earthenware plates both functional and visually appealing for everyday dining.
Durability: Enamel vs Earthenware
Enamel plates boast superior durability due to their metal core coated with a vitreous enamel layer, making them resistant to chipping, scratching, and heat. Earthenware plates, composed of porous clay and fired at lower temperatures, are more fragile and prone to cracking or chipping under heavy use or drastic temperature changes. The long-lasting nature of enamel makes it ideal for outdoor or high-traffic use, while earthenware requires more careful handling.
Heat Resistance and Usability
Enamel plates offer superior heat resistance compared to earthenware, withstanding high temperatures without cracking or absorbing heat, making them ideal for cooking or serving hot food. Earthenware plates, while aesthetically pleasing and porous, tend to be more fragile and can crack under rapid temperature changes, limiting their usability for direct heat exposure. The non-porous, durable enamel surface provides easy cleaning and long-term usability, whereas earthenware requires careful handling due to its susceptibility to chipping and thermal shock.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Enamel plates offer a smooth, glossy finish with vibrant color options that enhance modern and retro kitchen aesthetics, making them highly versatile for a variety of design themes. Earthenware plates feature a rustic, handcrafted appearance with natural textures and earthy tones, appealing to those seeking a warm, organic look. Both materials provide distinctive aesthetic appeal but cater to different design preferences, with enamel excelling in bright, polished styles and earthenware emphasizing artisanal charm.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
Enamel plates resist stains and are dishwasher safe, requiring only gentle cleaning to avoid chipping the coating. Earthenware plates need more careful hand washing to prevent cracks and soak up stains, avoiding harsh detergents that can damage the porous surface. Proper maintenance extends enamel's durability and keeps earthenware's natural look intact, highlighting their different care demands.
Safety and Health Considerations
Enamel plates, made from steel coated with a vitreous enamel layer, are non-toxic, resistant to bacteria, and free from harmful chemicals like lead and cadmium when properly manufactured, making them safe for food use. Earthenware plates, composed of porous clay, can sometimes leach heavy metals if not glazed with food-safe materials, posing potential health risks with acidic or hot foods. Choosing enamel ensures better durability and non-porous surfaces that prevent bacterial growth, while earthenware requires careful selection and proper glazing to maintain safety and health standards.
Cost Comparison: Enamel vs Earthenware
Enamel plates generally cost less than earthenware due to their simpler manufacturing process and use of metal cores, making them a budget-friendly choice for everyday use. Earthenware plates, crafted from clay and often hand-finished, tend to be pricier, reflecting the artisanal quality and durability. The price difference is influenced by factors such as material sourcing, production time, and design intricacy, with enamel offering a more cost-effective option for those seeking affordable and lightweight dishware.
Choosing the Right Plate for Your Needs
Enamel plates offer durability, resistance to chipping, and are ideal for outdoor use or heavy-duty everyday meals due to their metal core covered with a smooth, non-porous enamel coating. Earthenware plates provide a rustic aesthetic with excellent heat retention but are more porous and prone to chipping, making them better suited for gentle indoor dining or decorative purposes. Selecting the right plate depends on whether you prioritize sturdiness and ease of cleaning (enamel) or an artisanal look and warmth retention (earthenware).
Infographic: Enamel vs Earthenware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com