Bone china, known for its superior thermal insulation and durability, provides consistent heat retention, while carbon heating elements offer rapid heating response and high electrical conductivity. Comparing efficiency, carbon elements excel in quick temperature changes, whereas bone china delivers stable, long-lasting heat distribution.
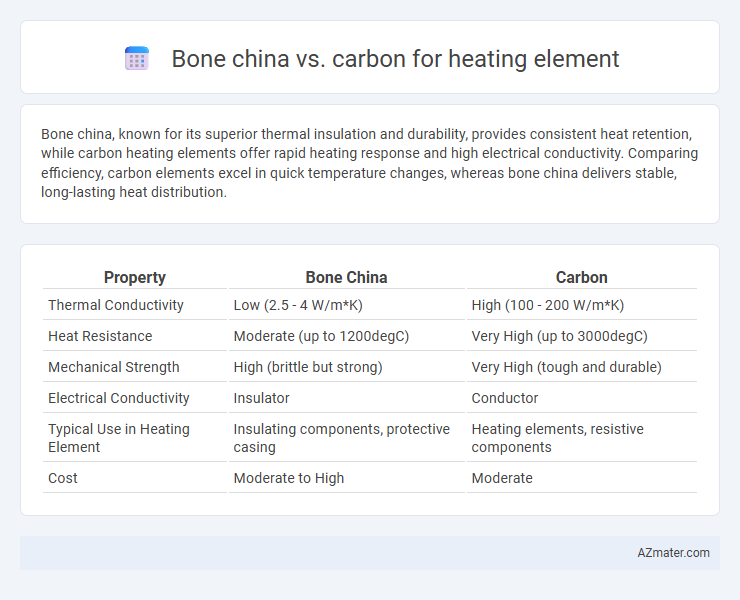
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bone China | Carbon |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (2.5 - 4 W/m*K) | High (100 - 200 W/m*K) |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 1200degC) | Very High (up to 3000degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | High (brittle but strong) | Very High (tough and durable) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Insulator | Conductor |
| Typical Use in Heating Element | Insulating components, protective casing | Heating elements, resistive components |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Moderate |
Introduction to Heating Element Materials
Bone china and carbon represent distinct material choices for heating element applications, each offering unique thermal and electrical properties. Bone china, primarily a ceramic composite, provides excellent thermal insulation and high-temperature stability but has limited electrical conductivity. Carbon, often used in forms like graphite or carbon fiber, delivers superior electrical conductivity and rapid heat response, making it ideal for efficient and responsive heating elements.
What is Bone China in Heating Elements?
Bone china in heating elements refers to a ceramic material known for its high strength, thermal resistance, and insulating properties, making it suitable for electrical heating applications. Composed primarily of porcelain clay combined with bone ash, it provides excellent durability and efficient heat distribution. Compared to carbon heating elements, bone china offers greater electrical insulation and resistance to thermal shock, enhancing safety and longevity in heating devices.
Understanding Carbon Heating Elements
Carbon heating elements offer superior thermal conductivity and faster response times compared to bone china, making them ideal for efficient heat transfer in industrial applications. Unlike bone china, a ceramic material primarily known for aesthetic and insulating properties, carbon heating elements can withstand higher temperatures and provide consistent energy distribution. Understanding the advantages of carbon heating elements is crucial for selecting materials that optimize performance and durability in heating systems.
Thermal Conductivity: Bone China vs Carbon
Bone china exhibits low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.9 to 1.1 W/m*K, making it a poor heat conductor and ideal for heat insulation in heating elements. Carbon, in contrast, has significantly higher thermal conductivity, ranging from approximately 50 to 2,000 W/m*K depending on the form, enabling rapid heat transfer and efficient energy distribution. This stark difference makes carbon preferable for heating elements requiring quick and uniform heating, whereas bone china suits applications demanding heat retention and insulation.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Bone china heating elements typically exhibit lower durability and shorter longevity compared to carbon heating elements due to their fragile ceramic composition prone to thermal shock and cracking. Carbon heating elements offer superior durability, resisting high temperatures and repeated heating cycles without degradation, making them ideal for long-term use. The enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength of carbon materials significantly extend the heating element lifespan relative to bone china alternatives.
Energy Efficiency of Bone China and Carbon
Bone china heating elements demonstrate superior energy efficiency due to their excellent thermal insulation properties, which minimize heat loss and maintain consistent temperature with lower energy consumption. In contrast, carbon-based heating elements offer rapid heating but often result in higher energy usage because of less effective heat retention. The enhanced durability and lower thermal conductivity of bone china contribute to more sustainable and cost-effective heating solutions compared to carbon elements.
Safety Features and Risk Assessment
Bone china heating elements offer superior electrical insulation and resistance to thermal shock, reducing the risk of short circuits and overheating compared to carbon-based elements. Carbon heating elements, while efficient in conductivity, present higher risks of oxidation and structural degradation over time, which can cause safety hazards such as sparking or fire. Safety assessments favor bone china for applications requiring stable thermal performance and minimized risk of electrical faults.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Bone china heating elements generally have a higher initial cost due to the expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes involved. Carbon heating elements, favored for their affordability and durability, offer lower upfront expenses and reduced maintenance costs over time. Long-term cost analysis shows carbon elements provide better value with greater energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to bone china options.
Applications and Suitability for Different Uses
Bone china offers excellent thermal insulation and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for decorative heating elements and temperature-sensitive applications in medical or laboratory settings. Carbon heating elements excel in rapid, uniform heat distribution and high-temperature tolerance, suitable for industrial furnaces, electronics, and high-performance appliances. The choice depends on the specific heat conductivity, durability, and environmental exposure requirements of the intended application.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Heating Element Material
Bone china heating elements provide excellent electrical insulation and aesthetic appeal but lack durability and thermal shock resistance compared to carbon. Carbon heating elements exhibit superior thermal conductivity, longevity, and resistance to high temperatures, making them more efficient for demanding heating applications. Selecting carbon as the heating element material ensures optimal performance and durability in high-temperature environments, surpassing bone china in practical industrial use.
Infographic: Bone china vs Carbon for Heating element
 azmater.com
azmater.com