Steatite offers excellent electrical insulation with high mechanical strength and superior thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for rugged industrial applications. Porcelain provides outstanding dielectric properties and moisture resistance, commonly used in high-voltage insulators for outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
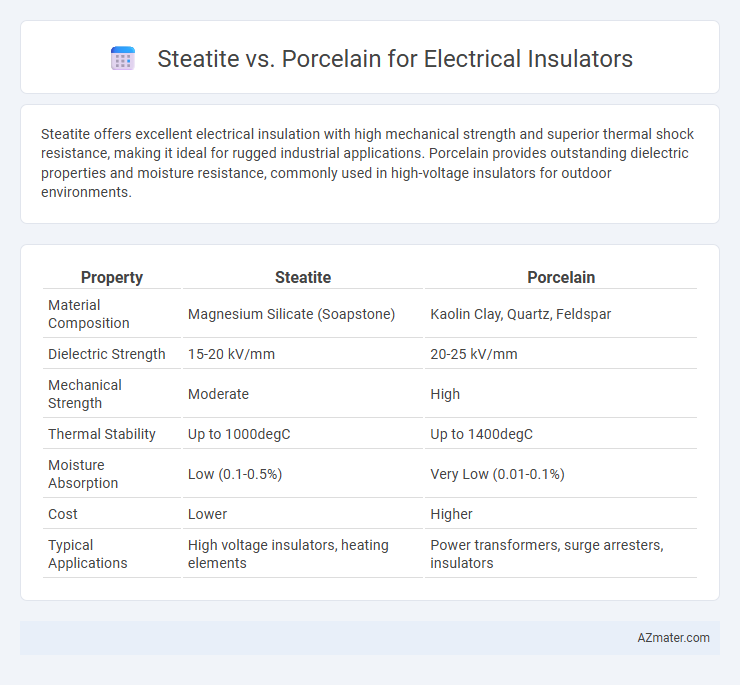
| Property | Steatite | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Magnesium Silicate (Soapstone) | Kaolin Clay, Quartz, Feldspar |
| Dielectric Strength | 15-20 kV/mm | 20-25 kV/mm |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1400degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.1-0.5%) | Very Low (0.01-0.1%) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | High voltage insulators, heating elements | Power transformers, surge arresters, insulators |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators play a critical role in preventing unwanted current flow and ensuring safety in electrical systems by resisting electrical conductivity. Steatite, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offers excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-voltage insulators in industrial applications. Porcelain insulators, made from fired clay with kaolin, provide superior mechanical durability and weather resistance, widely used in outdoor power transmission and distribution networks.
Overview of Steatite and Porcelain Materials
Steatite is a ceramic material composed primarily of talc, characterized by its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and resistance to heat and chemical corrosion, making it suitable for electrical insulators in demanding environments. Porcelain, made from a blend of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, offers superior dielectric strength, moisture resistance, and durability, which ensures reliable insulation performance in outdoor and high-voltage applications. Both materials provide effective electrical insulation, but steatite excels in mechanical robustness while porcelain is preferred for high-voltage and weather-resistant insulator applications.
Chemical Composition: Steatite vs Porcelain
Steatite, primarily composed of magnesium silicate (MgSiO3), offers excellent electrical insulation due to its dense and chemically inert nature. Porcelain consists mainly of kaolin (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), feldspar, and quartz, providing superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance in diverse environments. The chemical stability of steatite under high temperatures contrasts with porcelain's enhanced durability against weathering and chemical attack in electrical insulator applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Steatite offers higher mechanical strength and improved fracture resistance compared to porcelain, making it suitable for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Porcelain insulators, while possessing good mechanical strength, are generally more brittle and prone to chipping or cracking under impact. Steatite's superior compressive strength and toughness make it a preferred choice in high-stress electrical insulation environments.
Electrical Properties and Performance
Steatite electrical insulators exhibit high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them suitable for high-voltage applications with fluctuating temperatures. Porcelain insulators offer superior mechanical strength and high dielectric constant, ensuring reliable insulation in outdoor and high-humidity environments. Both materials provide effective electrical insulation, but steatite excels in thermal stability while porcelain delivers enhanced mechanical durability and moisture resistance.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Steatite exhibits excellent thermal resistance with a maximum operating temperature around 1000degC, making it highly suitable for applications requiring high heat endurance. Porcelain offers superior thermal stability due to its dense, vitrified structure, maintaining mechanical strength and insulating properties under fluctuating thermal conditions up to approximately 1300degC. The choice between steatite and porcelain hinges on the specific thermal load and environmental stability demands of electrical insulating components.
Durability and Lifespan
Steatite offers superior mechanical strength and high resistance to thermal shock, making it highly durable for electrical insulators in harsh environments. Porcelain, renowned for its excellent dielectric properties and weather resistance, typically provides a longer lifespan under normal operating conditions. Both materials exhibit low electrical conductivity, but the choice depends on specific application demands for durability versus extended service life.
Application Suitability in Industries
Steatite offers superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty electrical insulators in power distribution and industrial machinery. Porcelain excels in high-voltage applications due to its excellent dielectric strength and thermal stability, commonly used in transmission lines and substations. Industries requiring durability under harsh environmental conditions prefer steatite, while porcelain is favored for outdoor insulators exposed to extreme electrical stress.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Steatite electrical insulators are more cost-effective due to lower raw material and manufacturing costs compared to porcelain, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Porcelain insulators offer superior mechanical strength and weather resistance, but their higher production cost limits availability in some regions. Steatite's widespread availability and affordability make it a practical choice where moderate performance meets cost constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator
Steatite offers excellent mechanical strength and superior thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for high-stress electrical insulator applications. Porcelain provides outstanding electrical insulation and moisture resistance, suited for outdoor and high-voltage environments. Selecting the right insulator depends on the specific operational demands, balancing steatite's durability with porcelain's insulating reliability.
Infographic: Steatite vs Porcelain for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com